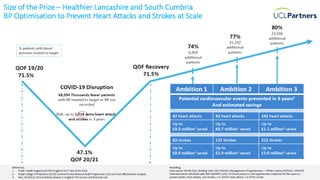
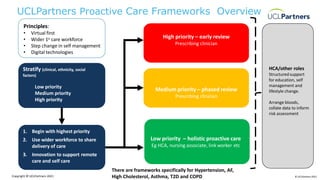
The document discusses the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on proactive care in primary care, emphasizing the shift to remote care and the disruption faced in managing long-term conditions. It outlines a framework to restore proactive care, focusing on utilizing a wider primary care workforce, digital technologies, and support for self-management to improve patient outcomes. The document includes specific incentive opportunities for cardiovascular disease prevention and highlights the importance of personalized care and shared decision-making in addressing health inequalities.