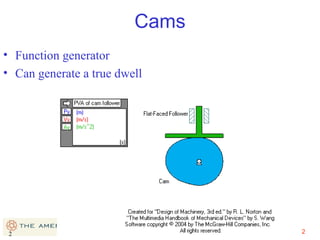
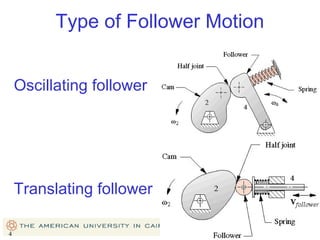
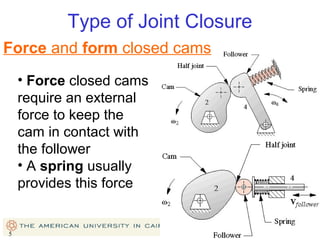
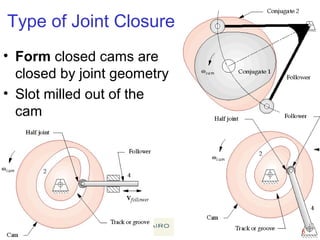
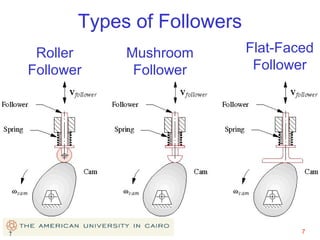
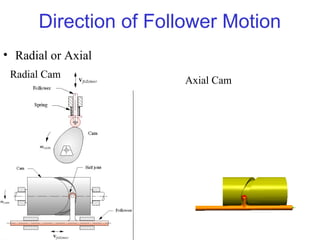
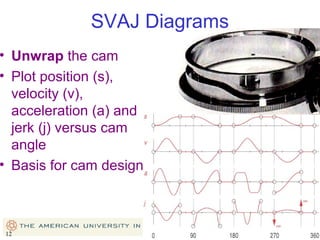
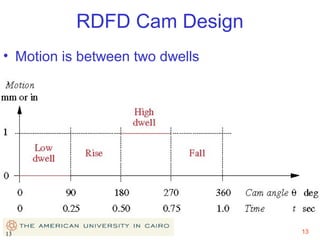
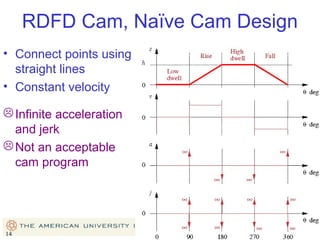
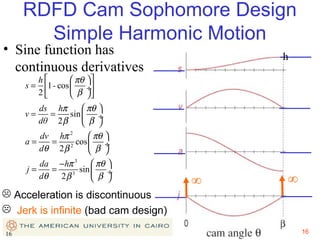
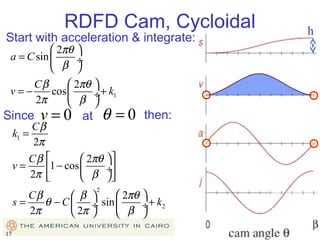
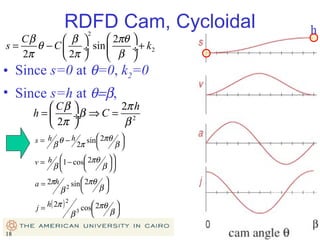
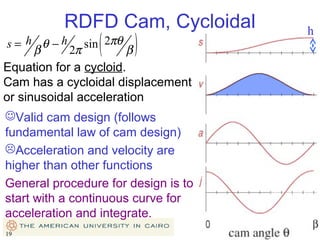
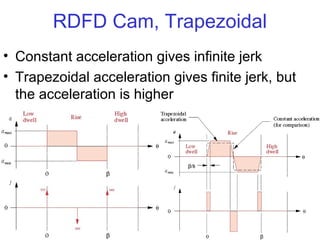
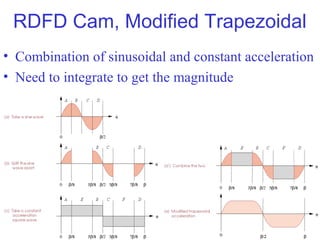
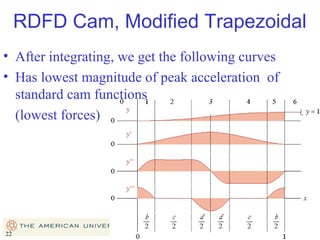
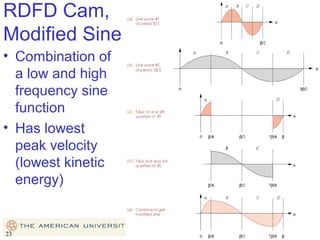
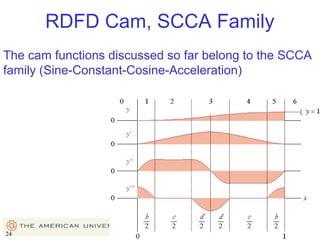
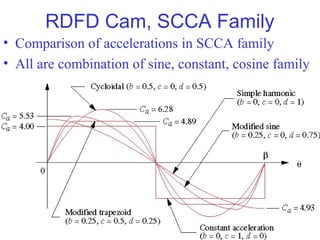
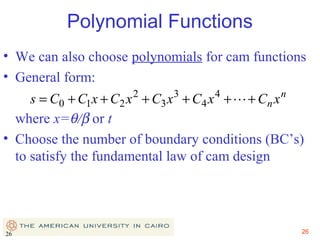
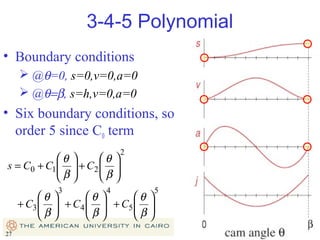
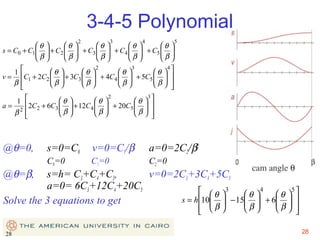
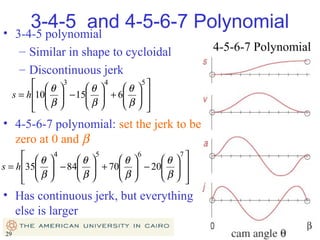
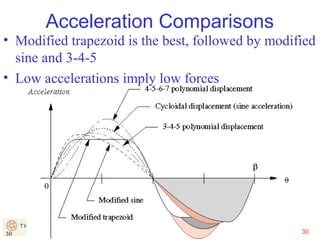
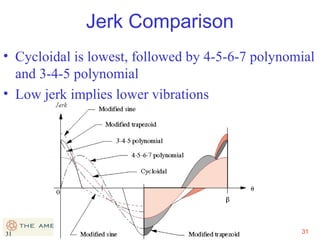
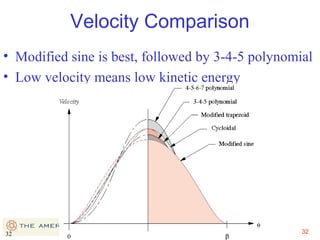
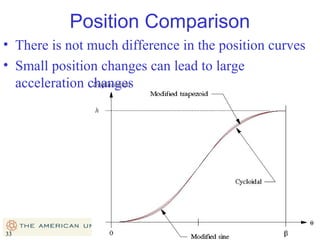
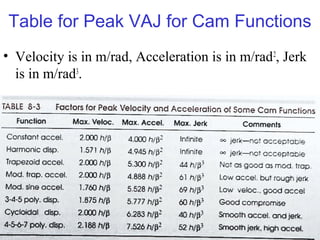
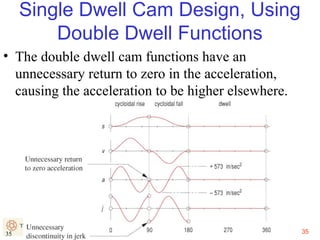
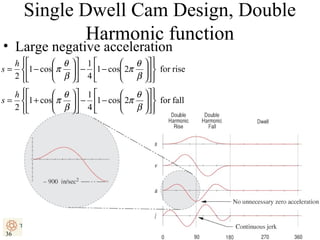
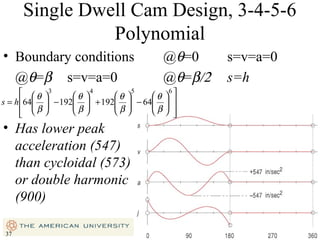
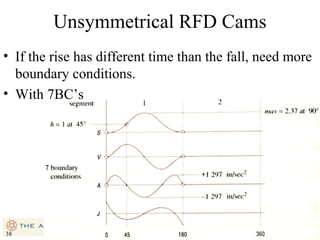
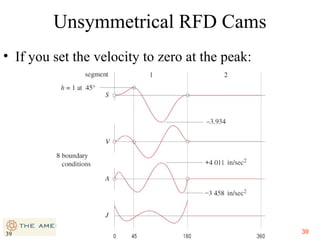
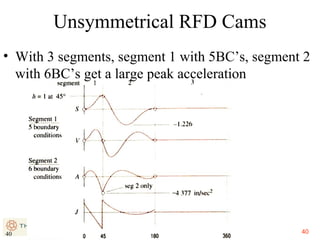
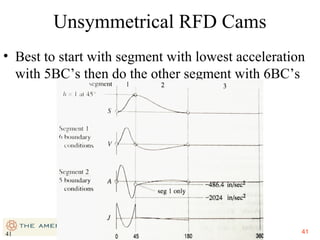
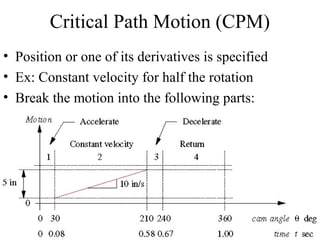
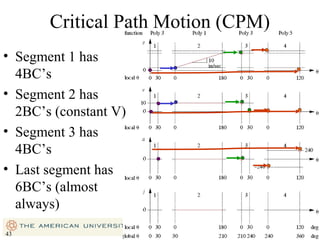
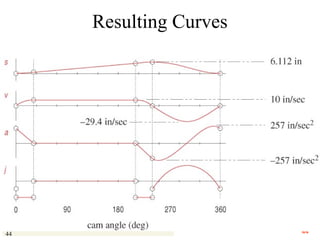
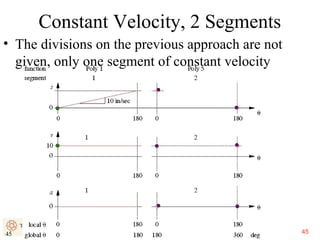
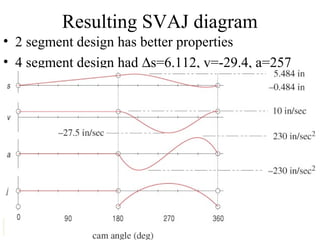
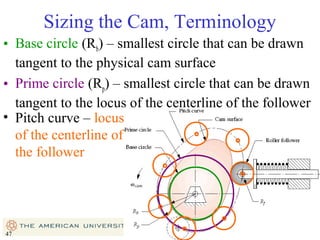
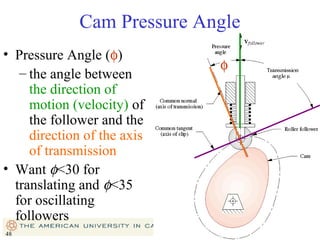
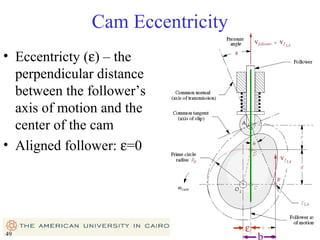
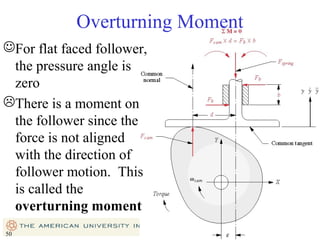
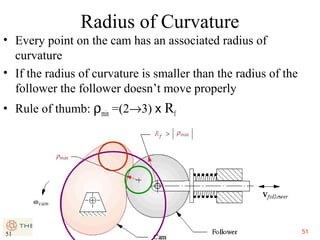
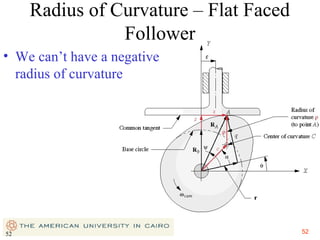
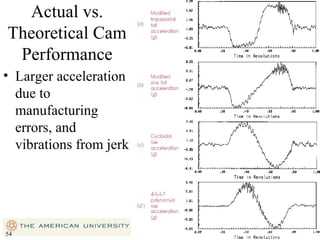
This document provides an overview of cam design principles and functions. It begins by defining different cam terminology such as follower motion types, joint closure types, follower types, and motion constraints. It then discusses common cam motion programs including rise-fall, rise-fall-dwell, and rise-dwell-fall-dwell. Several cam profile functions are analyzed that satisfy the fundamental law of cam design requiring continuous derivatives, including cycloidal, trapezoidal, and polynomial functions. Comparisons of the velocity, acceleration, jerk, and position profiles of different cam functions show that modified trapezoidal cams have the lowest peak acceleration while cycloidal and polynomial cams have the lowest jerk. The document concludes with considerations for single dwell cam design.