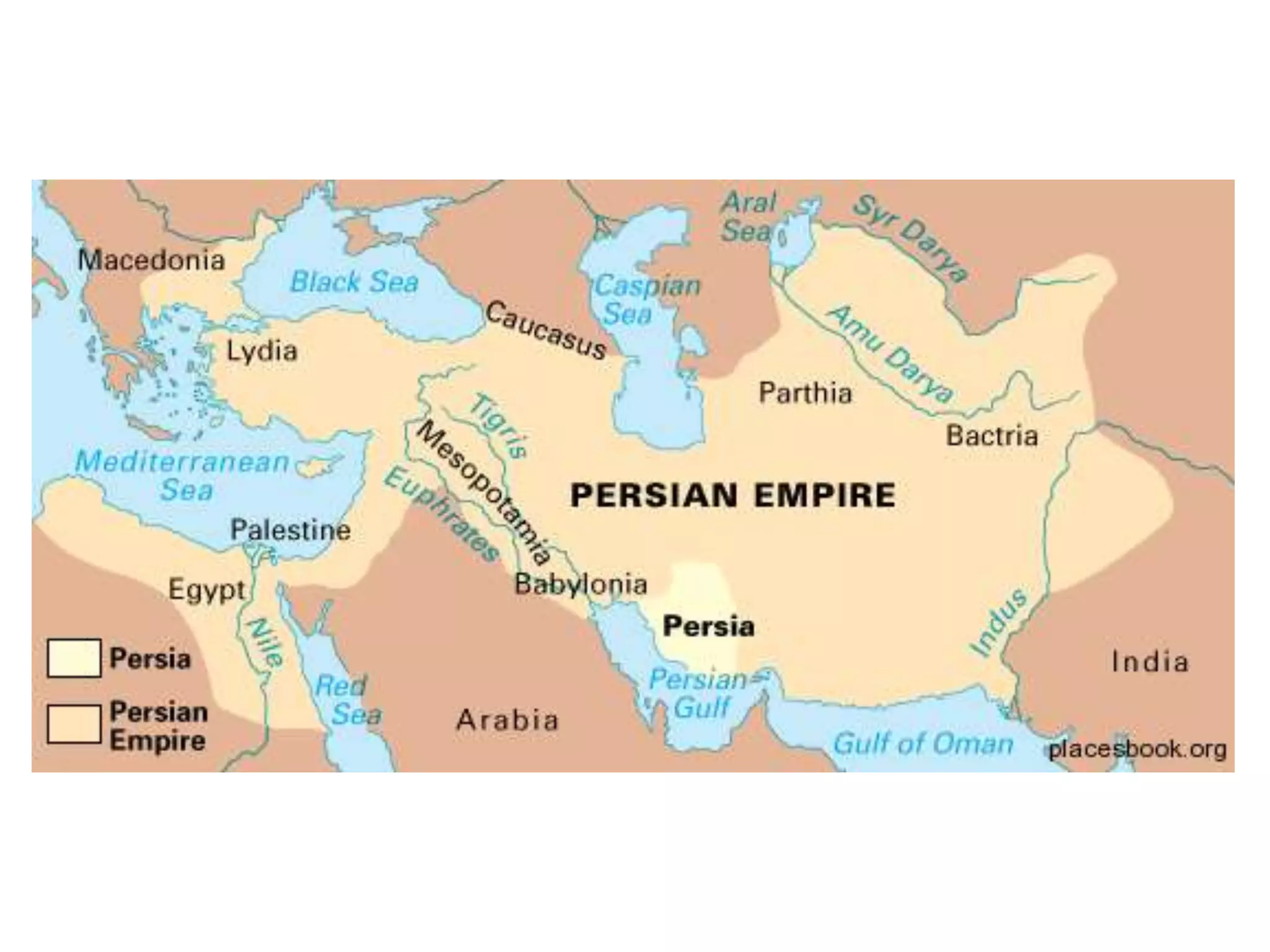
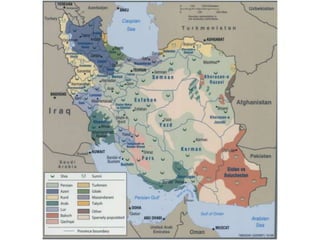
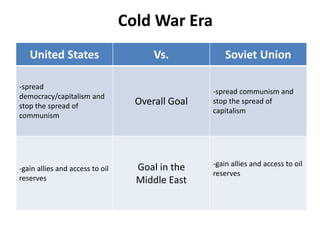
The document discusses the geopolitical context in the Middle East from World War 2 through the US invasion of Iraq in 2003. It notes that during WWII, the US and its allies wanted to secure oil supplies from the Middle East. It then discusses the Cold War dynamics between the US and USSR competing for influence in the region, the 1953 Iranian coup supported by the US and UK, and the 1979 Iranian Revolution overthrowing the US-backed Shah.