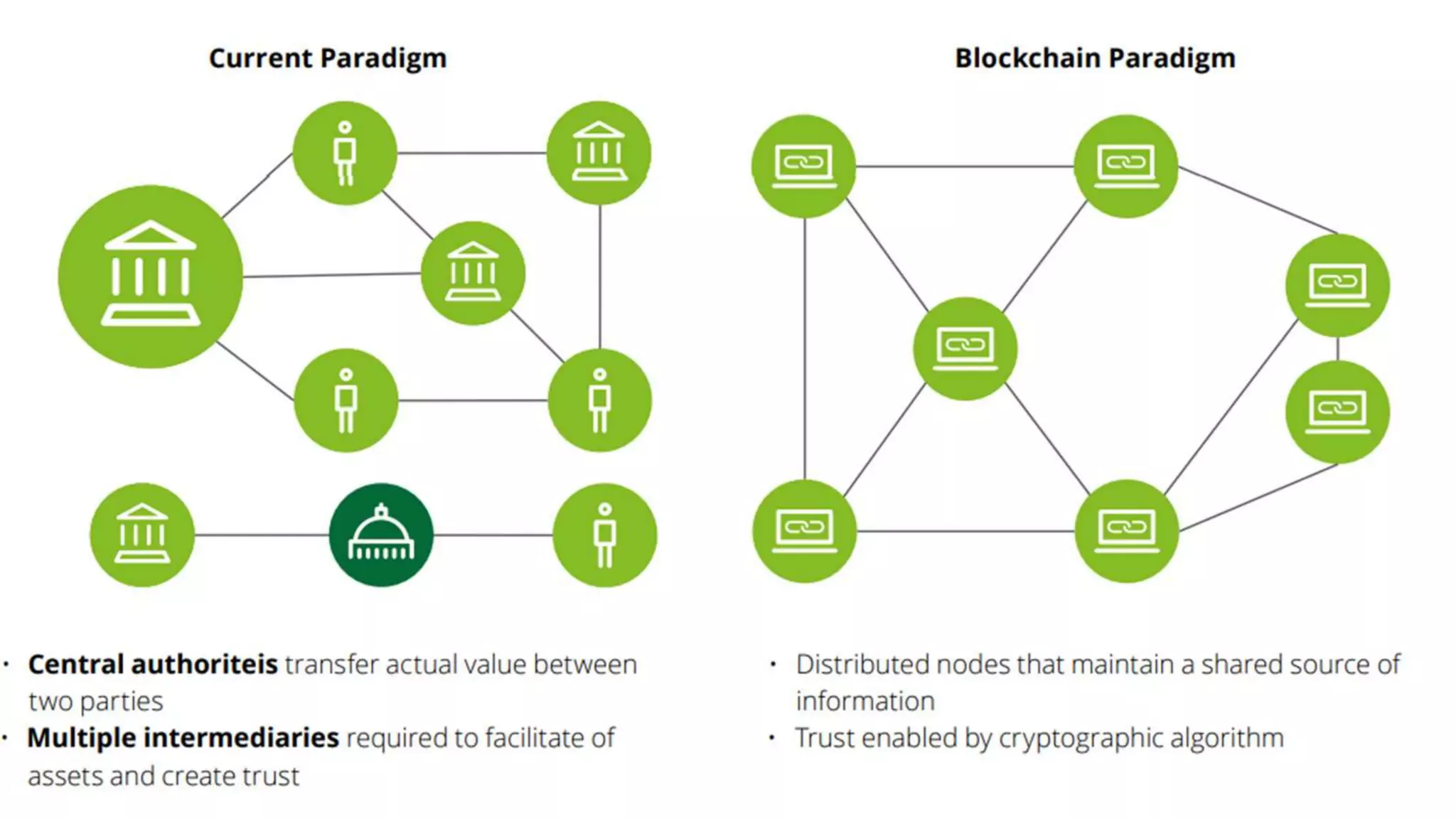
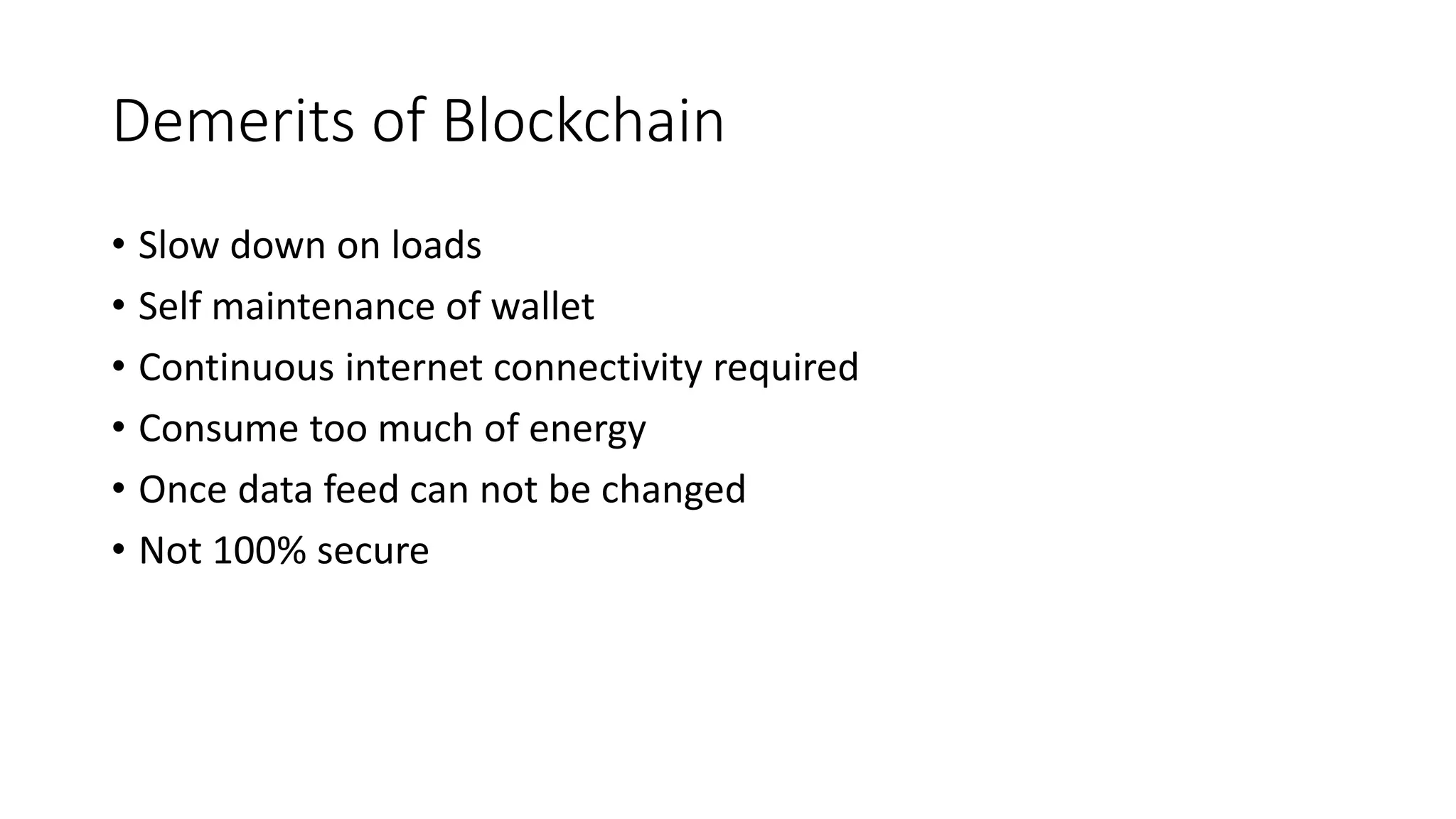
This document provides an introduction to blockchain and cryptocurrencies. It discusses the history of blockchain from 1991 when it was first described to 2009 when Bitcoin launched. It defines blockchain as an immutable time-stamped series of records distributed and managed by a peer-to-peer network. It also discusses the differences between centralized, decentralized, and distributed networks. The document outlines different types of blockchains and applications of blockchain like payments, supply chain monitoring, and medical recordkeeping. It notes both benefits like cost effectiveness and reduced reliance on trusted parties, as well as challenges like energy consumption and inability to change past data.