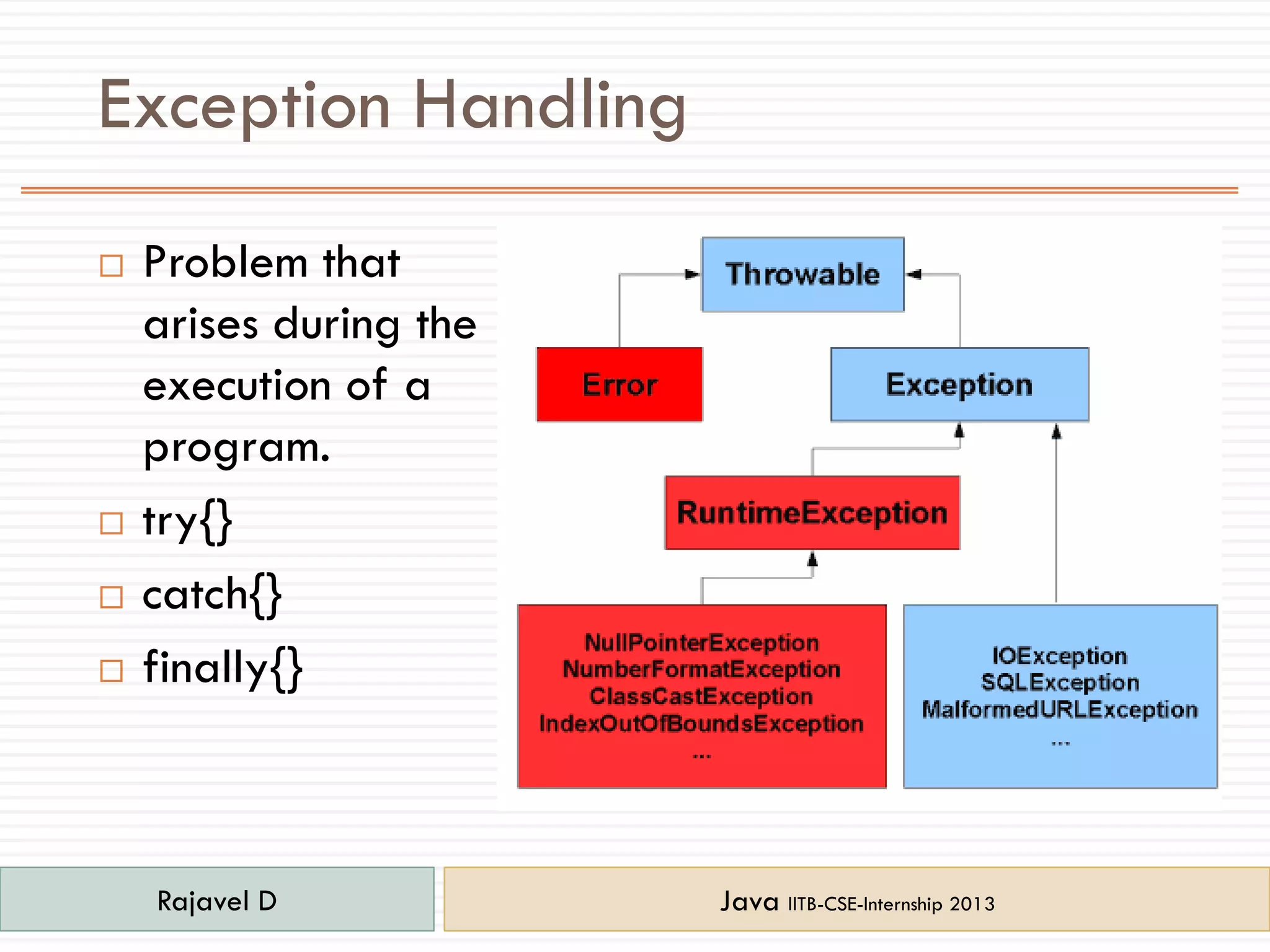
The document provides an overview of key concepts in Java including:
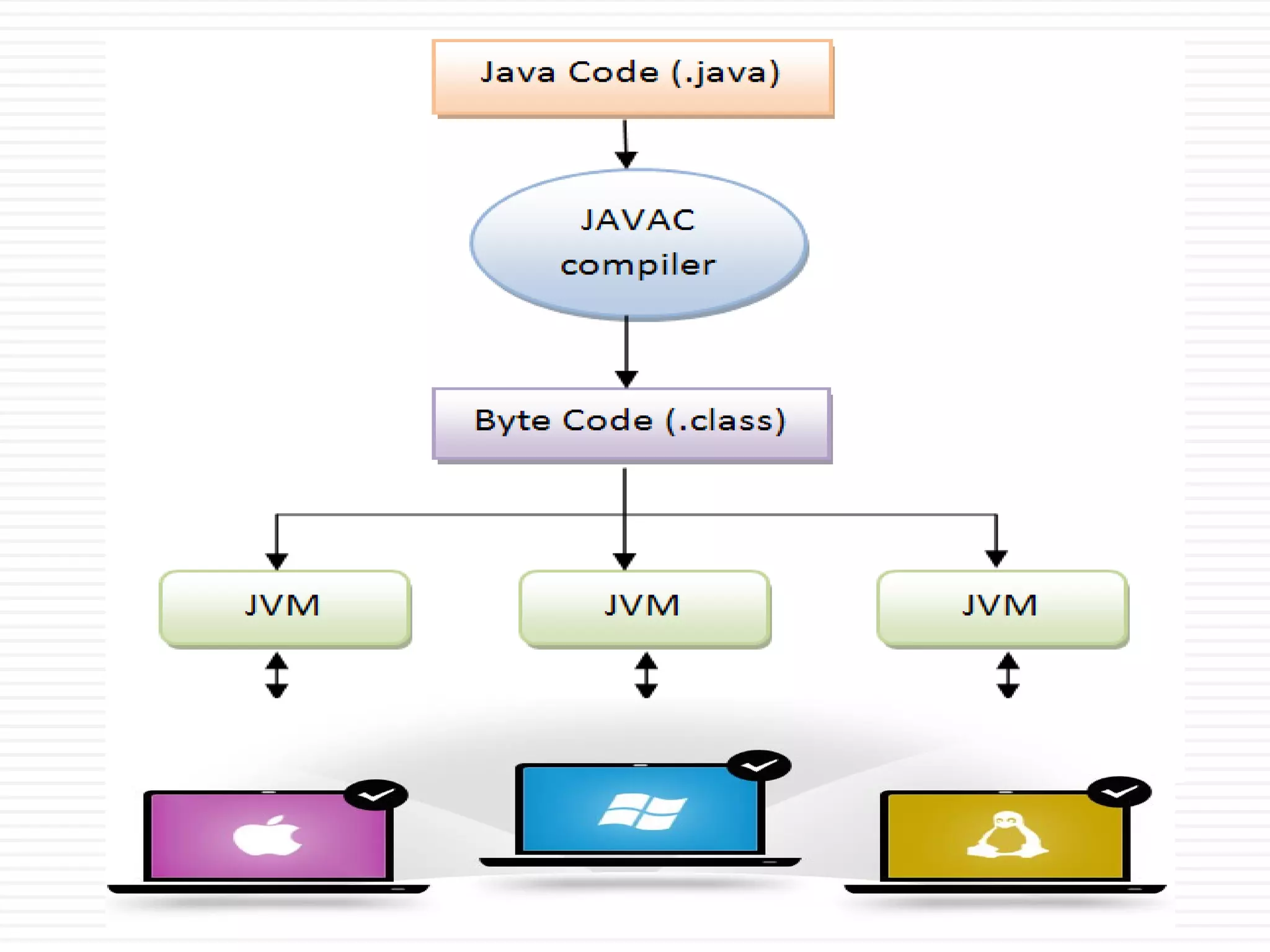
- Java is an object-oriented, platform independent language that is simple, secure, and allows for multi-threaded, high performance applications.
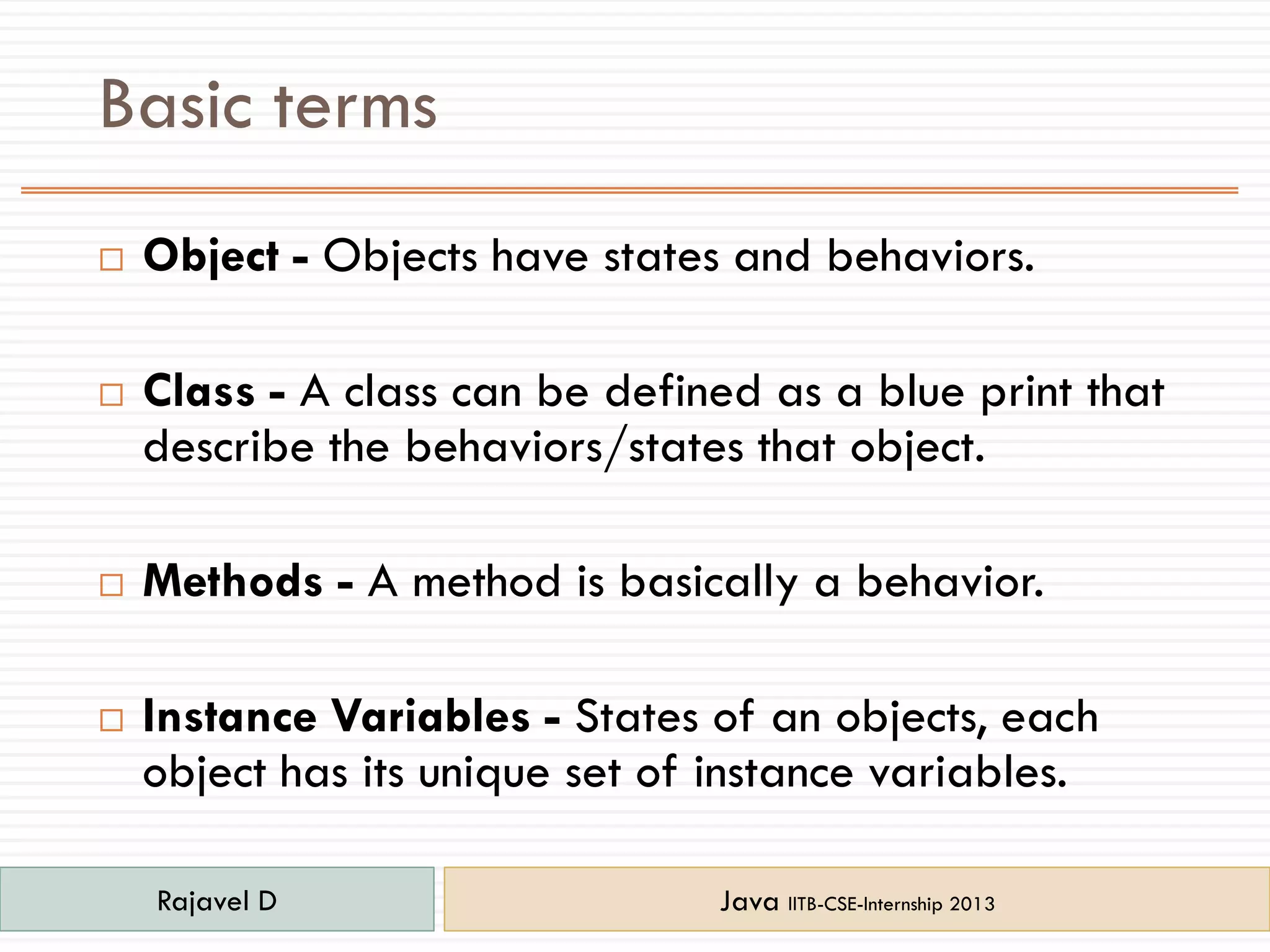
- Objects have states and behaviors defined by classes. Methods define behaviors and instance variables define states.
- Programming conventions like case sensitivity, class/method naming, and file naming are important to follow.
- The main() method marks the starting point of a Java program and its modifiers and parameters are explained.
- Object-oriented principles like abstraction, encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism are discussed at a high-level.
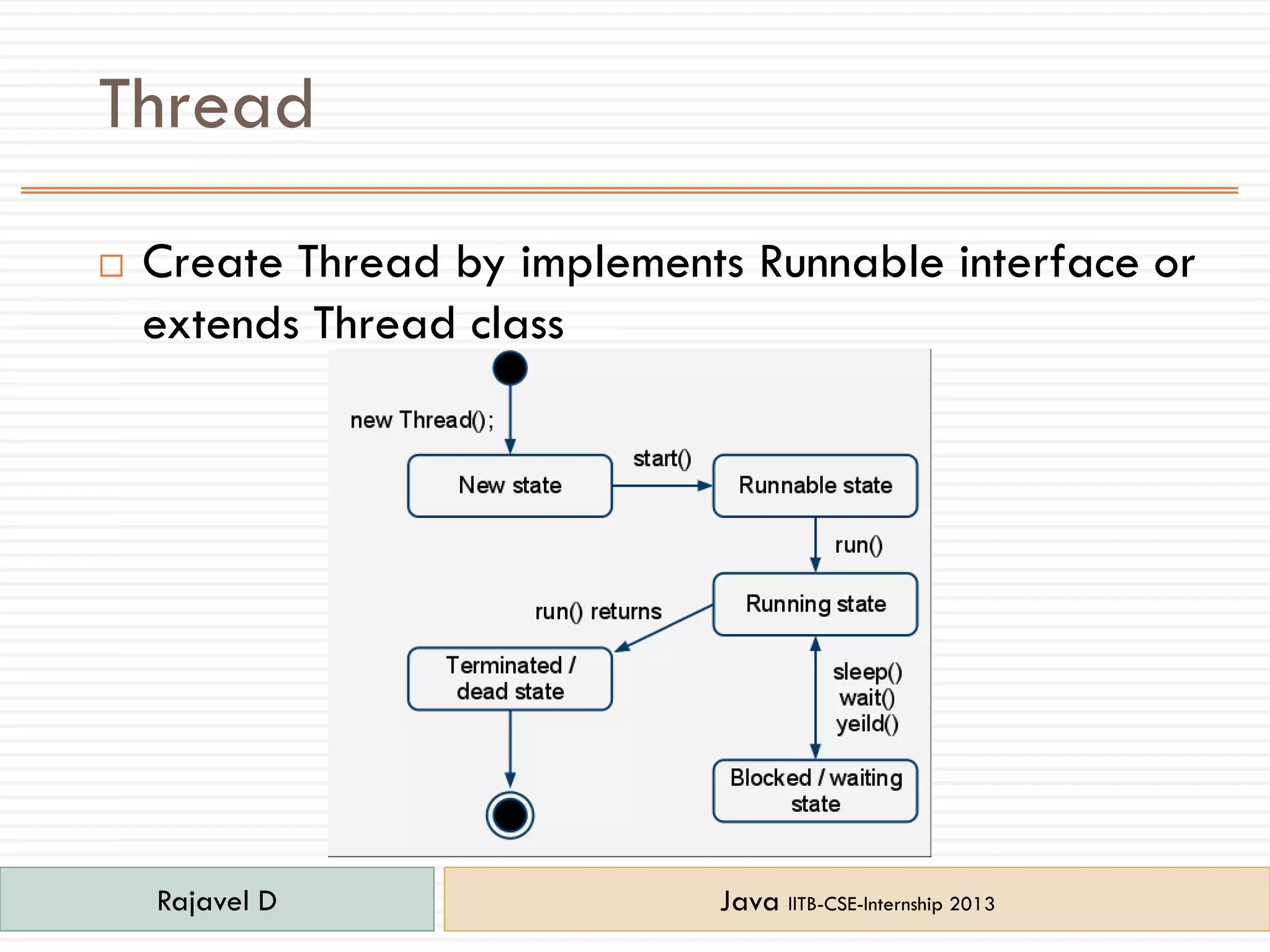
- Additional concepts covered include threads, exceptions, constructors, packages, and


![Simple Program
class HelloWorldApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HelloWorldApp hello = new HelloWorldApp();
hello.sayHello();
}
public void sayHello(){
System.out.println(“Hello”);
}
}
O/P : Hello
Rajavel D Java IITB-CSE-Internship 2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-130514103014-phpapp02/75/Java-6-2048.jpg)