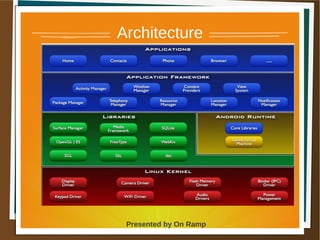
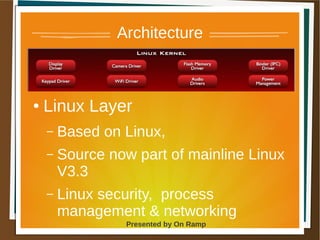
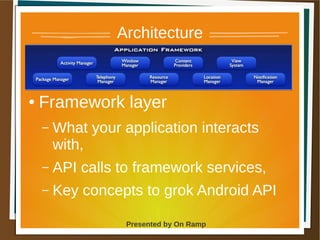
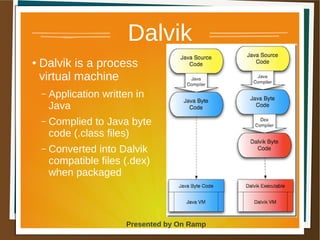
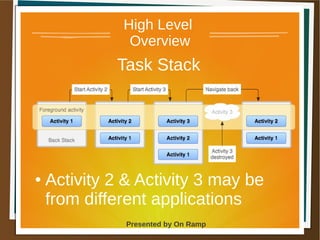
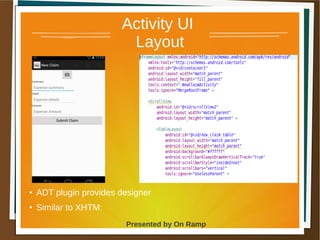
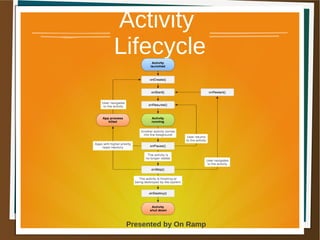
The document provides a comprehensive overview of the Android platform, detailing its architecture, supported languages, and key components necessary for building Android applications. It explains essential concepts like intents, activities, services, and the lifecycle of components within the Android framework. Additionally, it touches on development environments, security measures, and application configuration, emphasizing the unique nature of Android applications compared to web or desktop applications.