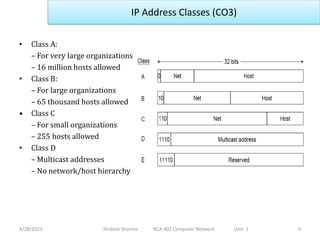
This document discusses IP addresses and subnetting. It begins by explaining that each network interface has a unique IP address. IP addresses are 32 bits long and contain a network and host portion, allowing for a two-level address hierarchy. The document then covers IP address classes and explains subnetting allows a single IP address to span multiple physical networks by using host ID bits as a subnet ID. Subnet masks allow hosts to determine if another IP is on the same subnet.