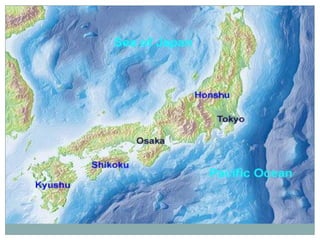
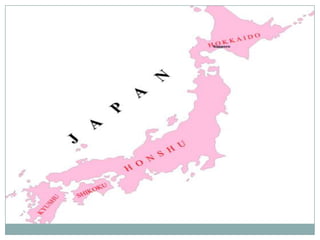
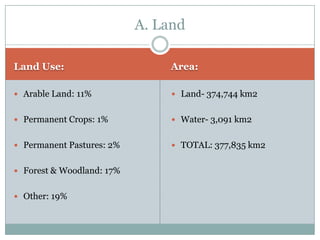
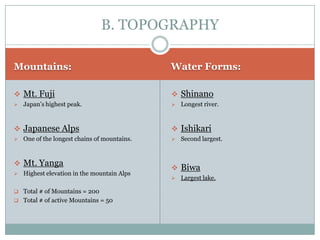
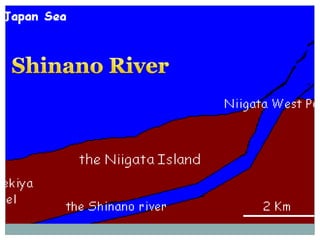
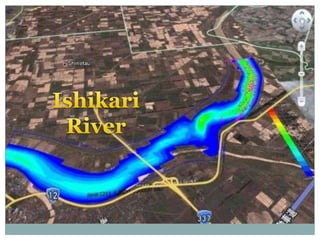
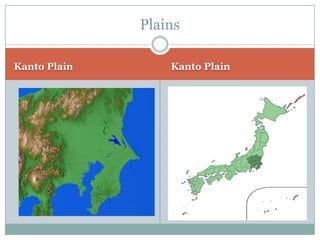
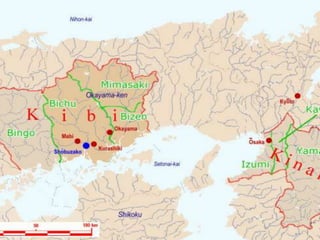
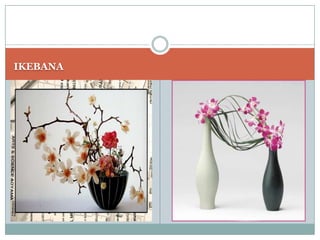
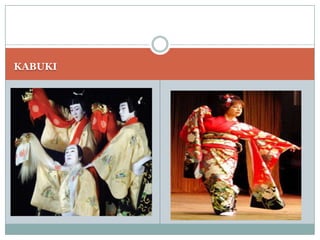
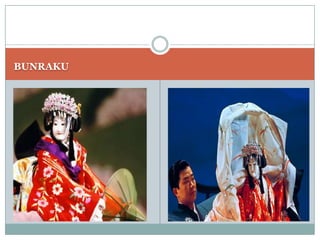
Japan, officially known as Nihon or Nippon, consists of four major islands and has distinct geographical features including mountains, plains, and significant water bodies. The country experiences a temperate climate with variations influenced by monsoons and oceanic currents, and the majority of its population practices Shintoism. Japanese culture is characterized by a blend of tradition and modernity with a strong appreciation for nature and the arts.