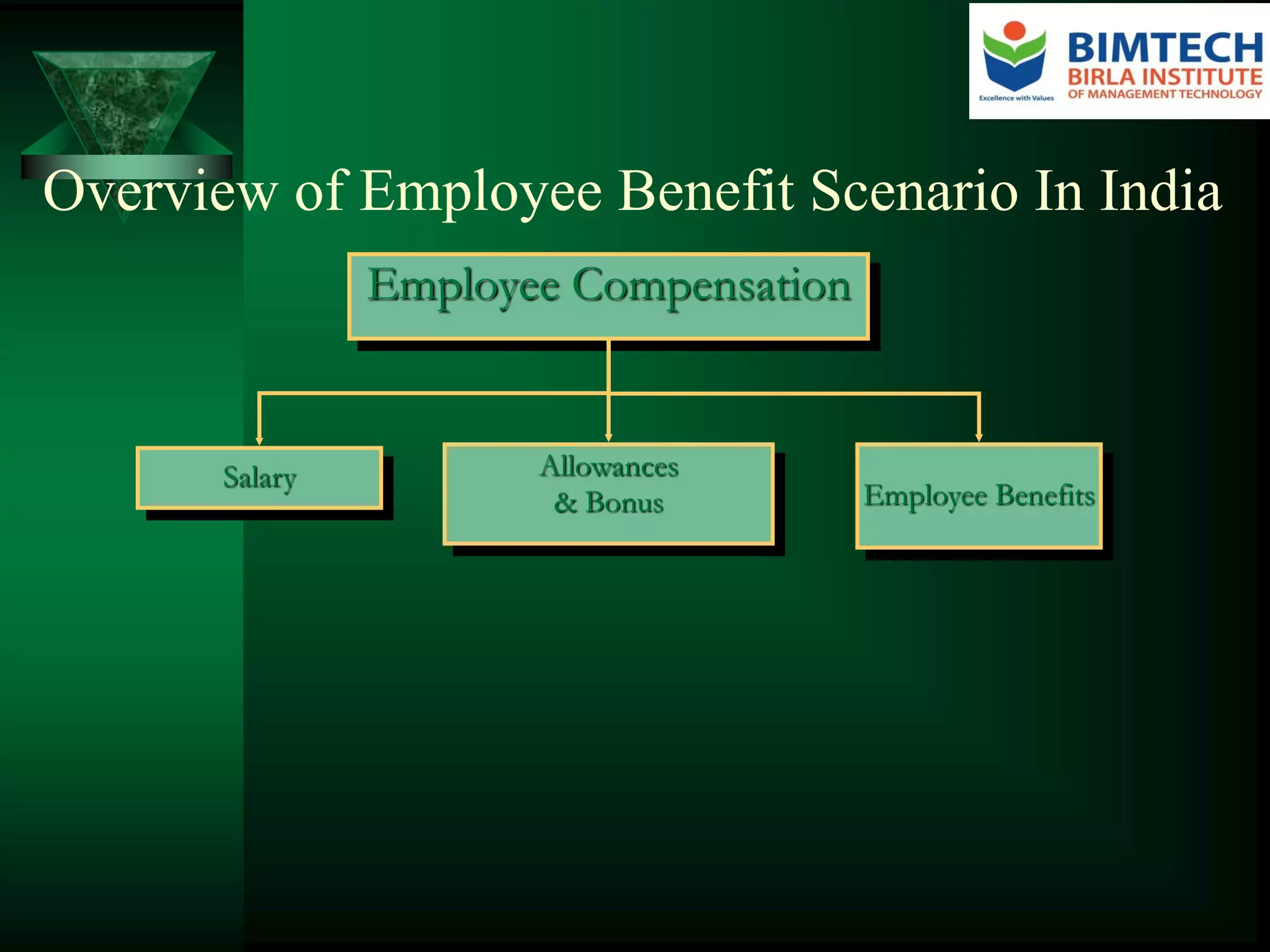
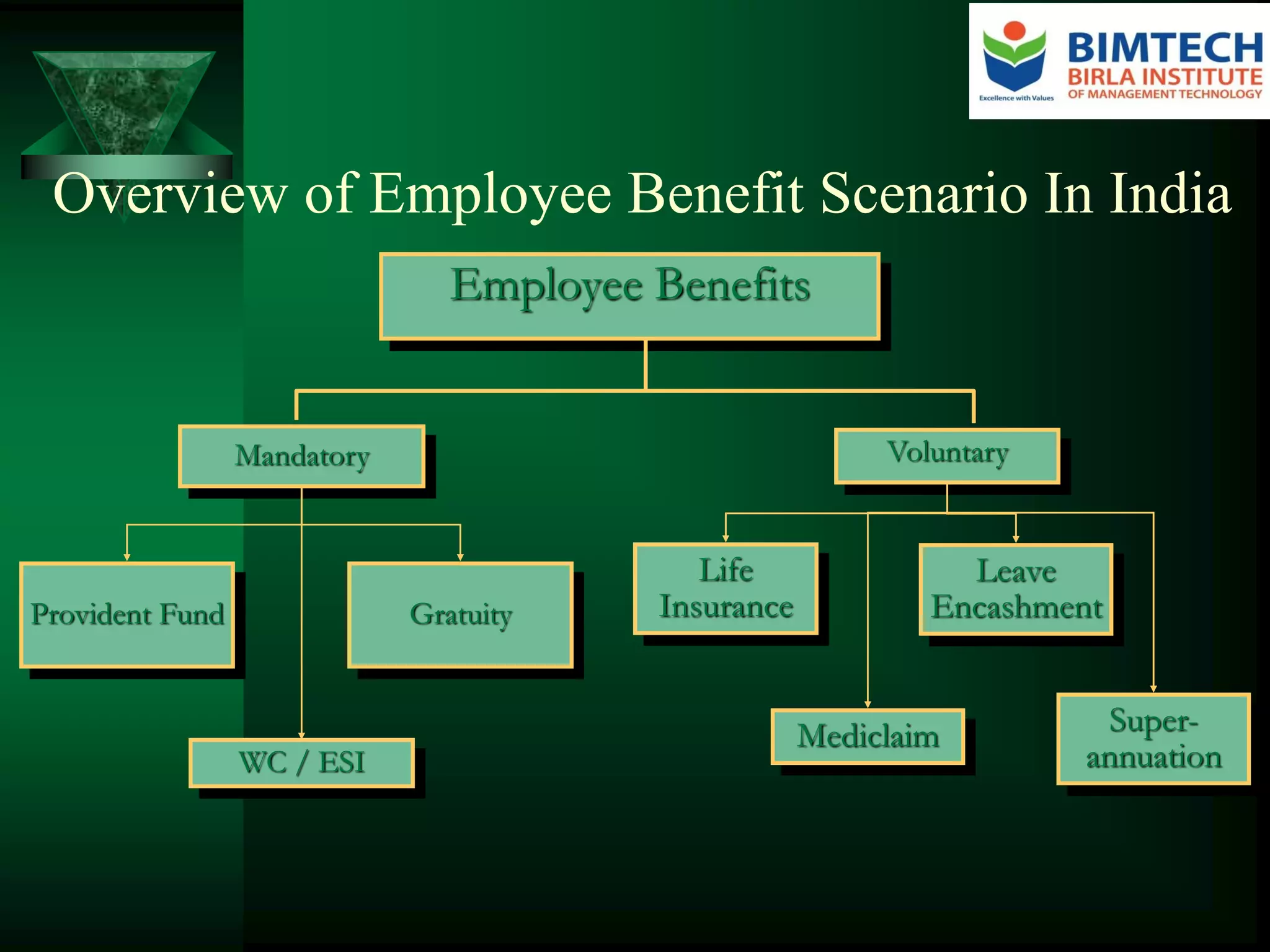
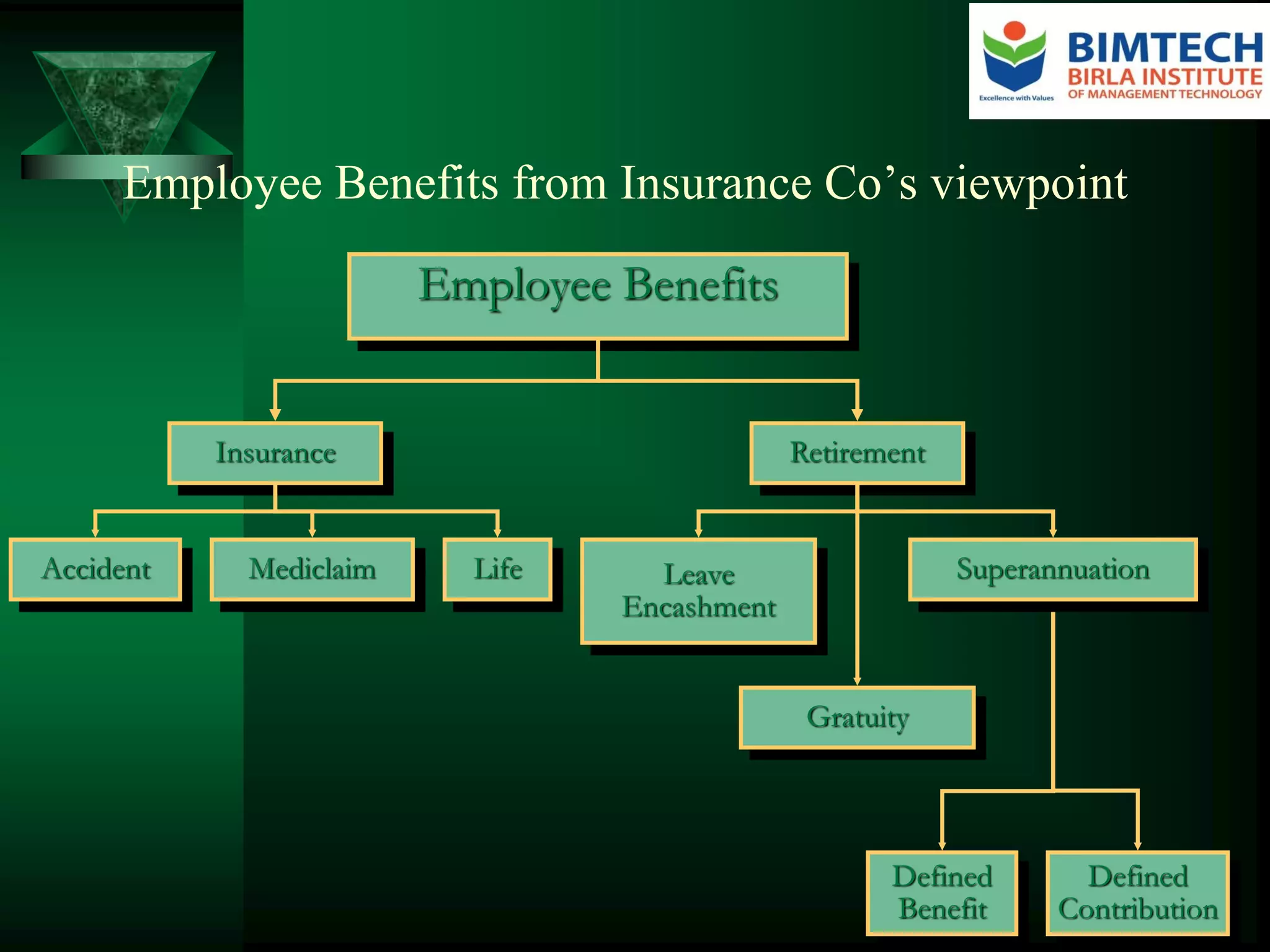
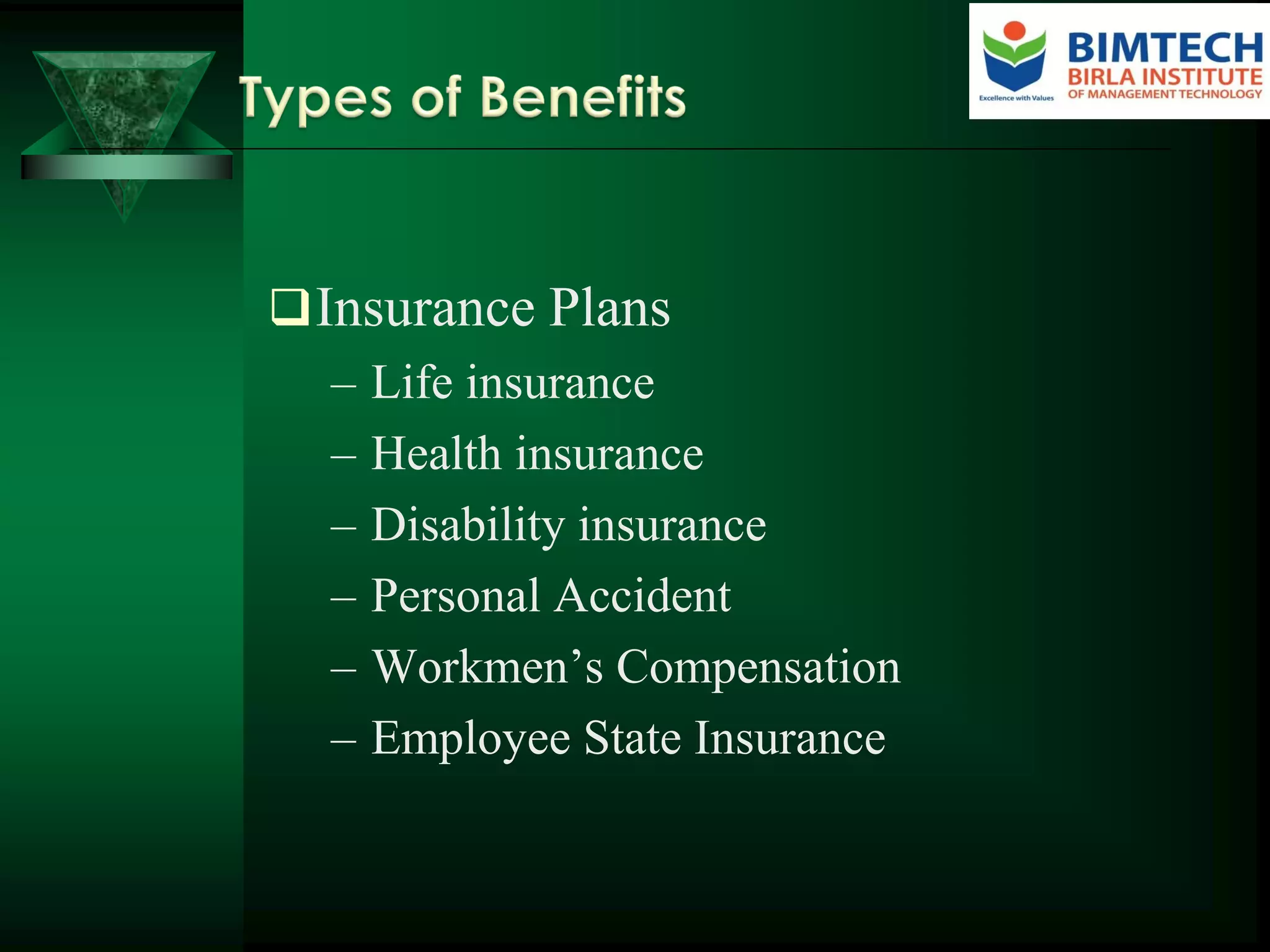
Employee benefits are non-wage compensation provided to employees in addition to their normal wages or salaries. They are growing in cost and complexity, now commonly accounting for a fourth or more of employee compensation expenses. Employers provide benefits to improve staff retention and attraction, motivate employees, foster good morale, and improve employee health and welfare, among other reasons. Benefits include mandatory programs like provident funds and voluntary benefits like life insurance. Trends in benefits include rising healthcare costs driving innovative solutions and more defined contribution retirement plans. Issues shaping benefits design include improving perceived value, controlling costs, communicating benefits, and engaging and satisfying employees within regulatory compliance.