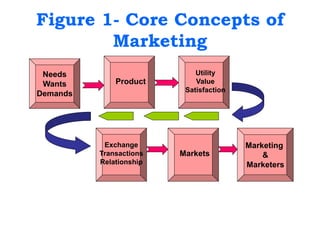
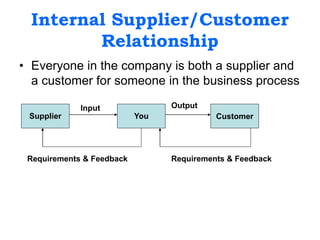
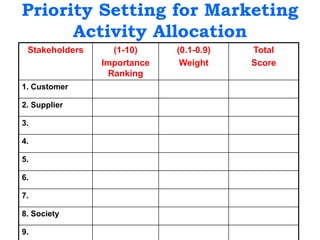
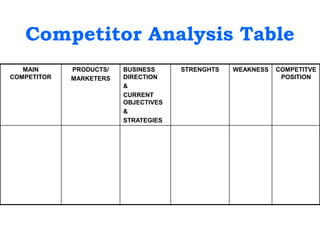
This document provides an overview of an introduction to marketing course. It includes sections on marketing terminology, core concepts of marketing, marketing management, traditional vs total quality marketing, the marketing planning process, and the 4Ps and 7Ps of marketing. It also discusses new roles for marketers, stakeholder analysis, priority setting, and competitor analysis. Group exercises are included throughout to apply the concepts. The goal is to give students foundational knowledge of key marketing topics.