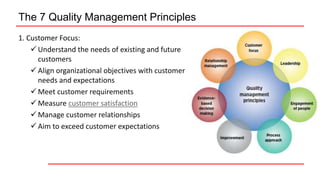
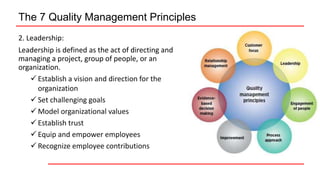
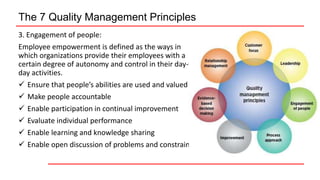
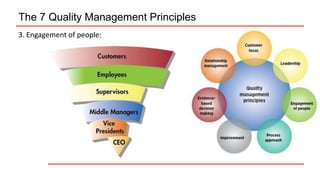
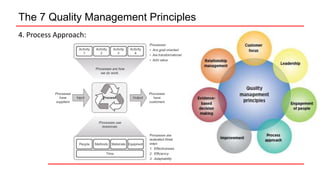
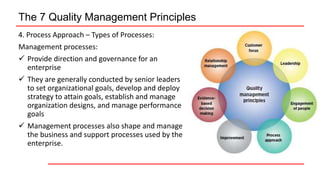
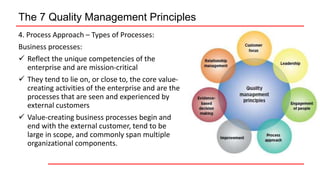
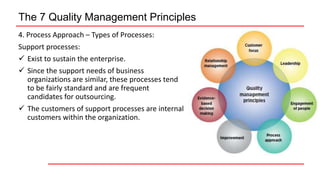
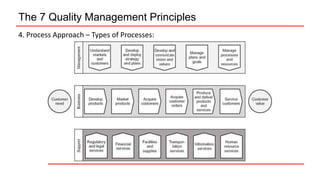
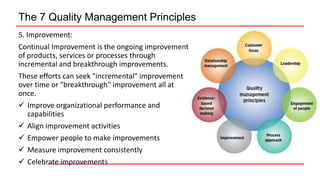
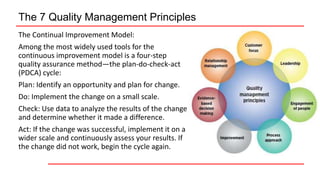
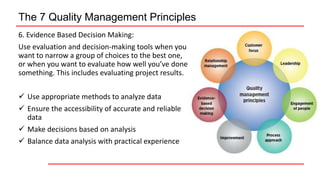
This document provides an overview of ISO 9001 implementation guidelines and quality management principles. It discusses the need for a quality management system and factors to consider when establishing one, including understanding customer and stakeholder needs and expectations. The document also outlines the seven quality management principles: customer focus, leadership, engagement of people, process approach, improvement, evidence-based decision making, and relationship management. It provides details on each principle and emphasizes the importance of continual improvement through methods like the PDCA cycle.