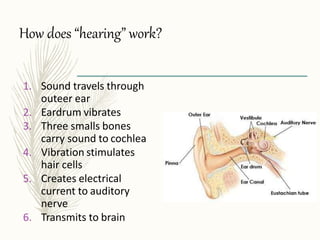
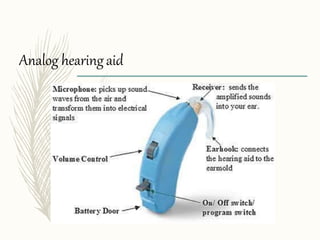
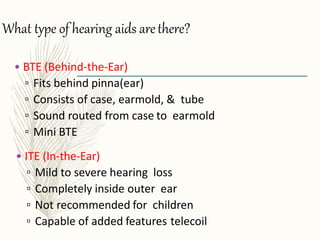
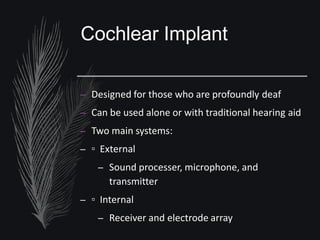
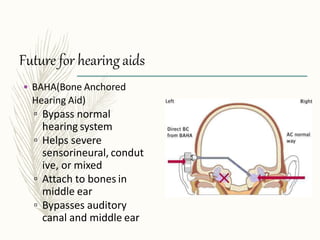
Hearing aids are small electronic devices that amplify sound to help people with hearing loss. They have three basic parts: a microphone that picks up sound, an amplifier that makes sounds louder, and a speaker that sends the amplified sound into the ear. There are two main types of hearing loss - conductive, which is caused by sound being obstructed in the ear and is often treatable with surgery, and sensorineural, which damages the inner ear and is the most common type helped by hearing aids. Modern hearing aids come in various styles like BTE (behind-the-ear) or CIC (completely-in-canal) and can be either analog models or digital models, which have more flexibility to adjust