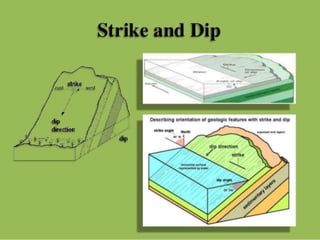
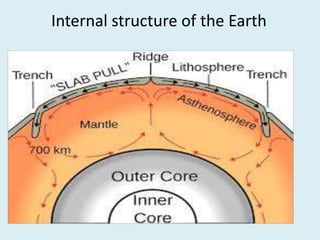
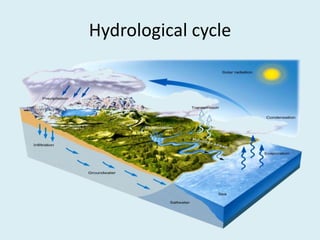
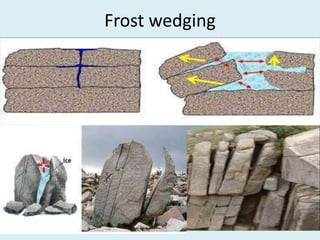
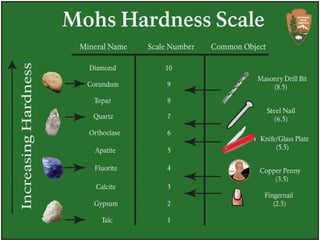
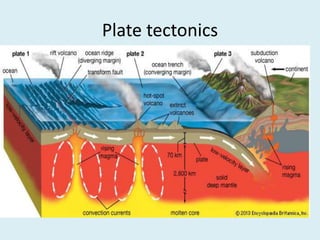
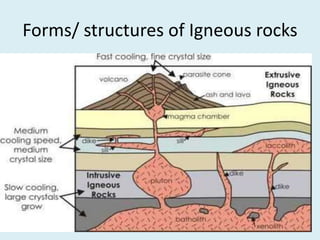
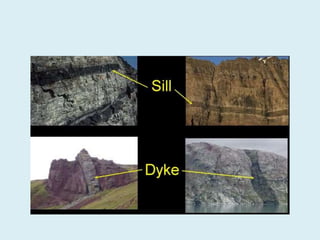
The document discusses various geological concepts including the rock cycle, weathering processes, rock types, plate tectonics, and volcanic eruptions. It also summarizes several case studies of engineering failures caused by geological factors, such as dam failures due to weaknesses in rock foundations and infiltration of water. Geology is shown to be important for engineering projects to design structures that are stable and protected based on the local geological conditions.




























![Tigra Dam failure
• (also spelled "Tig Dam") creates a freshwater reservoir on the Sank
River, about 23 km from Gwalior, Madhya Pradesh, India[1] It plays a
crucial role in supplying water to the city.
• View from the Dam
• right side view
• The dam is 24 metres high at its crest, and 1341 m long.
• The reservoir has a capacity of 4.8 million cubic metres
• A dam constructed on this site in 1915 failed on the afternoon of
19 August 1917,
• due to infiltration into its sandstone foundations. A
• bout 10,000 people were killed downstream.[3]
• A subsequent structure failed in 1999](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoengineringgeologyp-191105165301/85/Introduction-to-Engineering-geology-37-320.jpg)
![St. Francis Dam
• The dam was designed and built between 1924 and 1926
• by the Los Angeles Department of Water and Power,
• The department was under the direction of its general
manager and chief engineer, William Mulholland.
• At 11:57 p.m. on March 12, 1928, the dam catastrophically
failed, and the resulting flood took the lives of what is
estimated to be at least 431 people.[2][3]
• The collapse of the St. Francis Dam is considered to be one
of the worst American civil engineering disasters of the
20th century and remains the second-greatest loss of life in
California's history](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoengineringgeologyp-191105165301/85/Introduction-to-Engineering-geology-38-320.jpg)