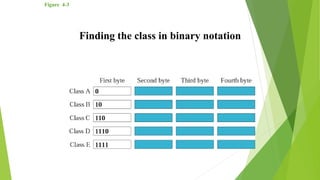
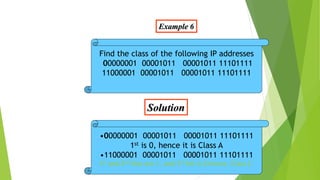
This document discusses IP addresses and classful addressing. It introduces the different classes of IP addresses (A, B, C, D, E), how the address space is divided among them, and how to determine the class of an IP address in binary, decimal, and dotted-decimal notation. It also discusses how IP addresses are composed of a netid and hostid portion.