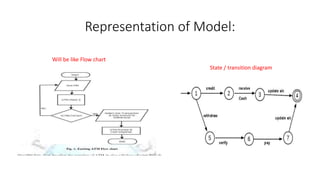
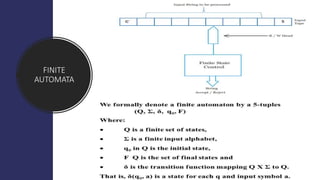
Theory of computation is the study of how problems can be solved using formal mathematical models of computation that reflect real-world computers. It includes automata theory, which studies abstract machines and how they can be used to solve problems. Models of computation are represented using tools like flow charts, state transition diagrams, and transition tables. Theory of computation has applications in areas like text processing, web browsing, compiler design, and artificial intelligence. It builds on fields like set theory, model theory, and computability theory. Key topics covered include finite automata, regular expressions and languages, context-free grammars and languages, and the undecidability of some computational problems.







![TYPES OF FA
1. Deterministic Finite Automata (DFA)
2. Non- Deterministic Finite Automata (NFA)
Both are defined by 5 tuples but there is difference in :
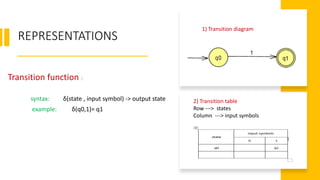
Transition function
DFA: Q x Σ -> [Q] - output is single state
NFA : Q x Σ -> {Q} - output is in many states](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtoautomatatheory-220110085958/85/Intro-to-automata-theory-11-320.jpg)
![NFA
δ(q0,b)= {q0,q1}
NFA
δ(q0,1)= {q0,q2}
δ(q0,0)= {q0,q1}
δ(q2,1)= {q3}
δ(q2,1)= ∅
DFA
δ(q0,b)= [q0]
δ(q0,a)=[ q0,q1]
∅ - no null transitions
Guess the type of FA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtoautomatatheory-220110085958/85/Intro-to-automata-theory-12-320.jpg)