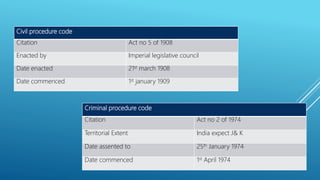
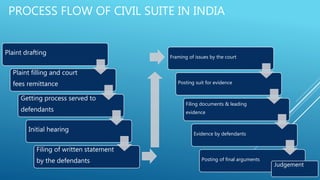
This document provides an introduction to civil and criminal procedure codes in India. It discusses the Civil Procedure Code of 1908, which regulates the functioning of civil courts, and the Criminal Procedure Code of 1974, which provides the framework for investigation and prosecution of crimes. The document outlines the key aspects and processes defined in each code, including filing cases, court hierarchy and jurisdiction, rights of parties, investigation process for criminal cases, and sentencing guidelines. It also gives examples of recent civil cases related to the construction sector that involved summons, warrants, notices, and injunction orders.