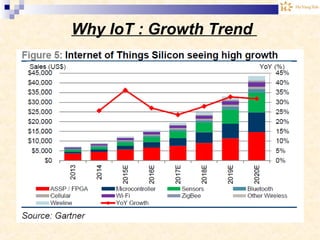
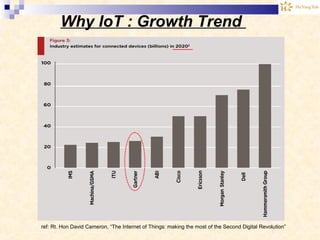
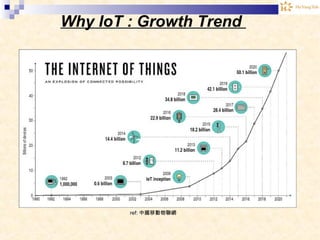
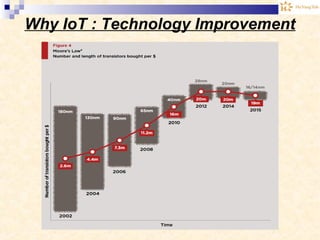
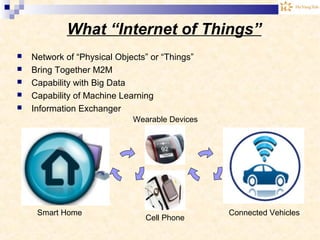
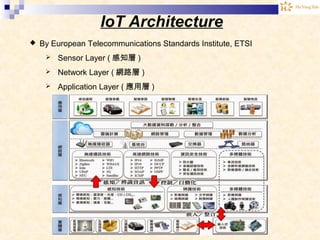
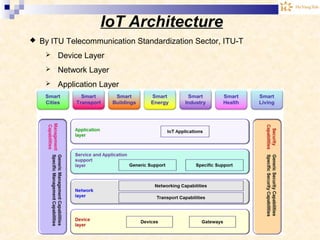
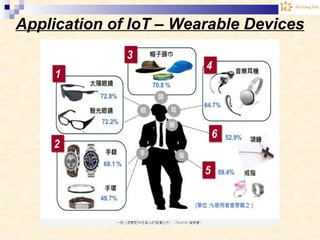
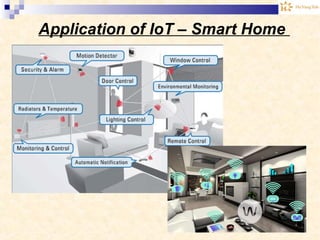
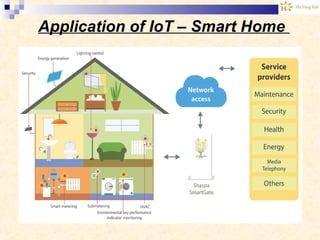
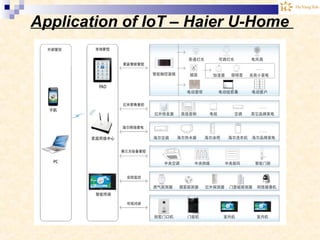
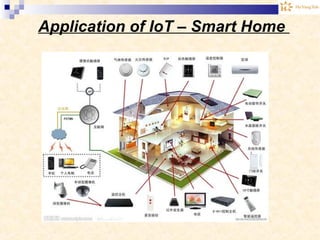
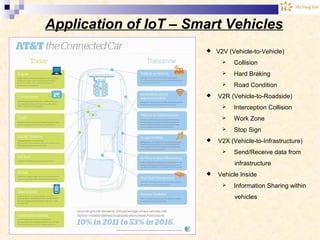
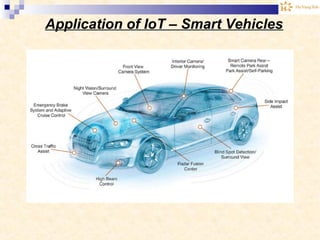
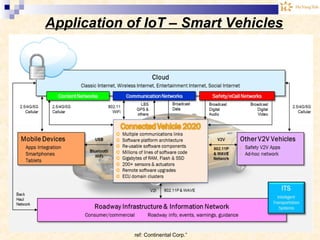
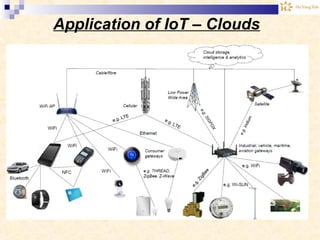
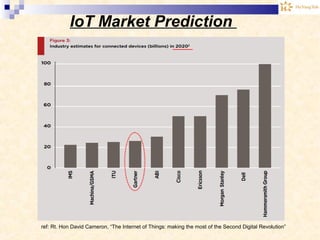
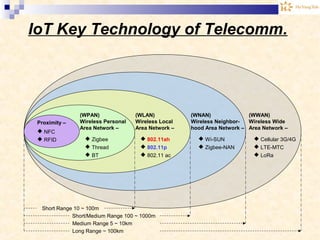
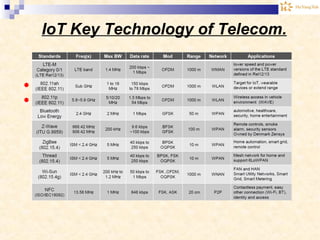
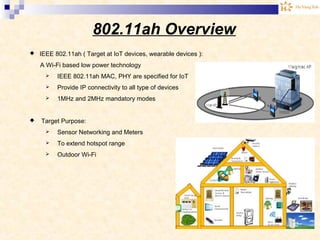
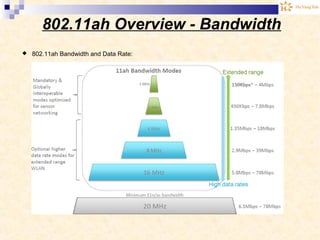
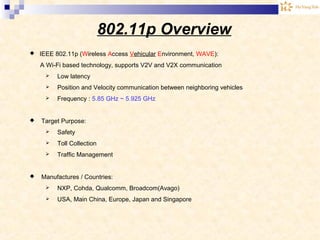
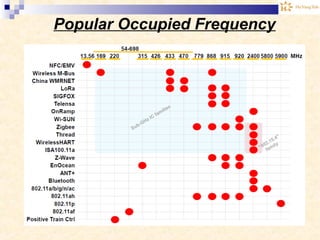
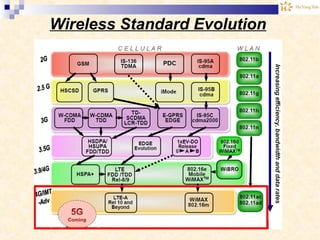
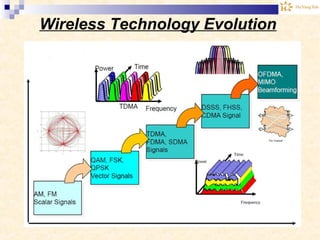
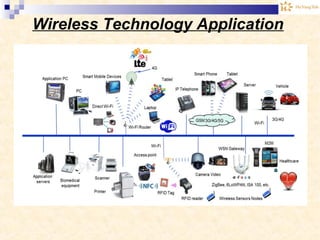
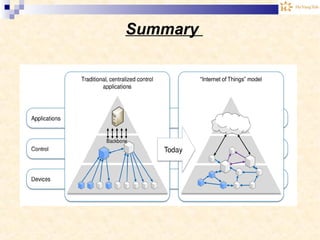
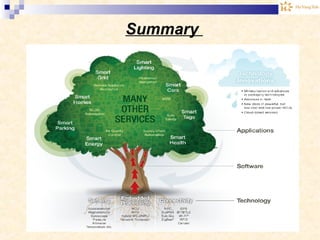
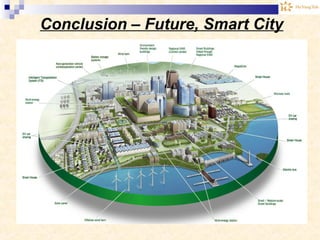
The document discusses the Internet of Things (IoT). It provides an overview of IoT, including its definition as a network of physical objects connected via sensors and software. Examples of IoT applications mentioned include wearable devices, smart homes, smart vehicles, and clouds. The document also discusses IoT architecture, key enabling technologies like various wireless standards, market predictions showing rapid growth of IoT, and a vision of future smart cities enabled by IoT.