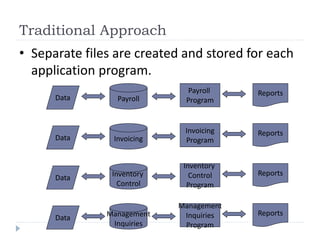
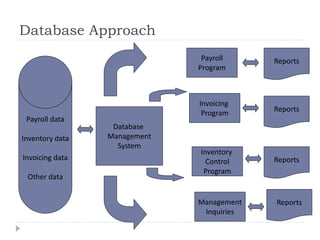
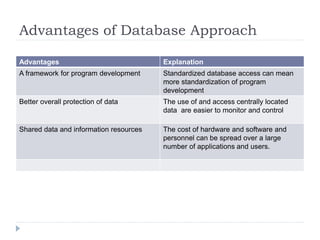
This document discusses data management concepts and database systems. It describes the hierarchy of data from bits to databases. Key concepts covered include data entities, attributes, and keys. The document compares the traditional approach of separate data files for each application to the database approach of centralized data management. Benefits of the database approach include reduced redundancy, improved integrity, and easier data access and updating. Components of a database system are also summarized, including hardware, software, people, procedures, and data.