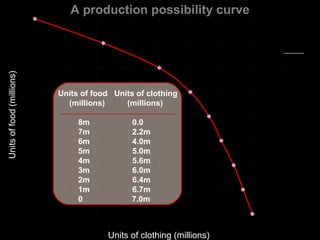
This document provides an introduction to economics. It outlines several learning objectives, including analyzing the concept of economics, understanding how economics plays a role in life, and comprehending the scope of economics. Several key economic terms are defined, such as economic goods, income, and scarcity. The document also discusses the theoretical and practical importance of economics. It explains the subject matter of economics deals with wealth and scarce resources. Finally, it provides overviews of various economic theories, concepts, and branches of economics such as microeconomics, macroeconomics, international economics, and managerial economics.