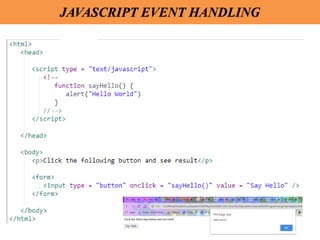
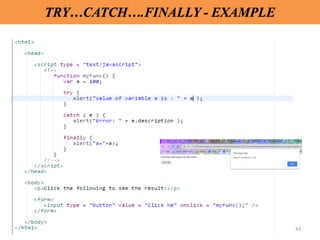
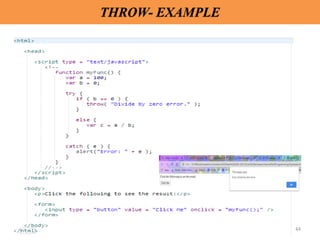
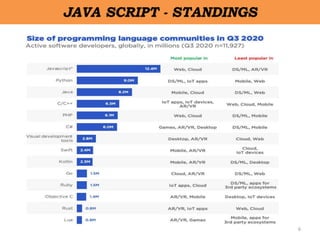
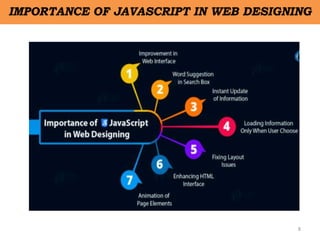
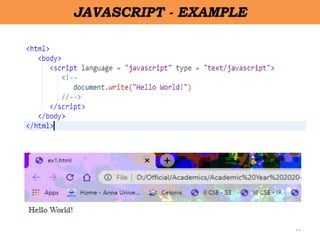
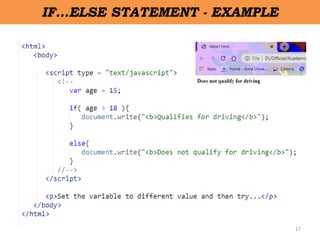
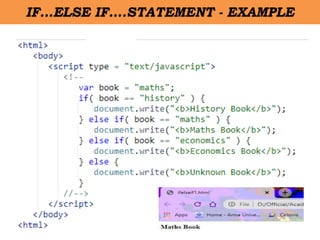
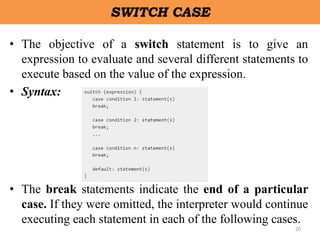
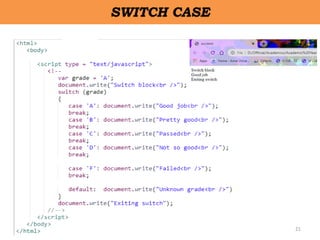
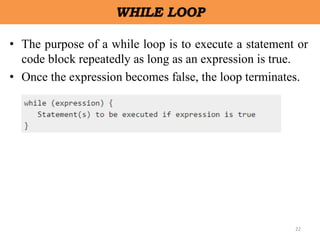
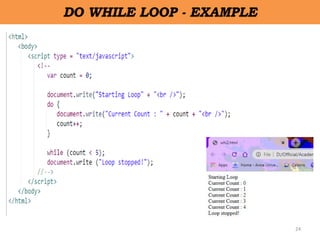
Client-side scripting is performed using JavaScript to generate code that runs in the browser without server processing. JavaScript is used to create dynamic and interactive web pages by adding functionality and behaviors. It is the most commonly used programming language for building websites. JavaScript allows client-side validation, user notifications, simple calculations and greater control of the web page interface.

















![28
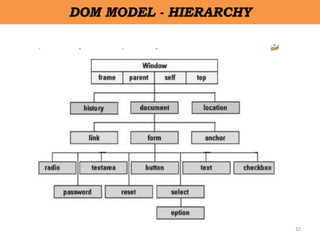
CREATING OBJECTS IN JAVASCRIPT
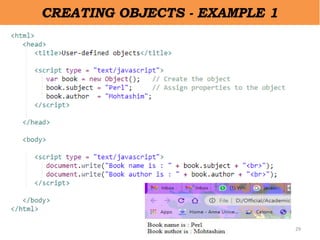
• There are 3 ways to create objects.
– By object literal
• var person = {firstName:"John", lastName:"Doe",
age:50, eyeColor:"blue"};
– By creating instance of Object directly (using new keyword)
• var objectname=new Object();
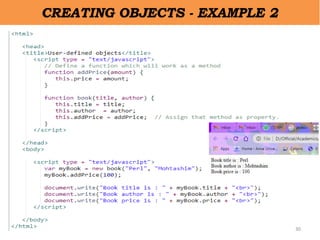
– Using Object Constructor [this operator]
• var myBook = new book("Perl", "Mohtashim");](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ipunit2-230101154002-ad0ea2f6/85/IP-Unit-2-pptx-28-320.jpg)
![34
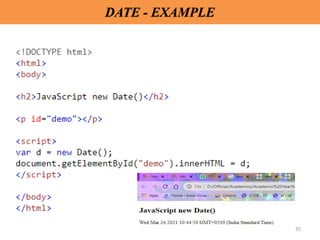
DATE
• The JavaScript date object can be used to get year,
month and day. You can display a timer on the webpage
by the help of JavaScript date object.
• 4 variant of Date constructor to create date object.
– new Date( )
– new Date(milliseconds)
– new Date(datestring)
– new Date(year,month,date[,hour,minute,second,millisecond])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ipunit2-230101154002-ad0ea2f6/85/IP-Unit-2-pptx-34-320.jpg)