This document discusses induction of labor, including common indications and contraindications, available methods, and risks. Some key points:
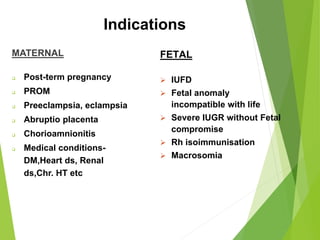
- Induction of labor is indicated when benefits of delivery outweigh continuing pregnancy, for maternal or fetal reasons like post-term pregnancy or fetal anomaly.
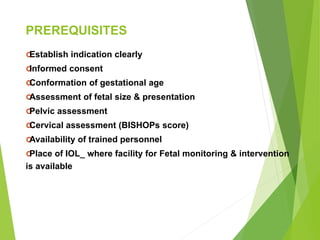
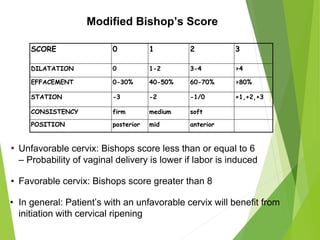
- Methods include mechanical (balloon catheters), chemical (prostaglandins like misoprostol, dinoprostone), and oxytocin. Choice depends on cervical status using the Bishop score.
- Risks include failed induction requiring C-section, uterine hyperstimulation, fetal distress. Careful patient selection and monitoring during induction are important.