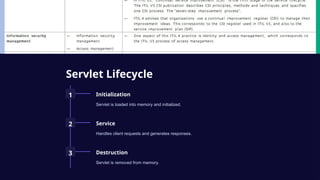
Servlets are Java programs that run on web servers, handling client requests and generating dynamic content. They perform tasks such as session management, HTTP request handling, and configuration via web.xml. Best practices for servlet development include modularity, error handling, security, and performance optimization.