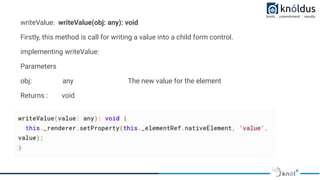
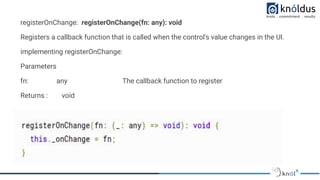
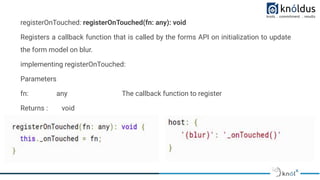
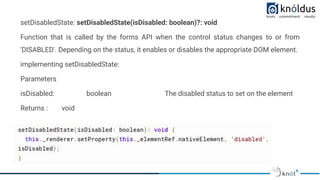
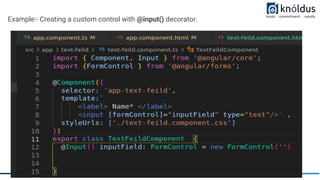
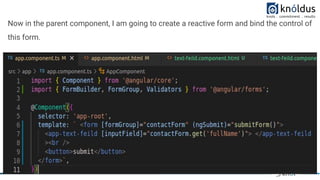
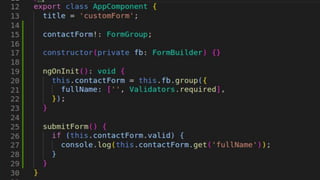
The document provides an introduction to creating custom form controls in Angular. It discusses how standard form controls work using control value accessors and how this can be leveraged to create custom controls. It describes the methods that must be implemented for the control value accessor interface: writeValue, registerOnChange, registerOnTouched, and setDisabledState. The document also presents an alternative approach to creating custom controls without using a control value accessor by instead leveraging the @Input() decorator and property binding. It provides an example of this approach and concludes with references for further information.