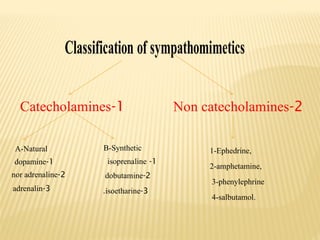
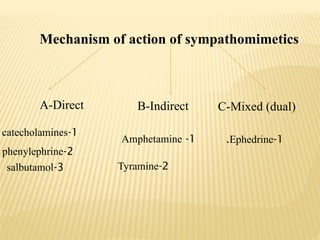
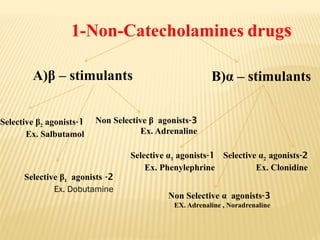
The document provides an overview of sympathomimetic drugs, which stimulate adrenoceptors and produce actions similar to the sympathetic system. It details the classification of these drugs into catecholamines and non-catecholamines, their mechanisms of action, and various clinical uses and contraindications for drugs like adrenaline, noradrenaline, dopamine, and dobutamine. Additionally, it covers selective and non-selective β and α agonists, their effects, side effects, and clinical applications in treating conditions such as asthma, shock, and hypotension.