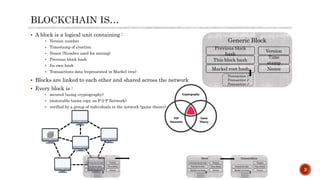
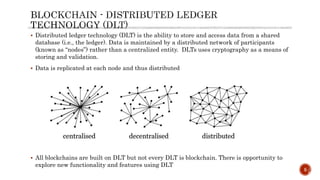
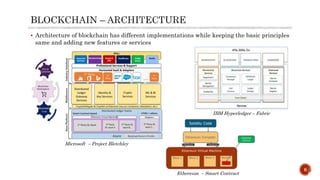
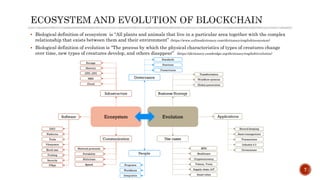
The document discusses digital transformation as essential for modern customer-centric business ecosystems, focusing on technologies like blockchain, which enables rapid business evolution through decentralization and secure data management. It highlights the foundational concepts of blockchain, its architecture, and different types, while emphasizing the impact on organizational processes, including changes in money, accounting, and fundraising models. Additionally, it touches on the technological opportunities and challenges that arise from adopting distributed ledger technologies.