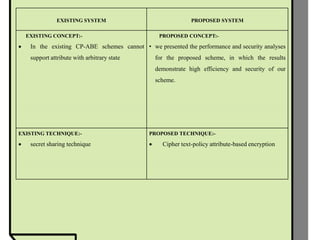
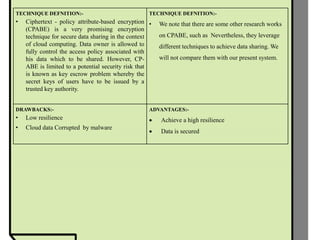
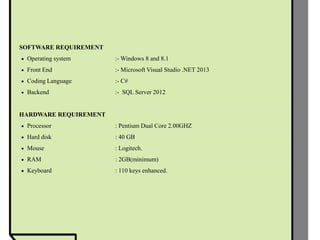
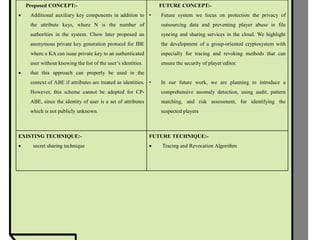
The document proposes improvements to attribute-based data sharing schemes for cloud computing. It aims to address the key escrow problem in ciphertext-policy attribute-based encryption (CP-ABE) schemes by introducing a two-party key issuance protocol. It also introduces the concept of attribute weights to improve attribute expression beyond binary values and simplify access policies.