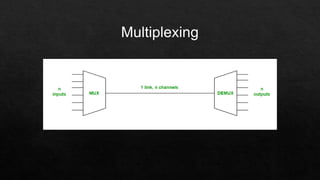
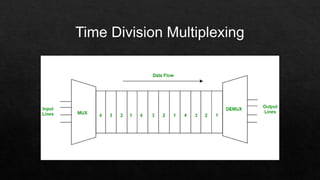
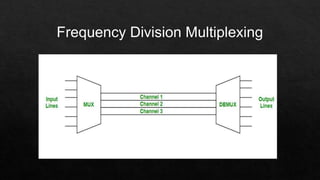
Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) allocates fixed time slots to different data streams to allow multiple streams to share a single communication channel. It interleaves data by assigning each source a unique time slot in a repeating cycle. TDM is commonly used for voice and data transmission over a single medium, optimizing resource use through temporal segmentation.