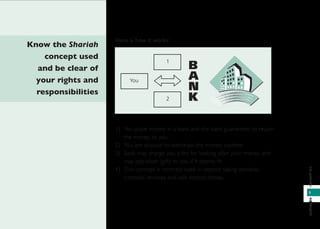
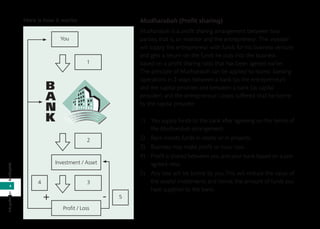
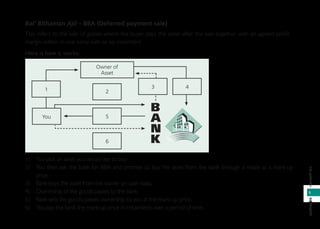
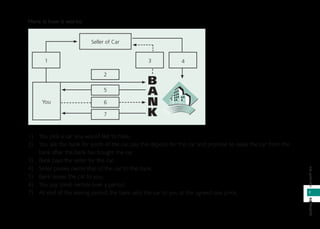
Islamic banking follows Shariah (Islamic law) which prohibits riba (interest) and gharar (excessive uncertainty). It was first established in Malaysia in 1983 and various concepts like mudharabah (profit-sharing), murabahah (cost-plus), and ijarah (leasing) are used. Islamic banks have Shariah committees that ensure compliance with Islamic principles. This document provides an overview of Islamic banking concepts and answers frequently asked questions about differences between Islamic and conventional banking and where to obtain Islamic banking services.