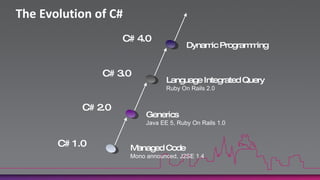
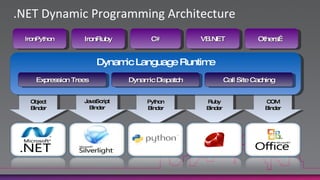
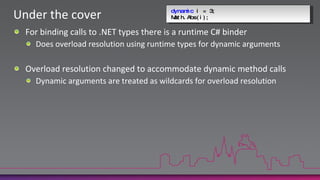
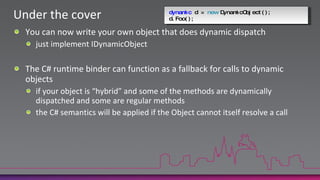
The document discusses the new dynamic type in C# 4.0. It allows variables to be treated dynamically at compile-time and their operations resolved at run-time. This is done by packaging operation details into CallSite objects that are interpreted by the Dynamic Language Runtime. The dynamic type supports method calls, property/indexer access, and operators on any variable or argument. It also improves COM interoperability and introduces covariance/contravariance.



![Dynamically Typed ObjectsCalculator calc = GetCalculator();int sum = calc.Add(10, 20);.NET objectobject calc = GetCalculator();TypecalcType = calc.GetType();object res = calcType.InvokeMember("Add",BindingFlags.InvokeMethod, null,newobject[] { 10, 20 });int sum = Convert.ToInt32(res);Dynamic Language objectScriptObject calc = GetCalculator();object res = calc.Invoke("Add", 10, 20);int sum = Convert.ToInt32(res);Statically typed to be dynamicdynamic calc = GetCalculator();int sum = calc.Add(10, 20);Dynamic method invocationDynamic conversion](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontocsharp4-0anddynamic-100809013617-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-c-sharp-4-0-and-dynamic-6-320.jpg)


![IDynamicObjectpublicabstractclassDynamicObject : IDynamicObject{publicvirtualobjectGetMember(GetMemberBinder info);publicvirtualobjectSetMember(SetMemberBinder info, object value);publicvirtualobjectDeleteMember(DeleteMemberBinder info); publicvirtualobjectUnaryOperation(UnaryOperationBinder info);publicvirtualobjectBinaryOperation(BinaryOperationBinder info, objectarg);publicvirtualobject Convert(ConvertBinder info); publicvirtualobject Invoke(InvokeBinder info, object[] args);publicvirtualobjectInvokeMember(InvokeMemberBinder info, object[] args);publicvirtualobjectCreateInstance(CreateInstanceBinder info, object[] args); publicvirtualobjectGetIndex(GetIndexBinder info, object[] indices);publicvirtualobjectSetIndex(SetIndexBinder info, object[] indices, object value);publicvirtualobjectDeleteIndex(DeleteIndexBinder info, object[] indices); publicMetaObjectIDynamicObject.GetMetaObject();}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontocsharp4-0anddynamic-100809013617-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-c-sharp-4-0-and-dynamic-11-320.jpg)

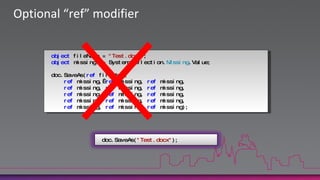
![object -> dynamic mappingWe need to cast((Excel.Range)xl.Cells[1,1]).Value2 = “ID”;xl.Cells[1,1].Value2 = “ID”;When the return type of a COM call is object you are forced to cast to a known typeMaking the code harder to understandIf the return type is dynamic, you can continue to “dot” on the return typeIf you typed something wrong the compiler won’t tell you](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontocsharp4-0anddynamic-100809013617-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-c-sharp-4-0-and-dynamic-13-320.jpg)
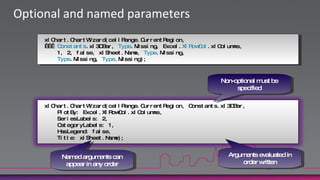



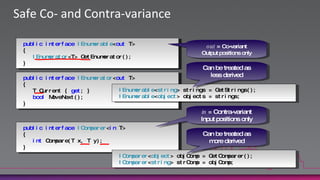
![Co- and Contra-variance.NET arrays are co-variantstring[] strings = GetStringArray();Process(strings);…but not safelyco-variantvoid Process(object[] objects) { … }void Process(object[] objects) { objects[0] = "Hello"; // Ok objects[1] = newButton(); // Exception!}Until now, C# generics have been invariantList<string> strings = GetStringList();Process(strings);C# 4.0 supports safe co- and contra-variancevoid Process(IEnumerable<object> objects) { … }void Process(IEnumerable<object> objects) {// IEnumerable<T> is read-only and// therefore safely co-variant}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontocsharp4-0anddynamic-100809013617-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-c-sharp-4-0-and-dynamic-19-320.jpg)







![ Quiz!classBase { publicvirtualvoid Foo(int x = 4, int y = 5) { Console.WriteLine("x:{0}, y:{1}", x, y); }}classDerived : Base { publicoverridevoid Foo(int y = 4, int x = 5) { Console.WriteLine("x:{0}, y:{1}", x, y); }}classProgram { staticvoid Main(string[] args) { Base b = newDerived(); b.Foo(x: 4, y: 5); }}Output:x:4, y:5x:5, y:4x:4, y:4x:5, y:5None of the aboveOutput:x:4, y:5x:5, y:4x:4, y:4x:5, y:5None of the above](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontocsharp4-0anddynamic-100809013617-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-c-sharp-4-0-and-dynamic-29-320.jpg)
