Embed presentation
Download to read offline
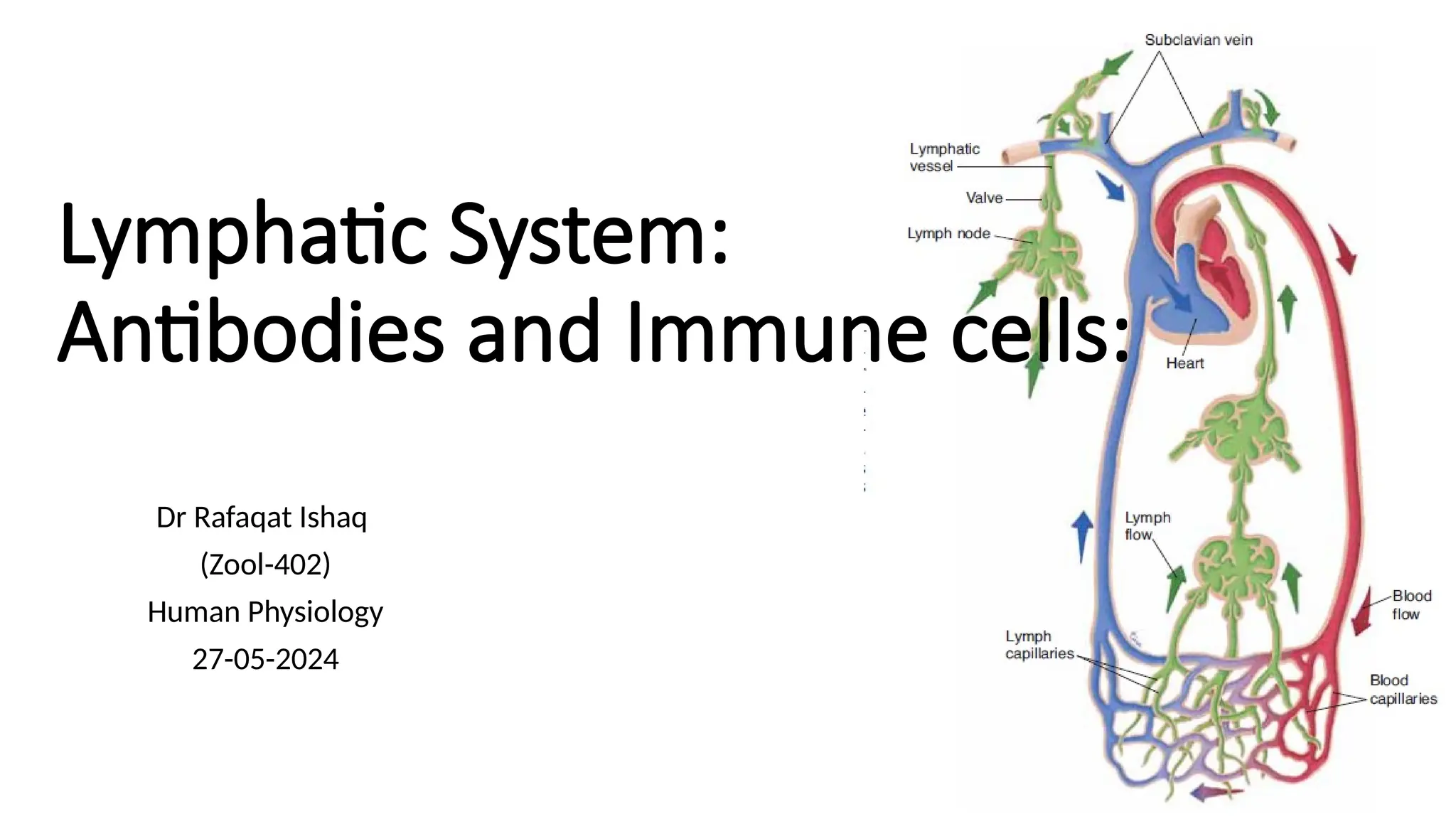

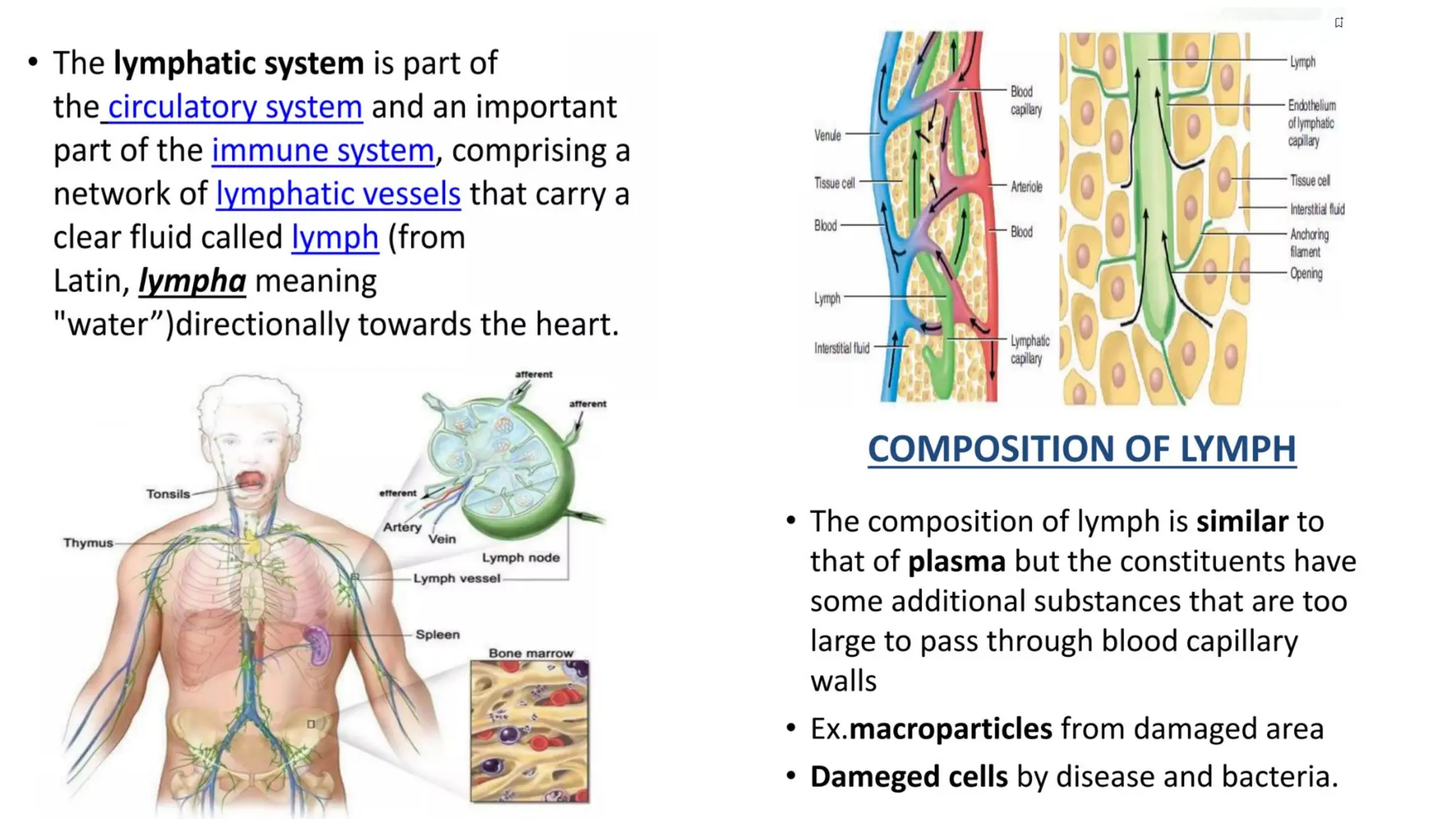
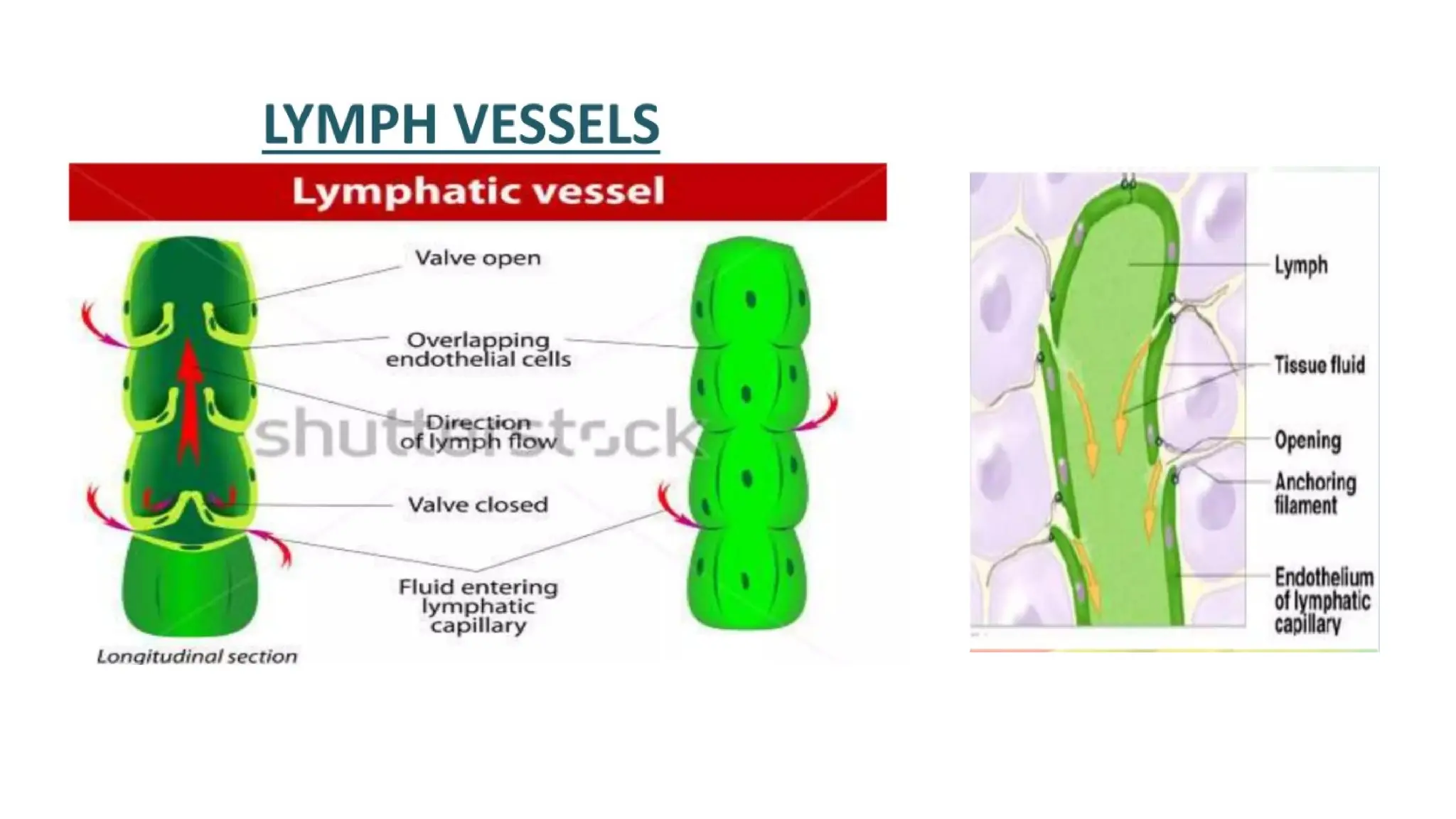
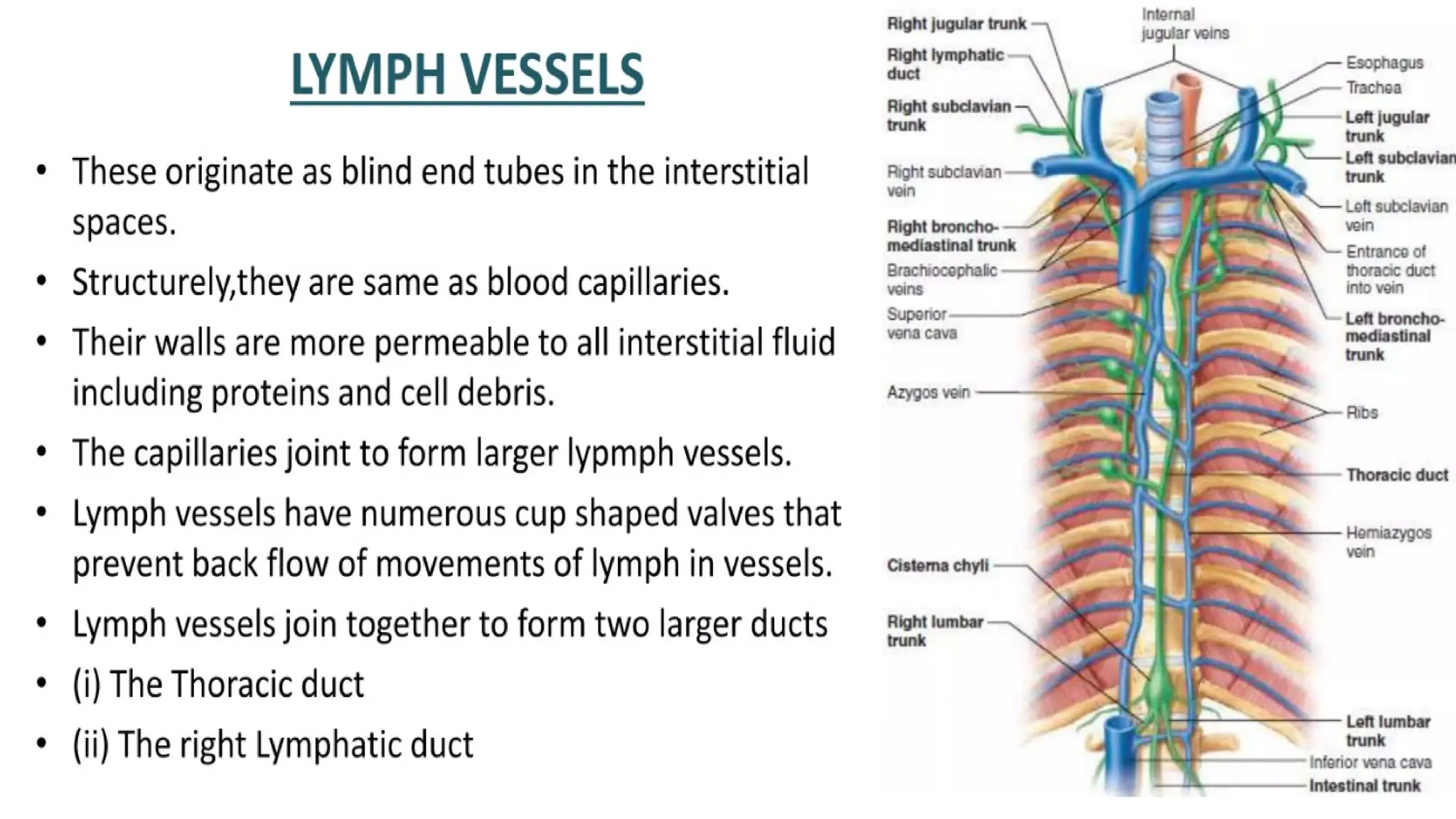
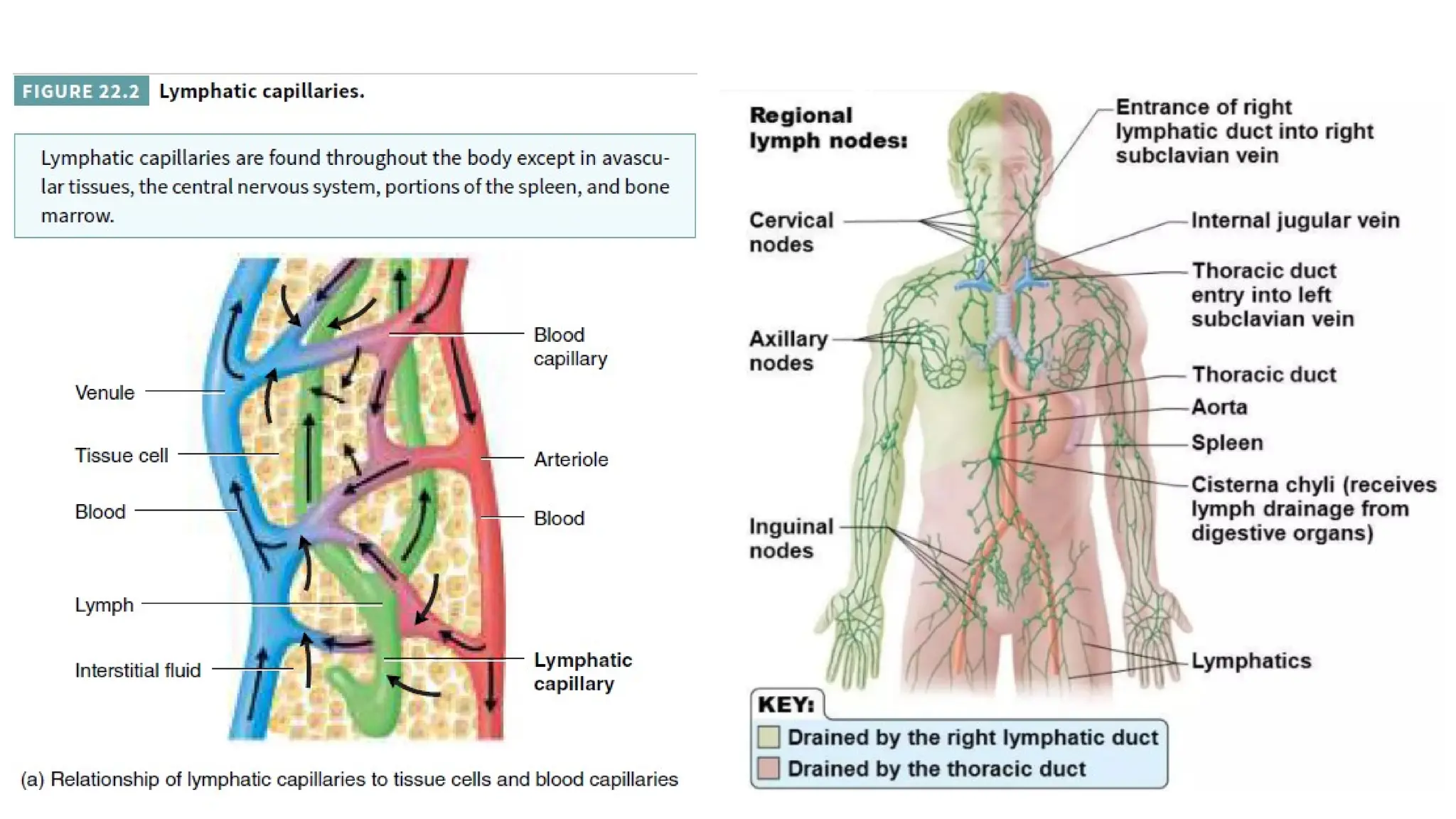
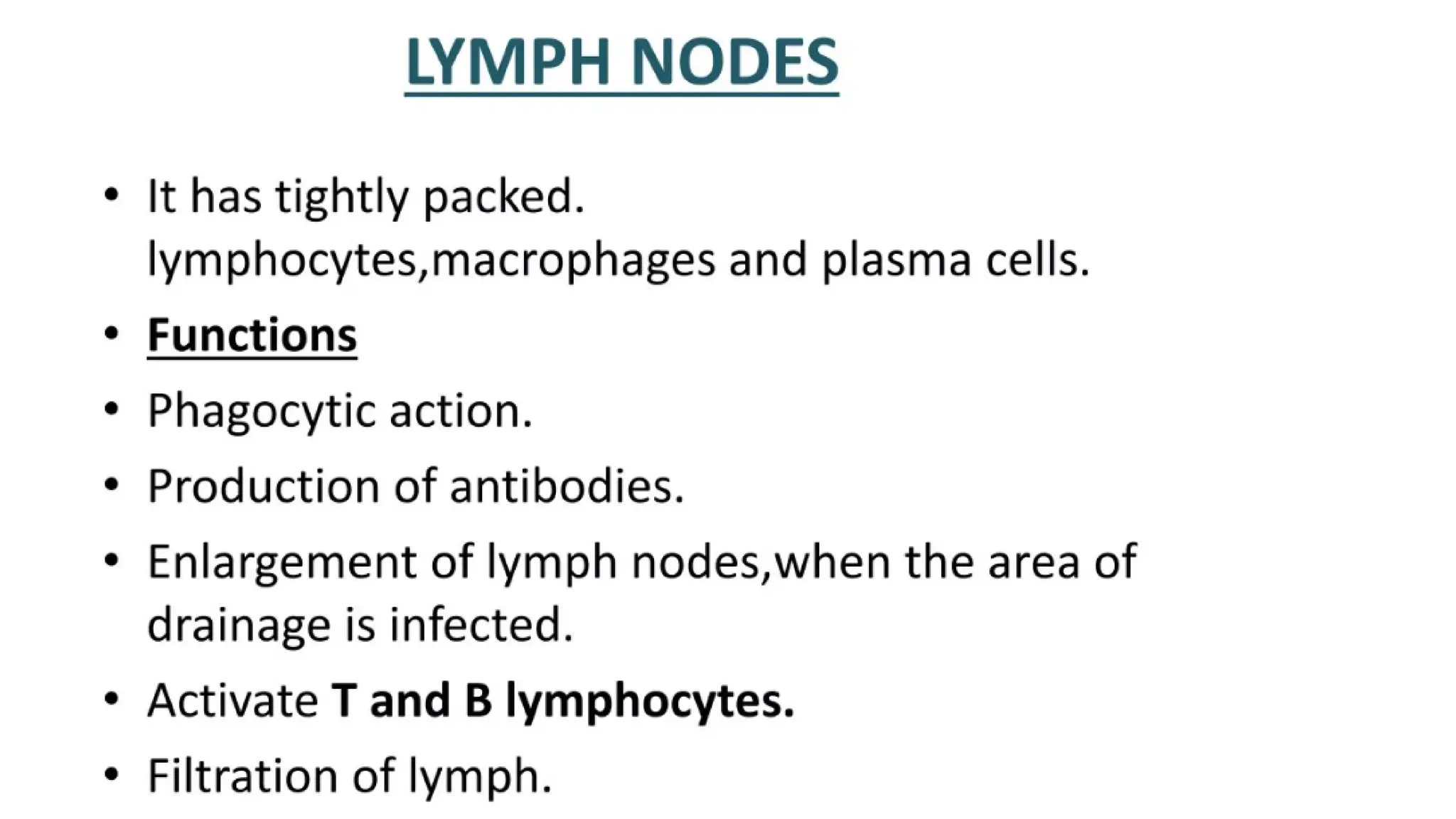

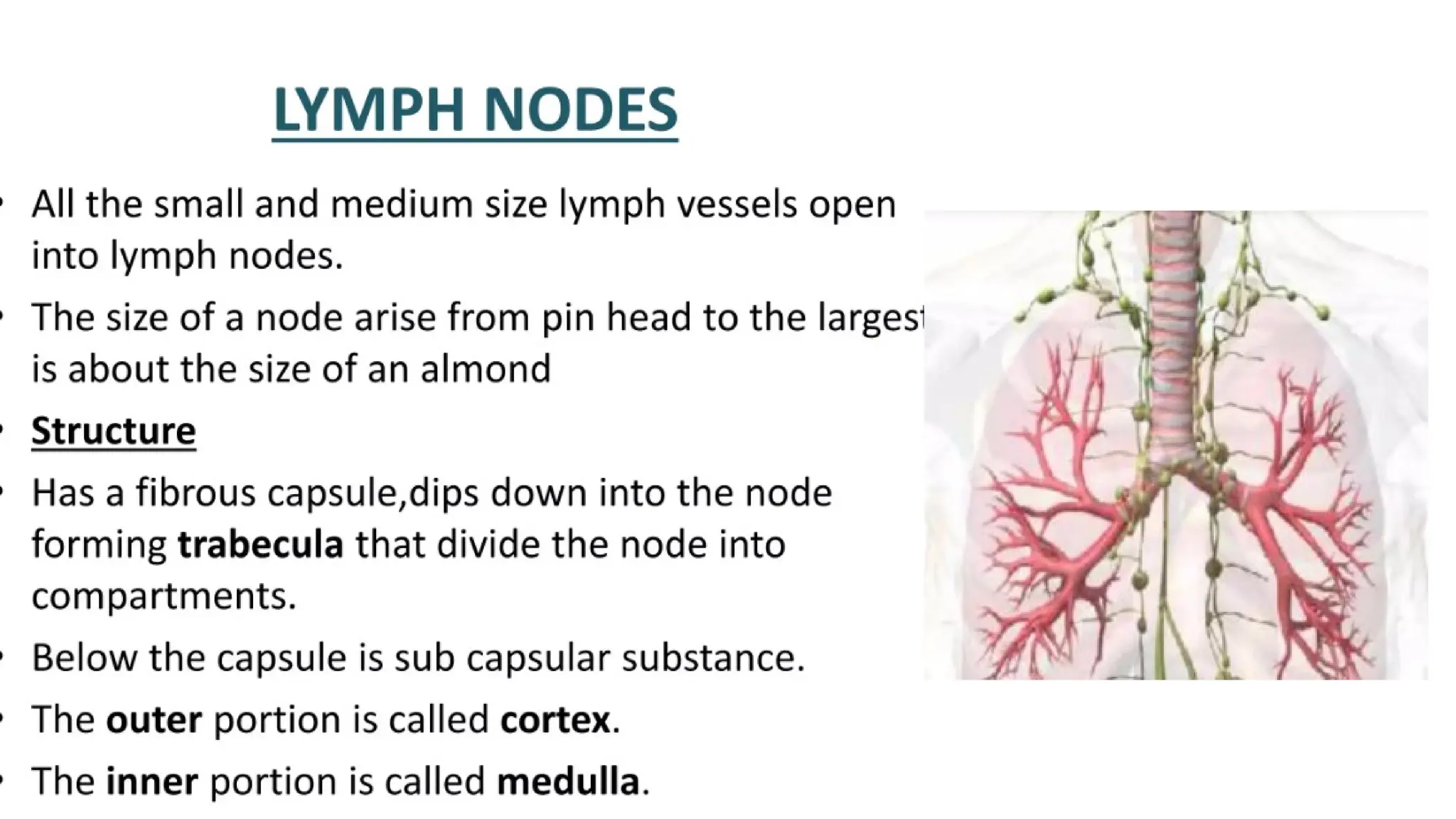
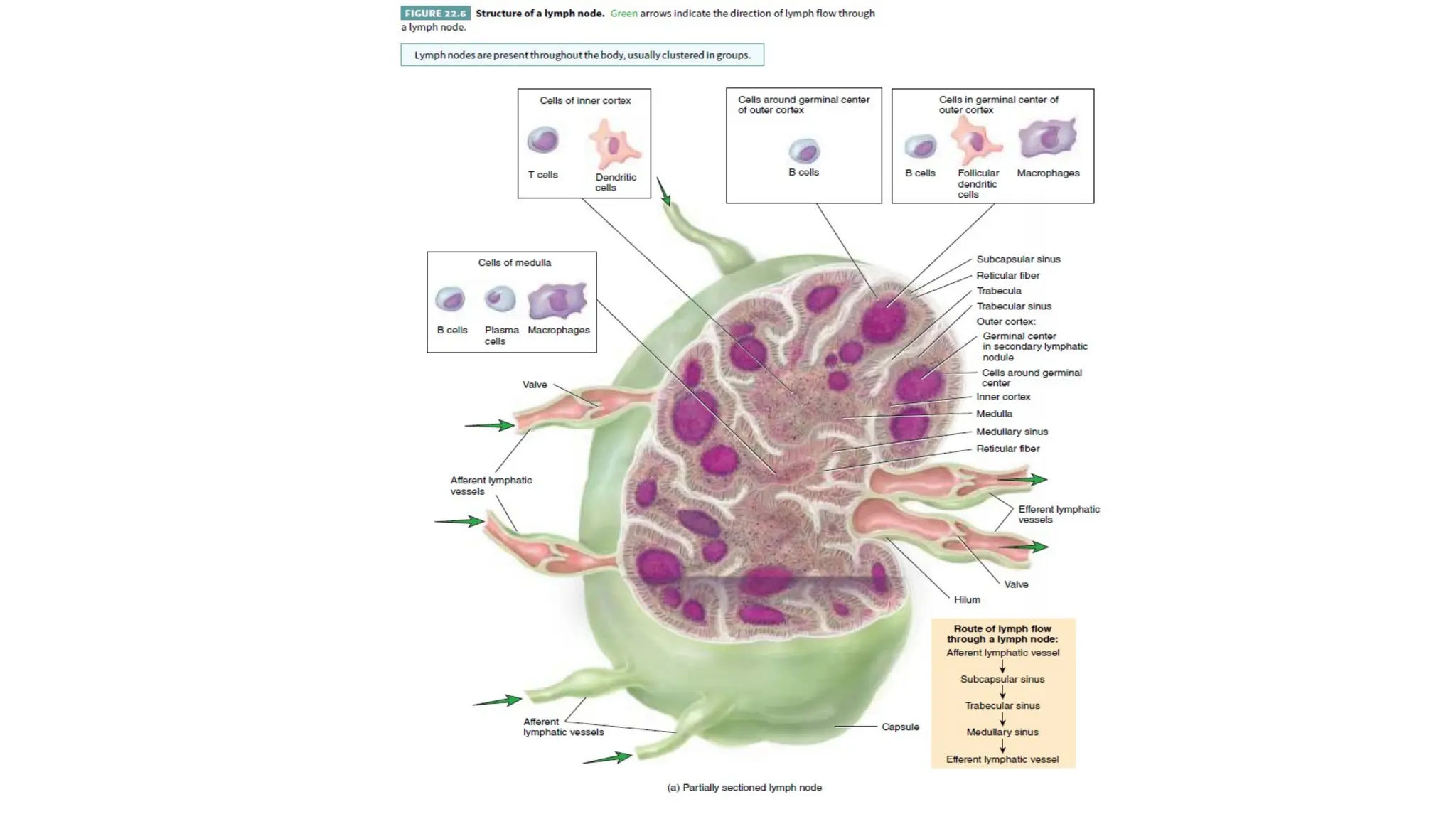

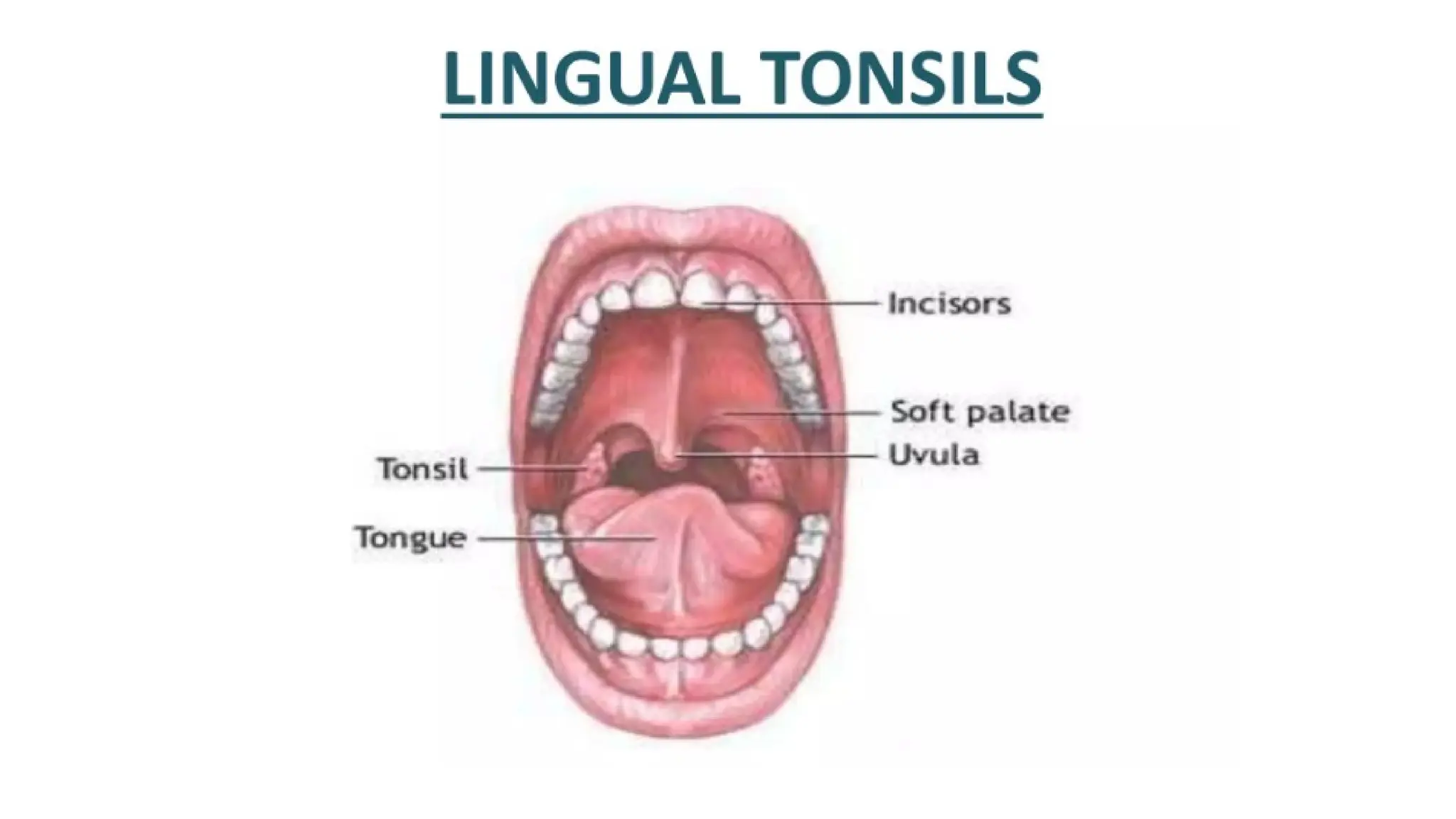

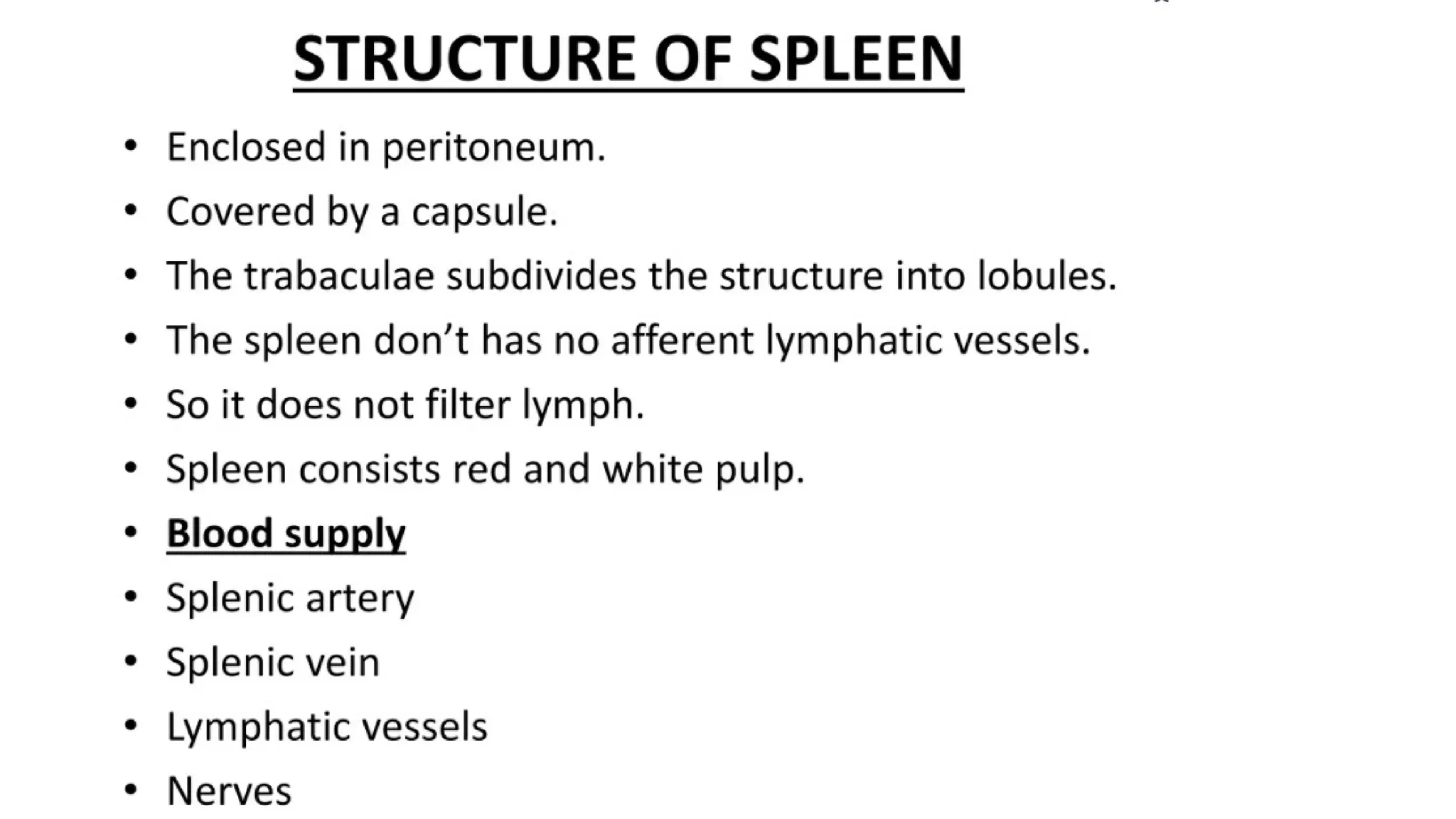
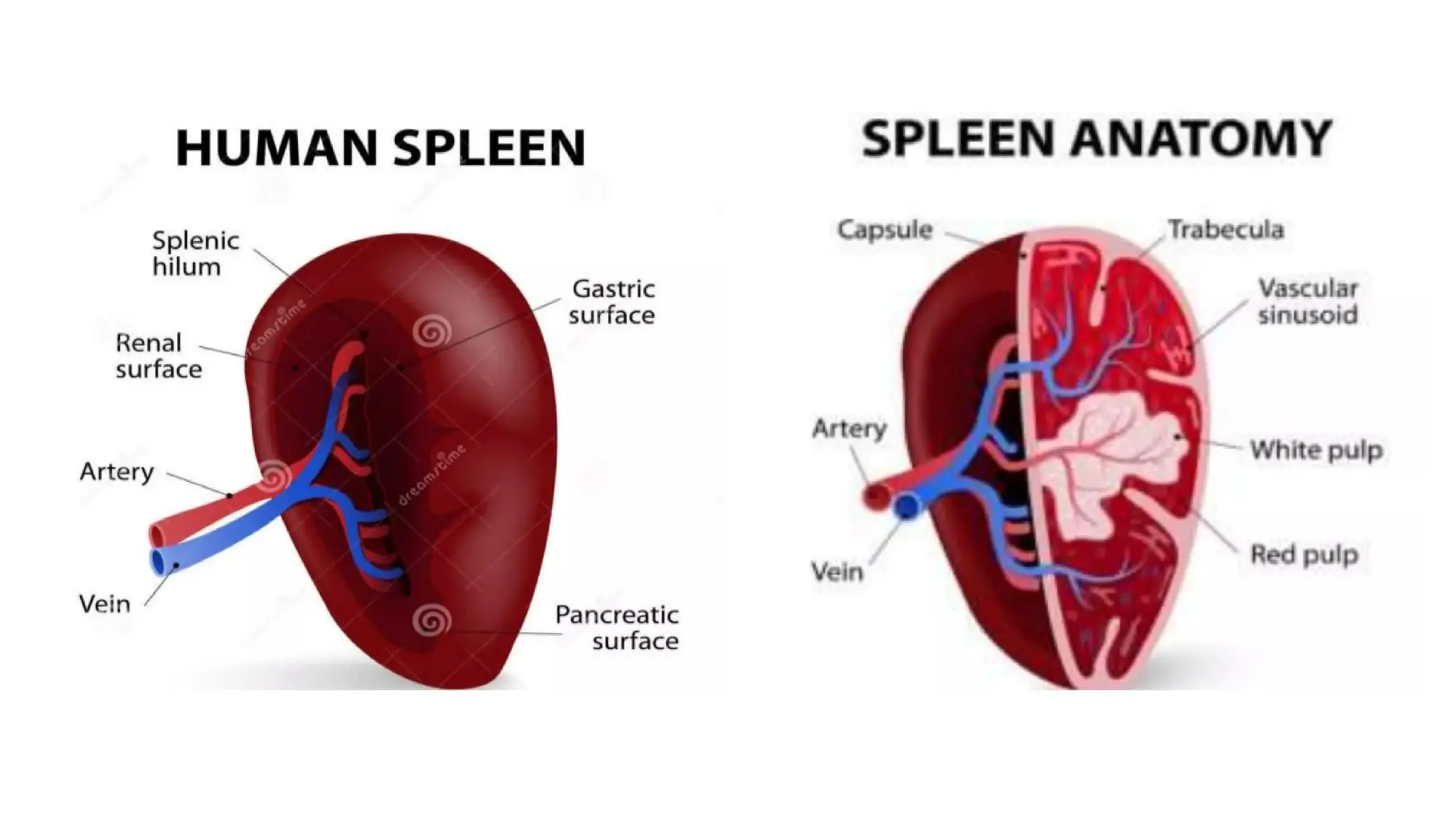

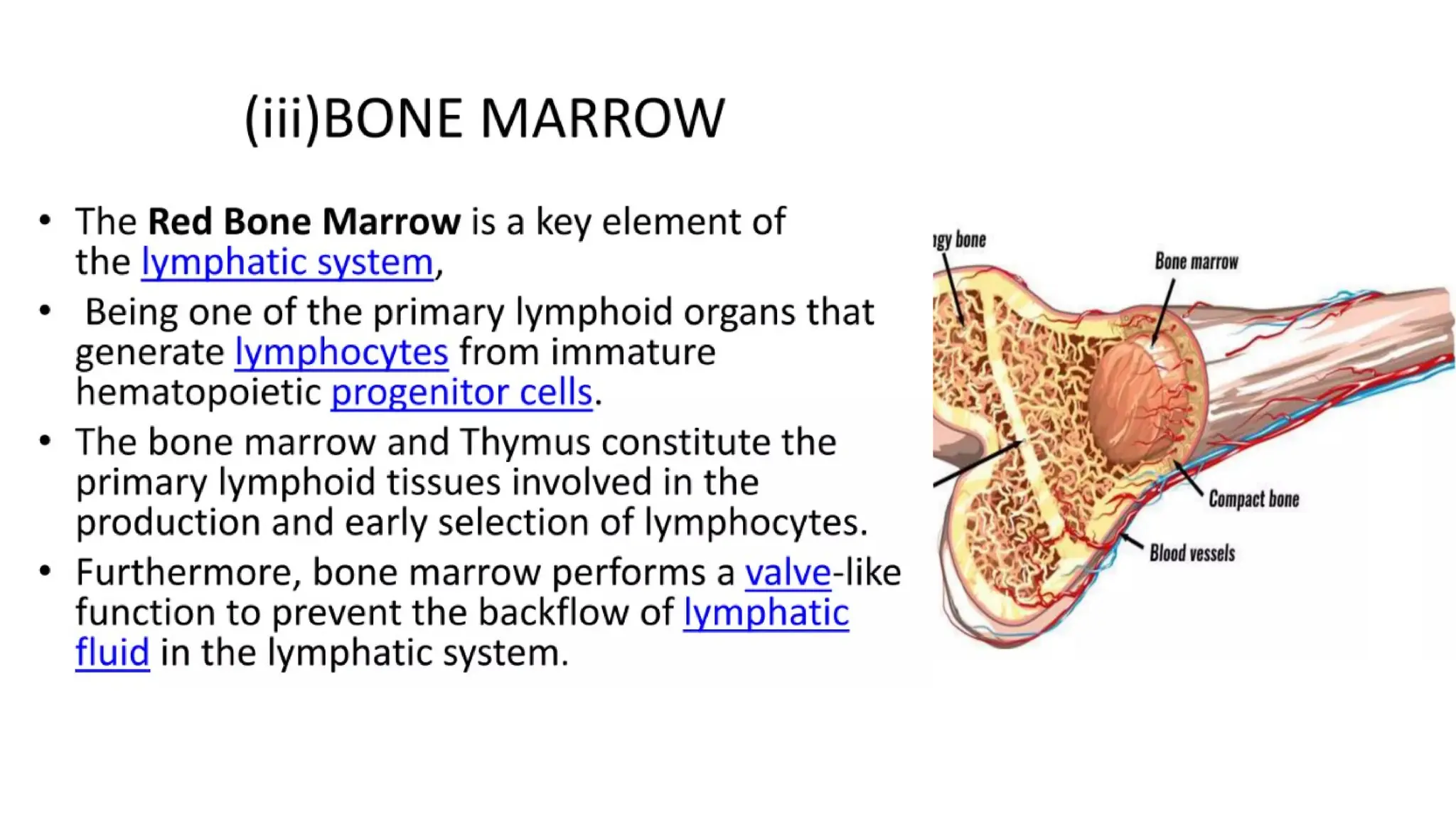
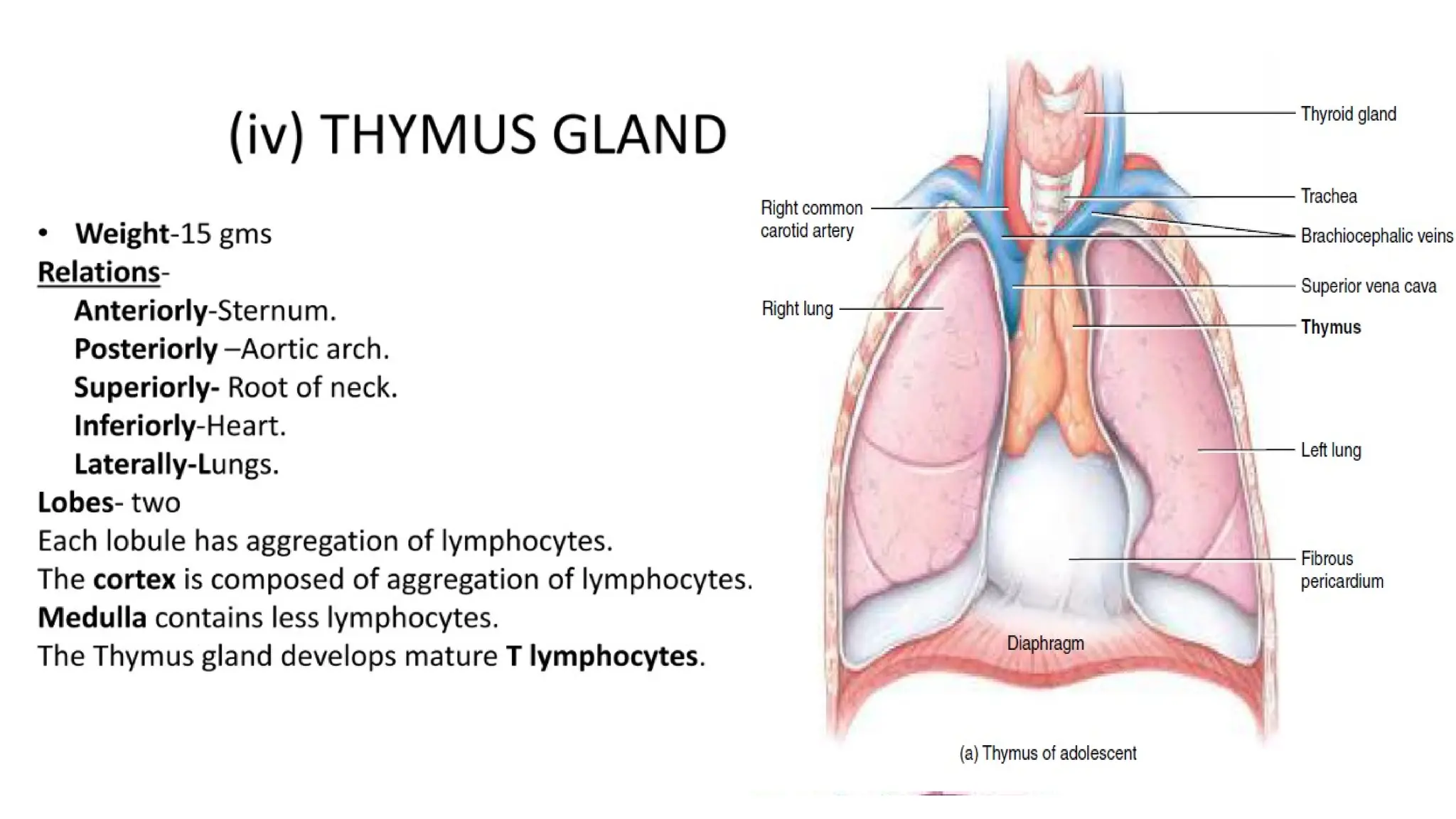
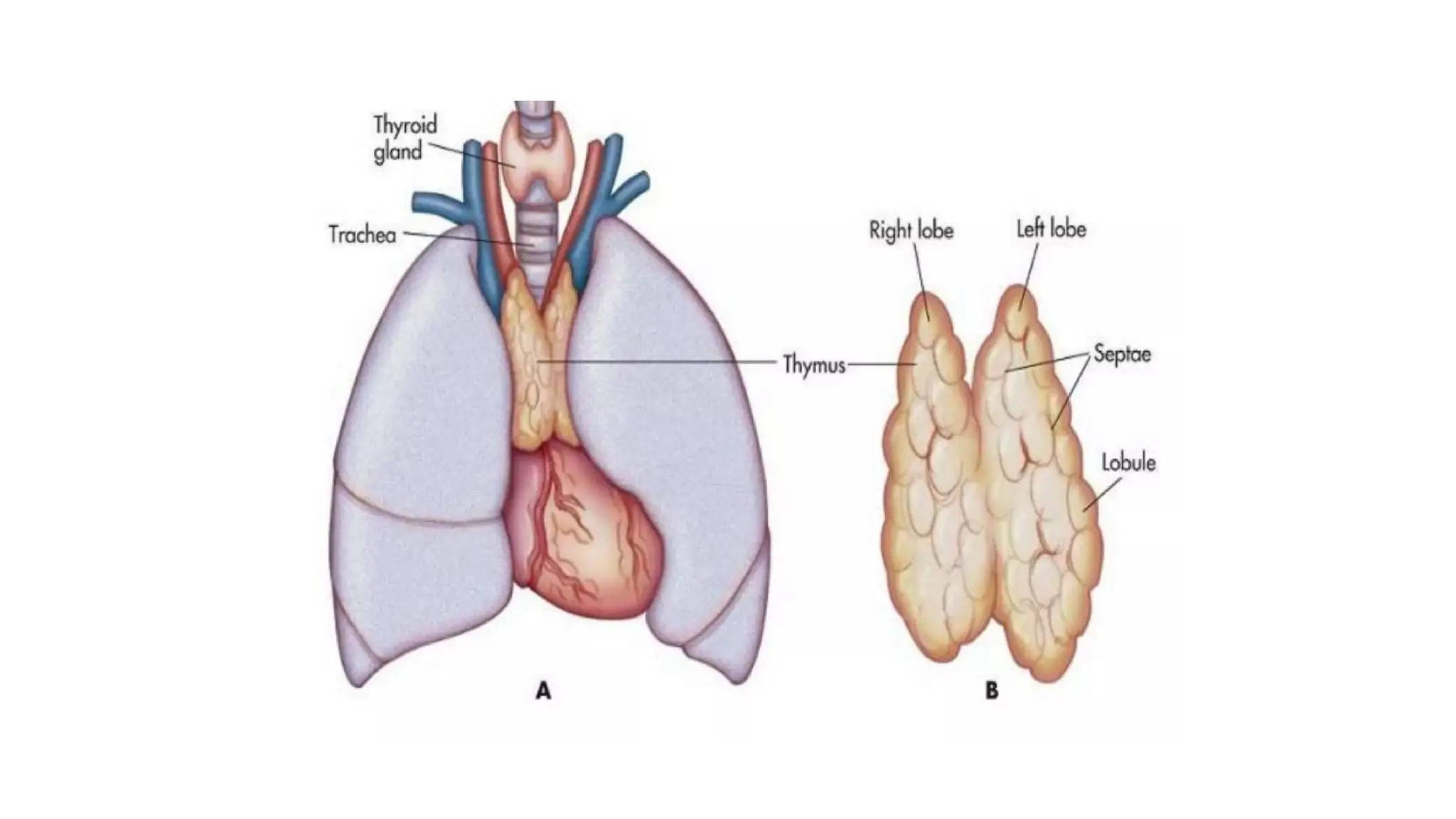
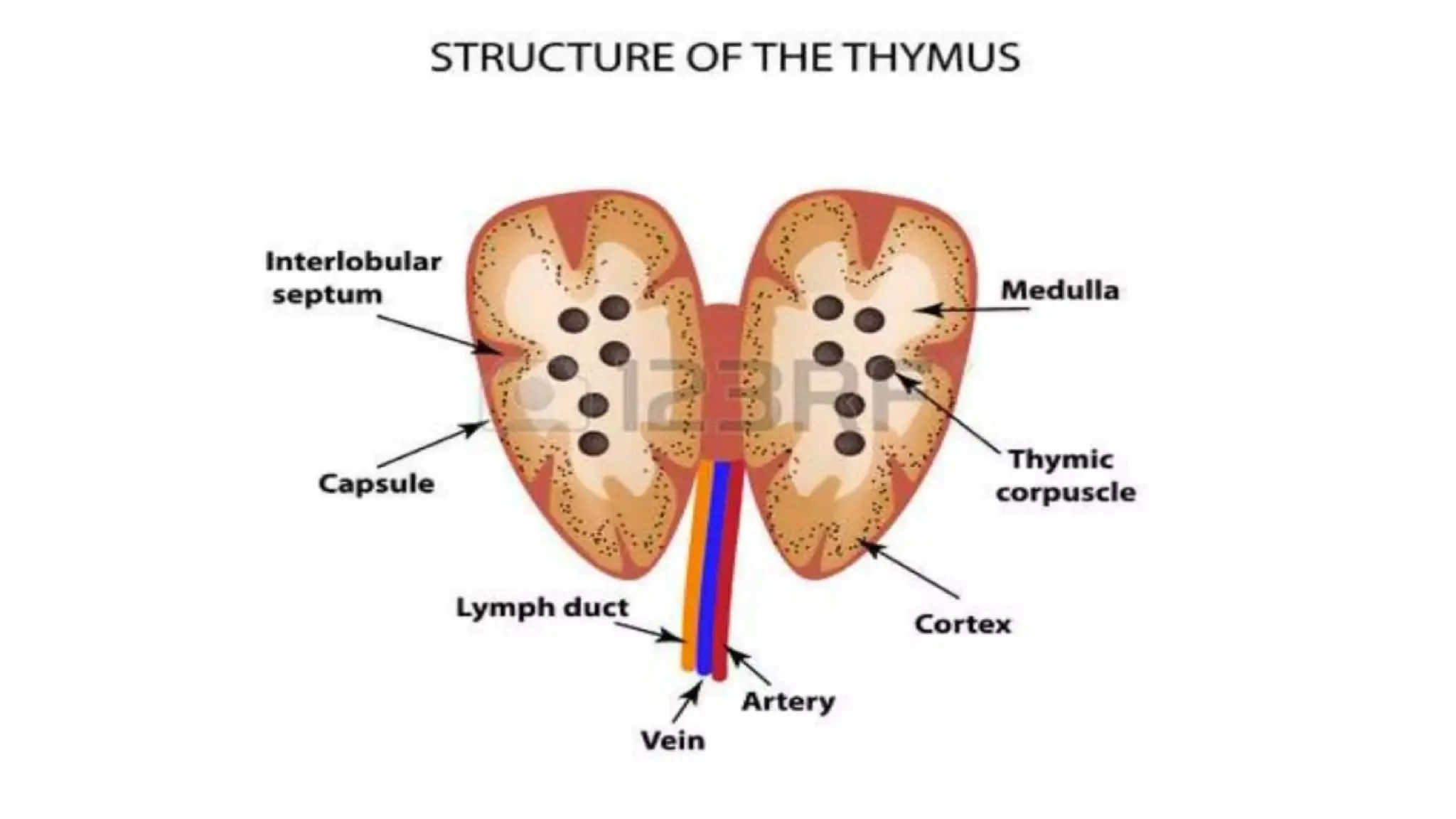

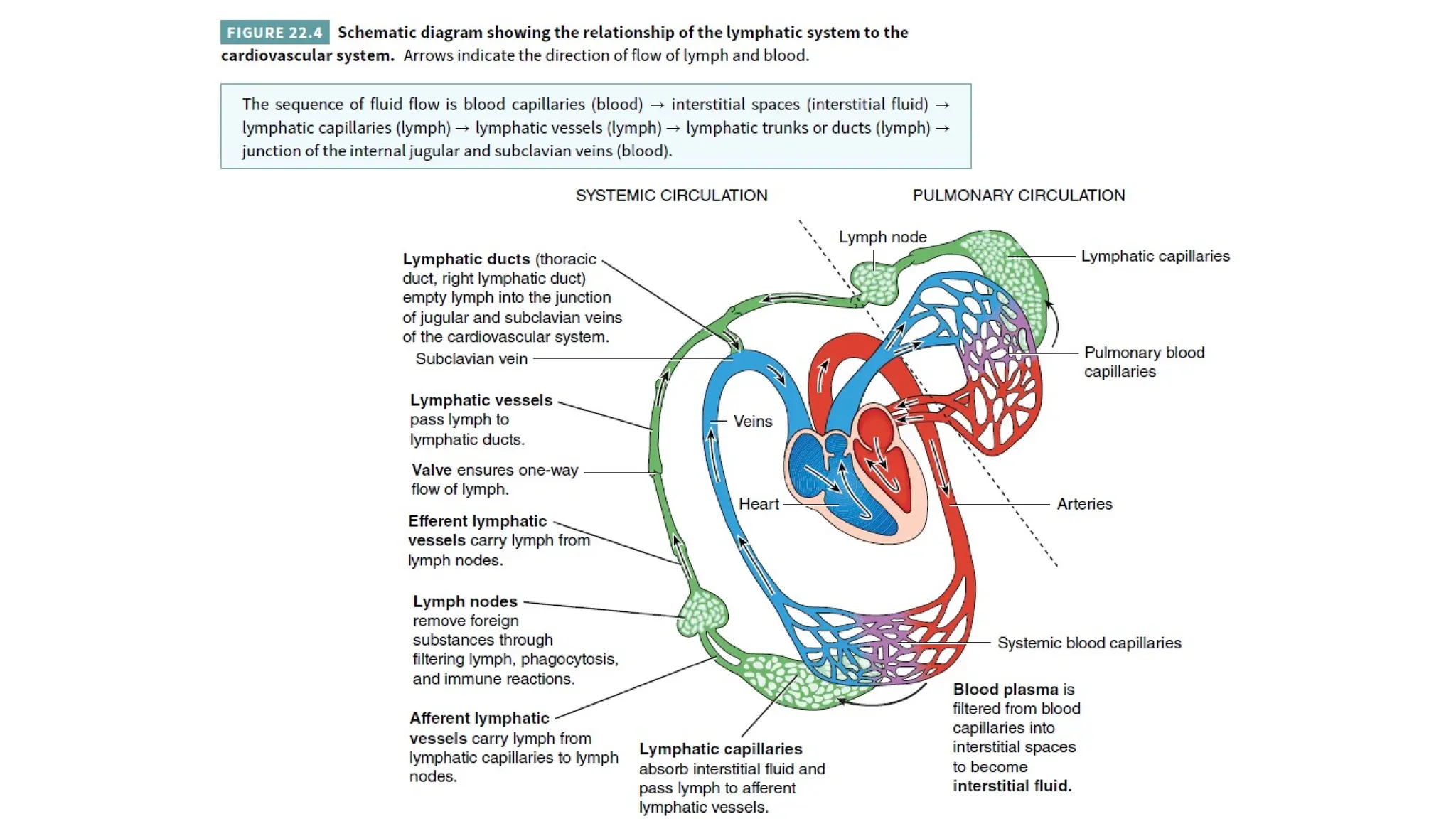
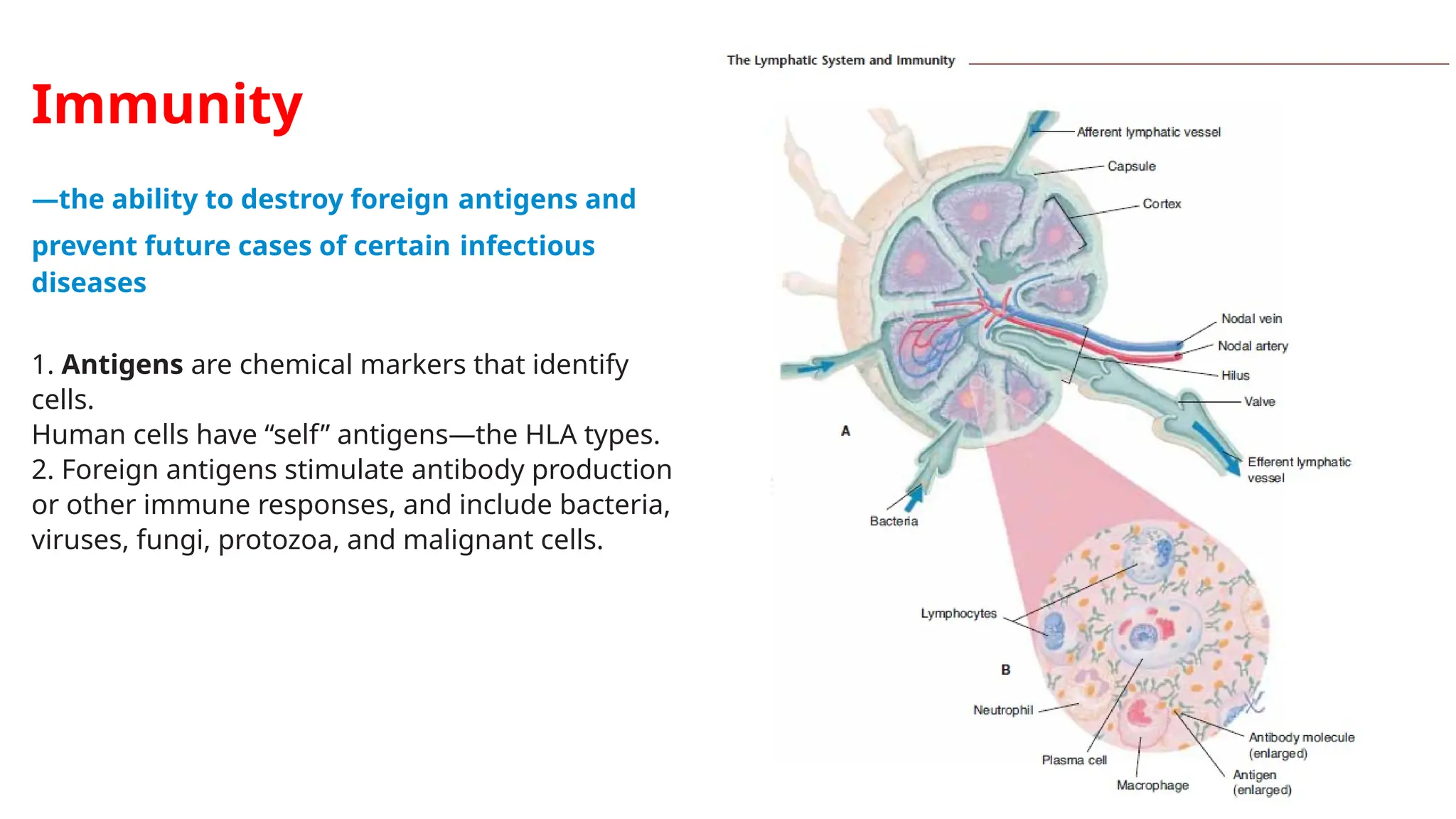
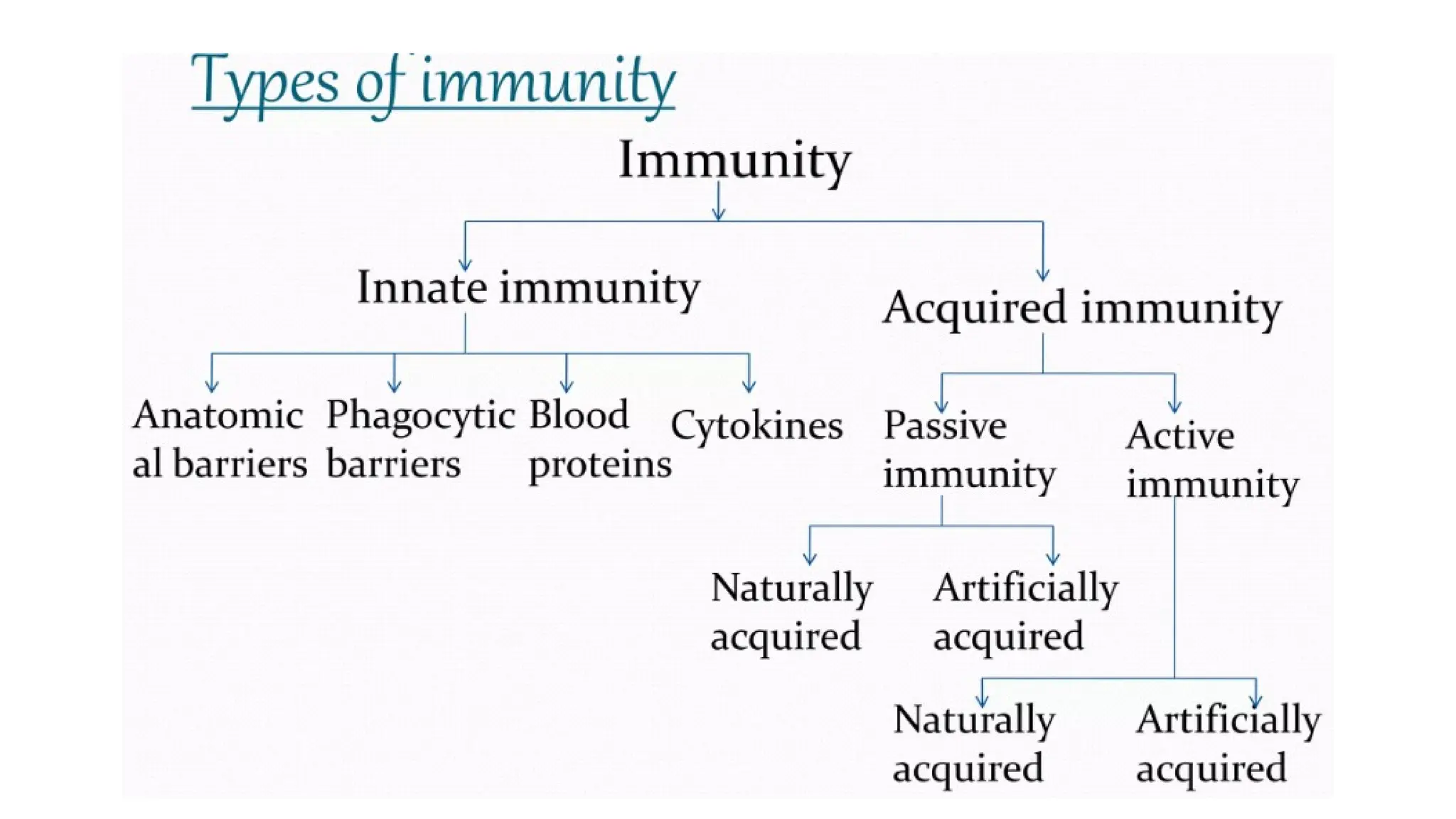
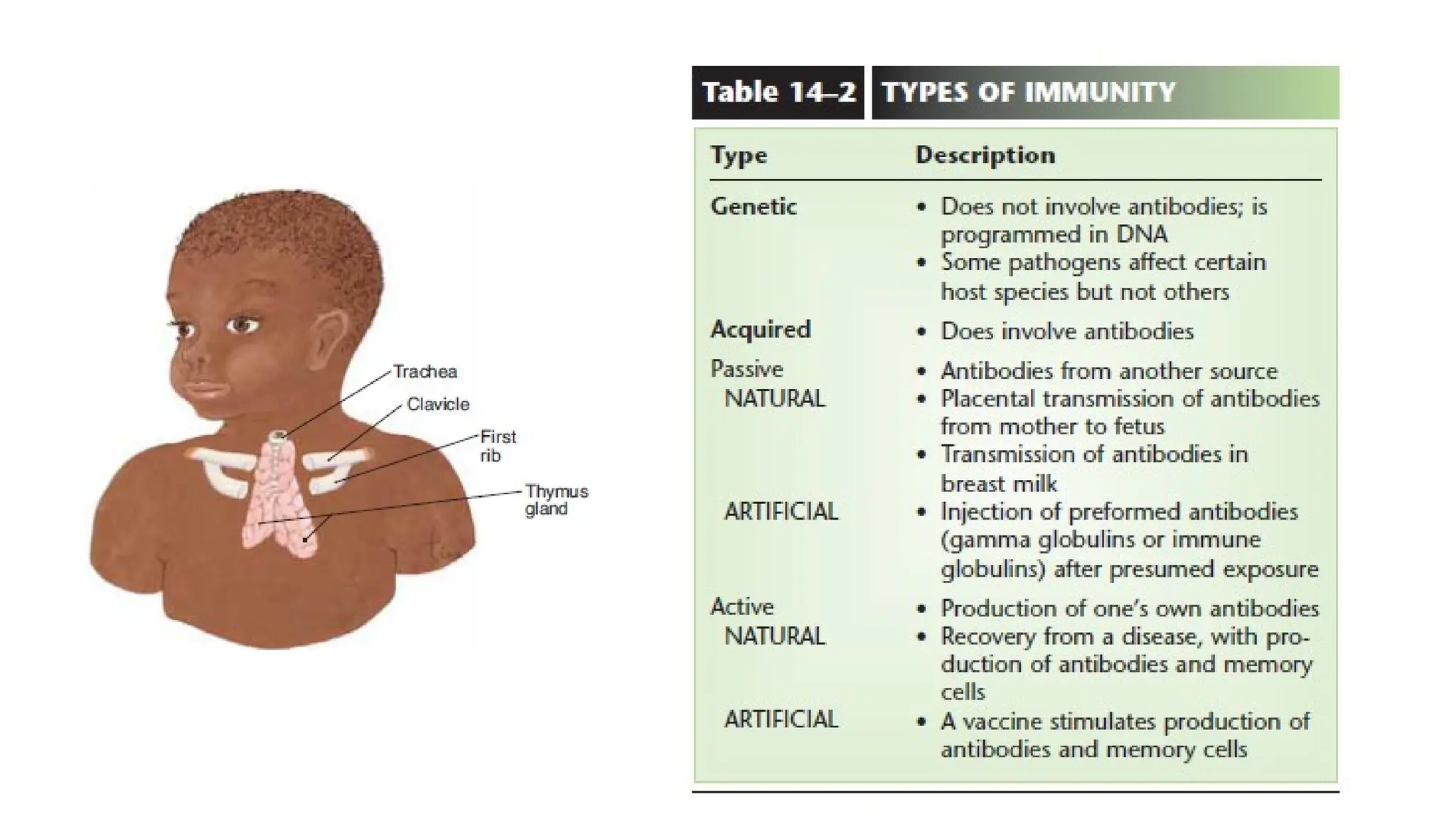
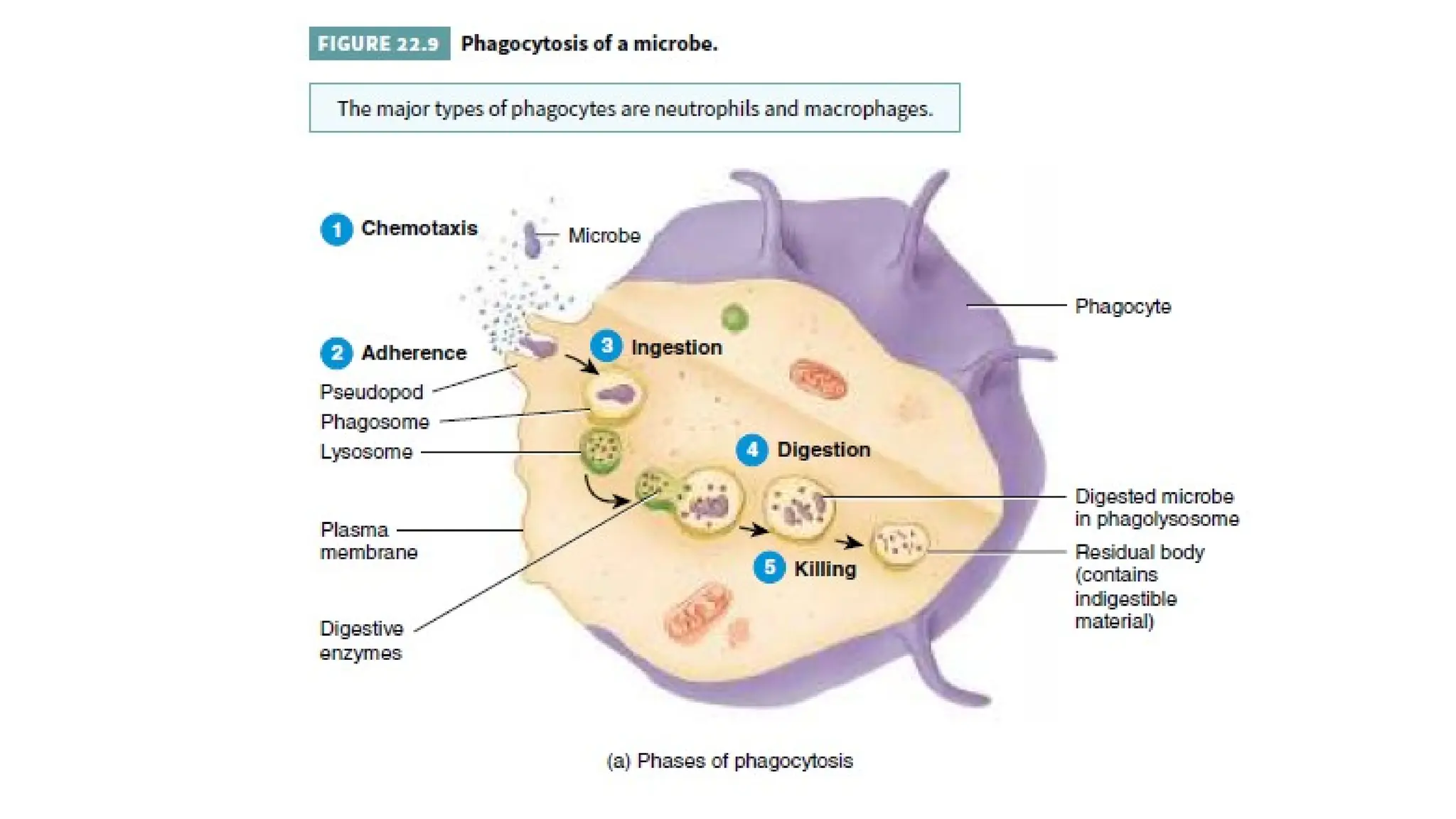

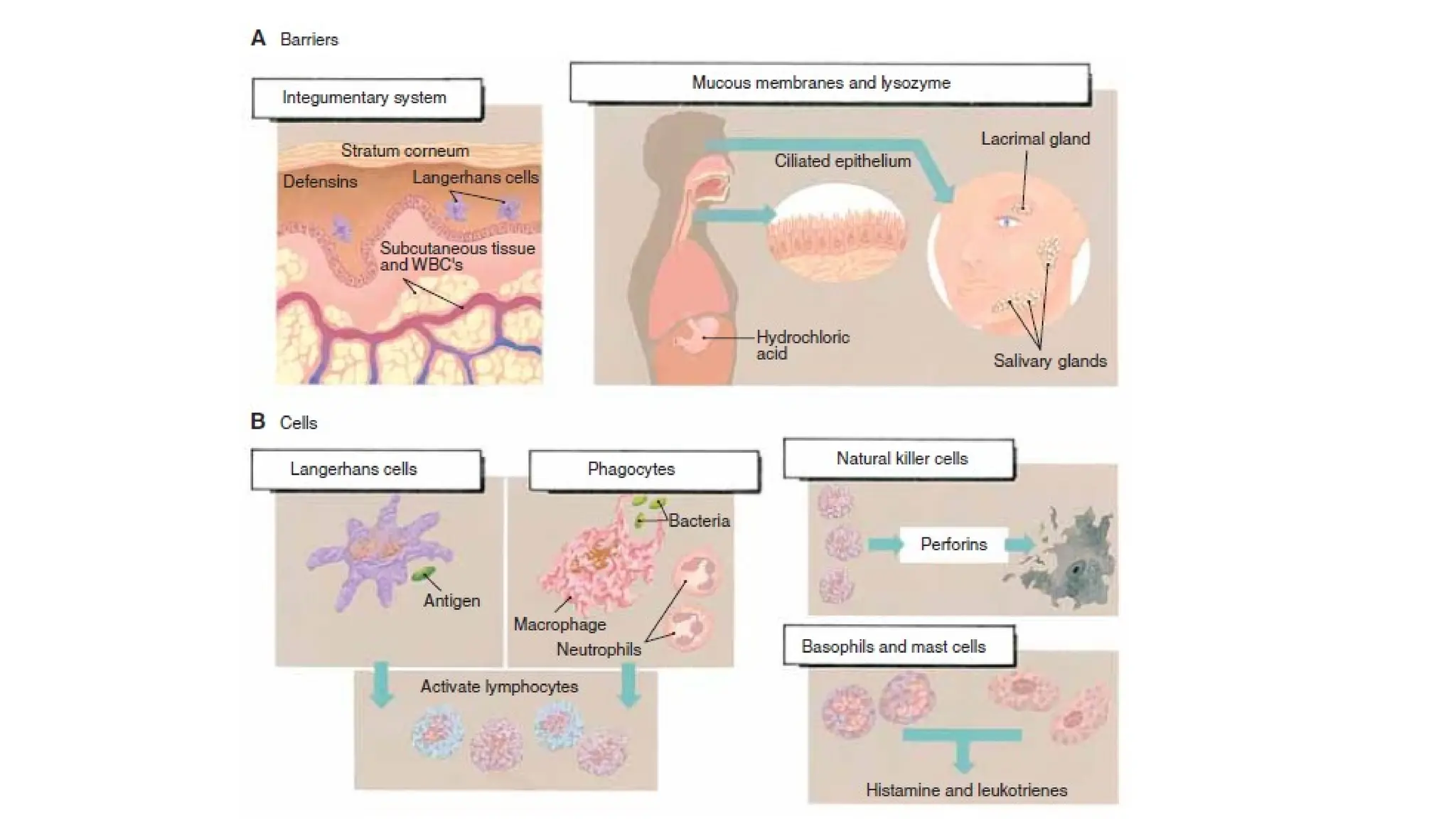
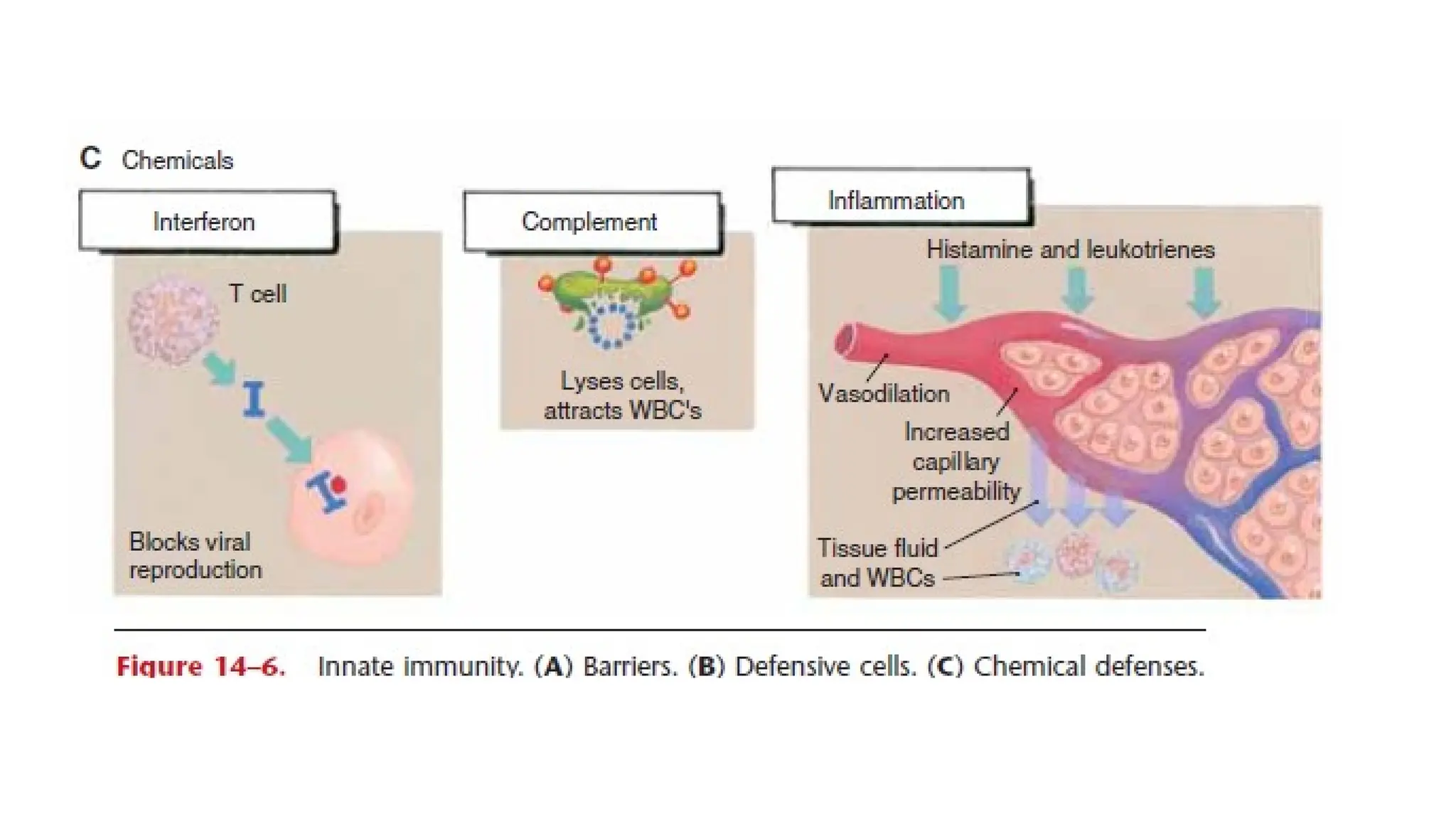
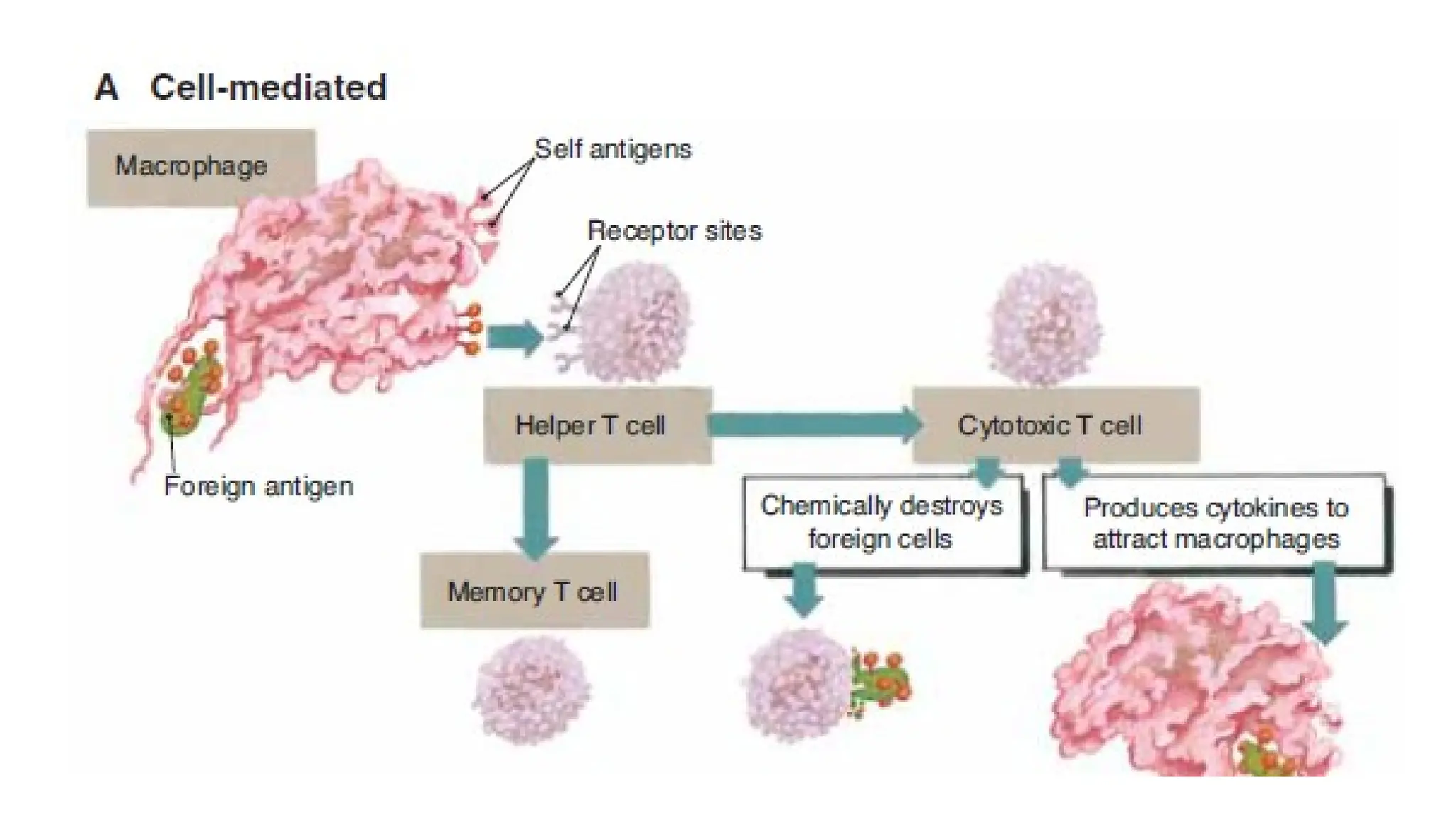
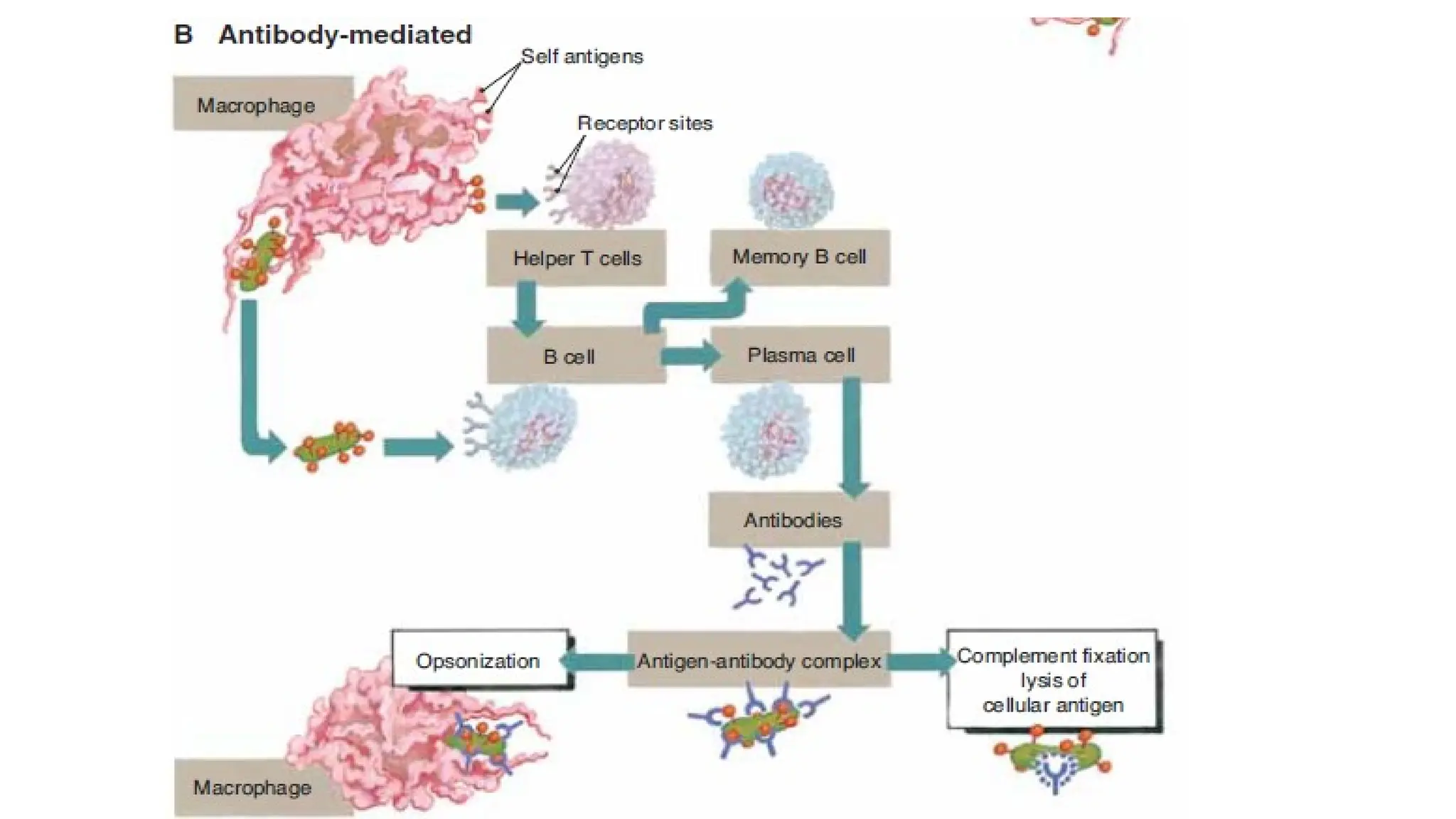
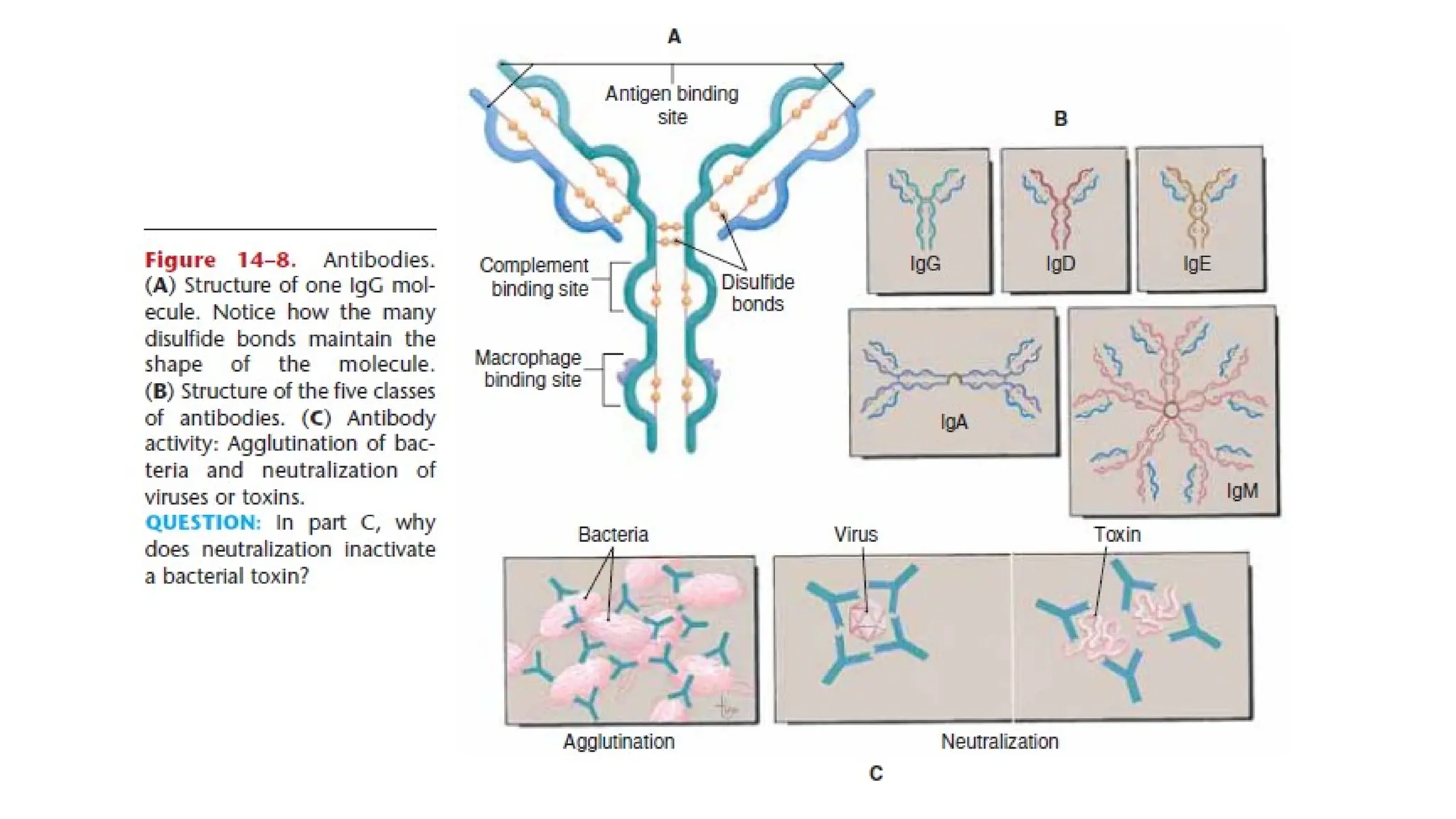
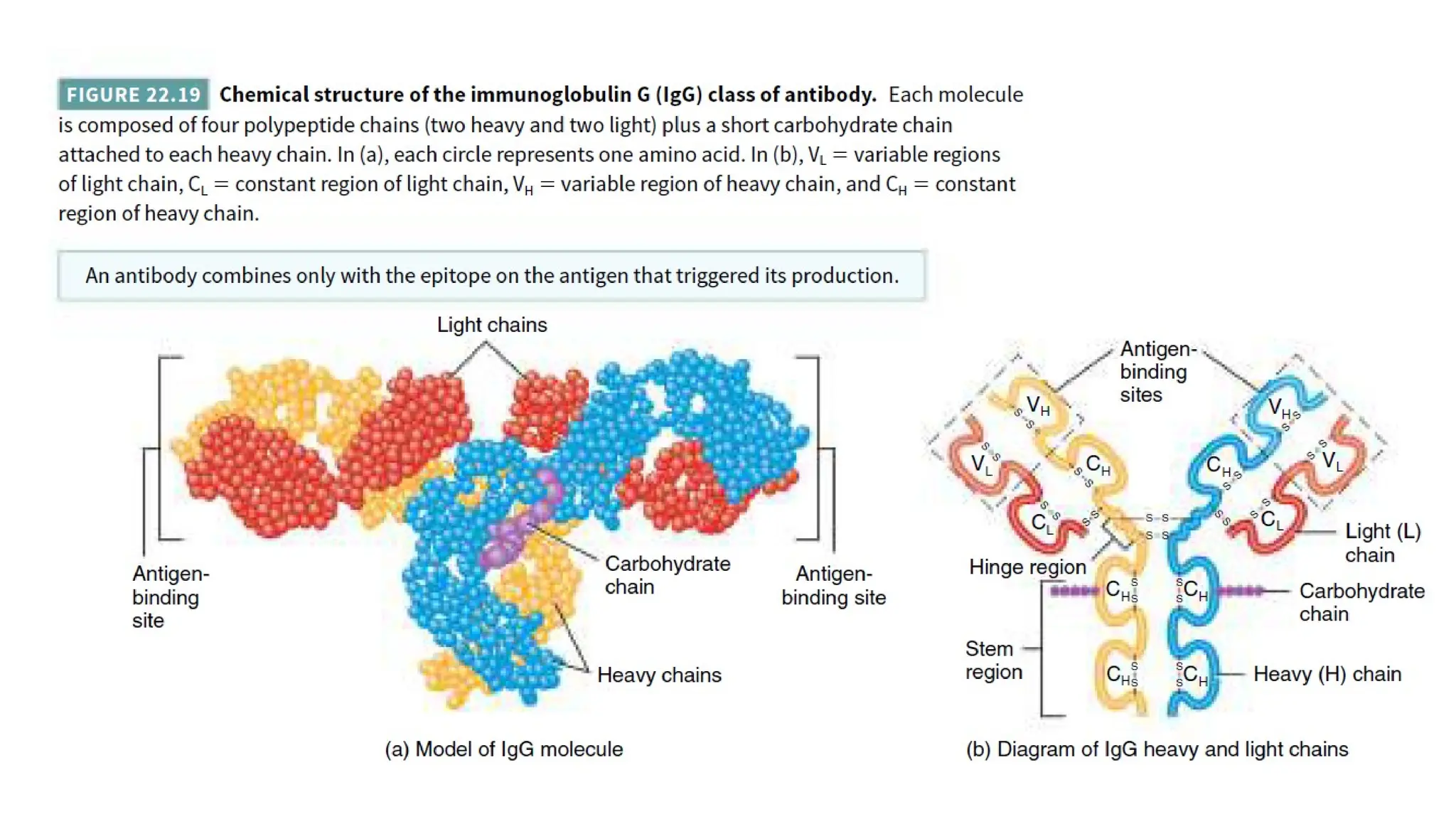
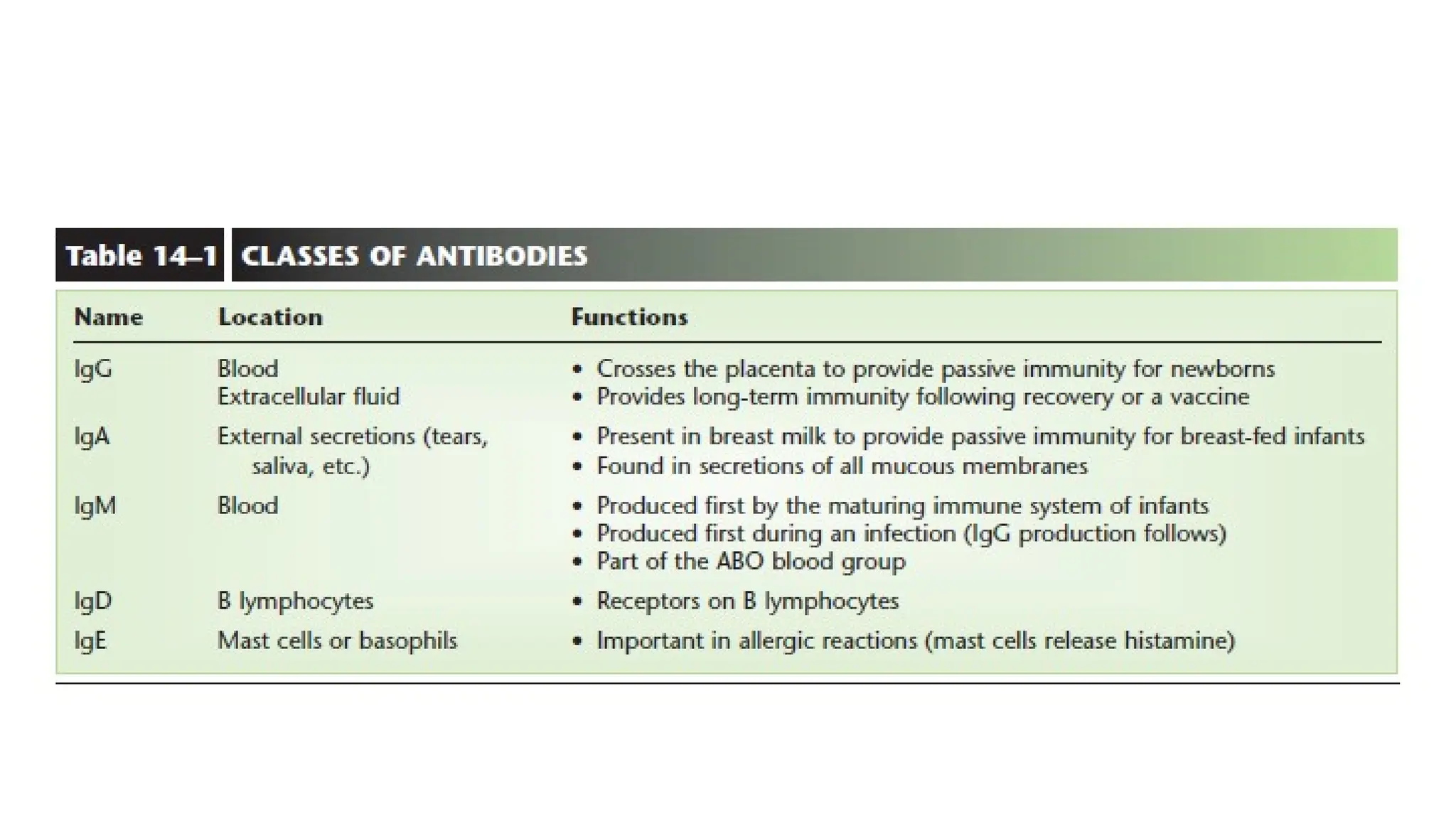
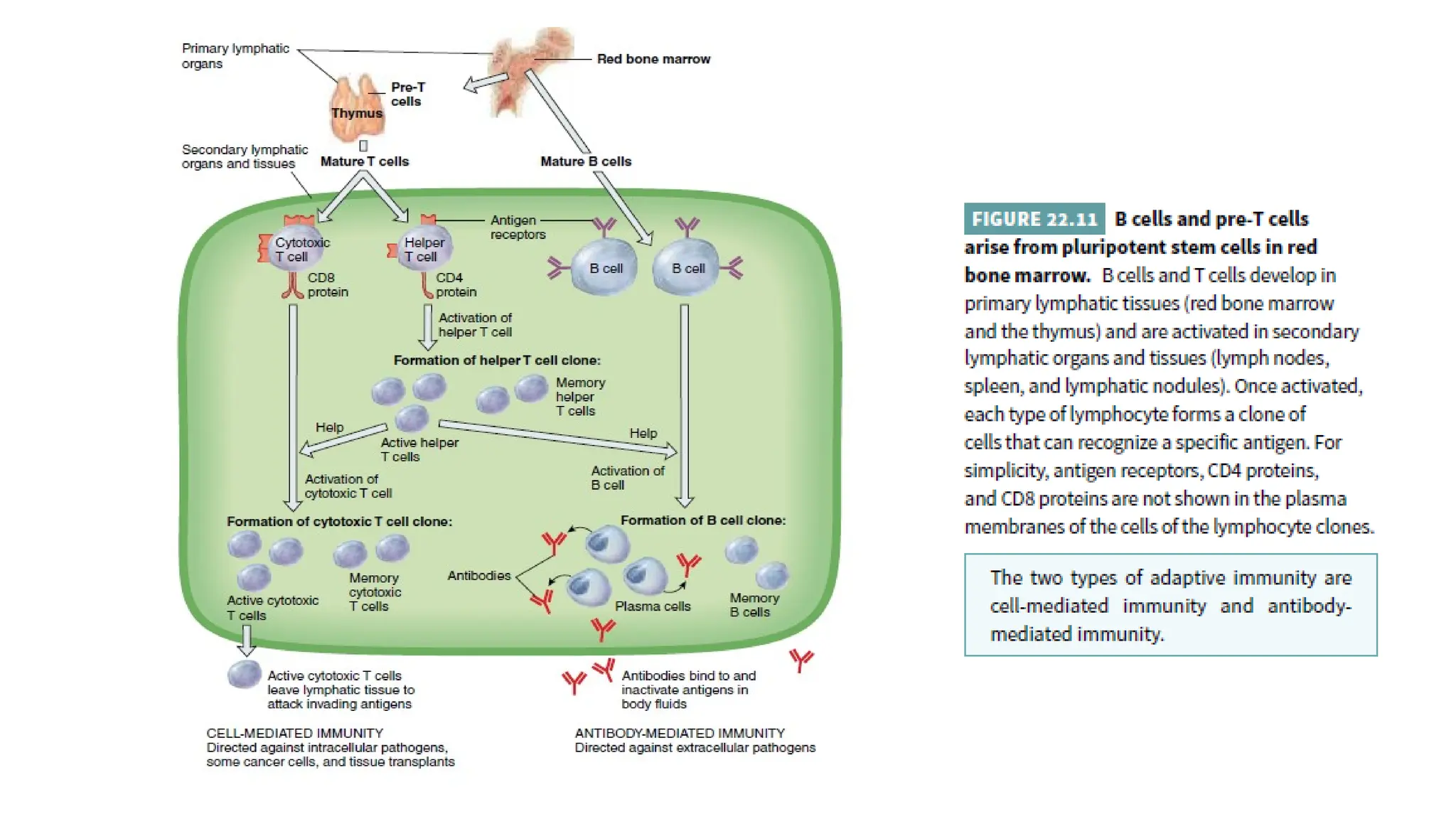
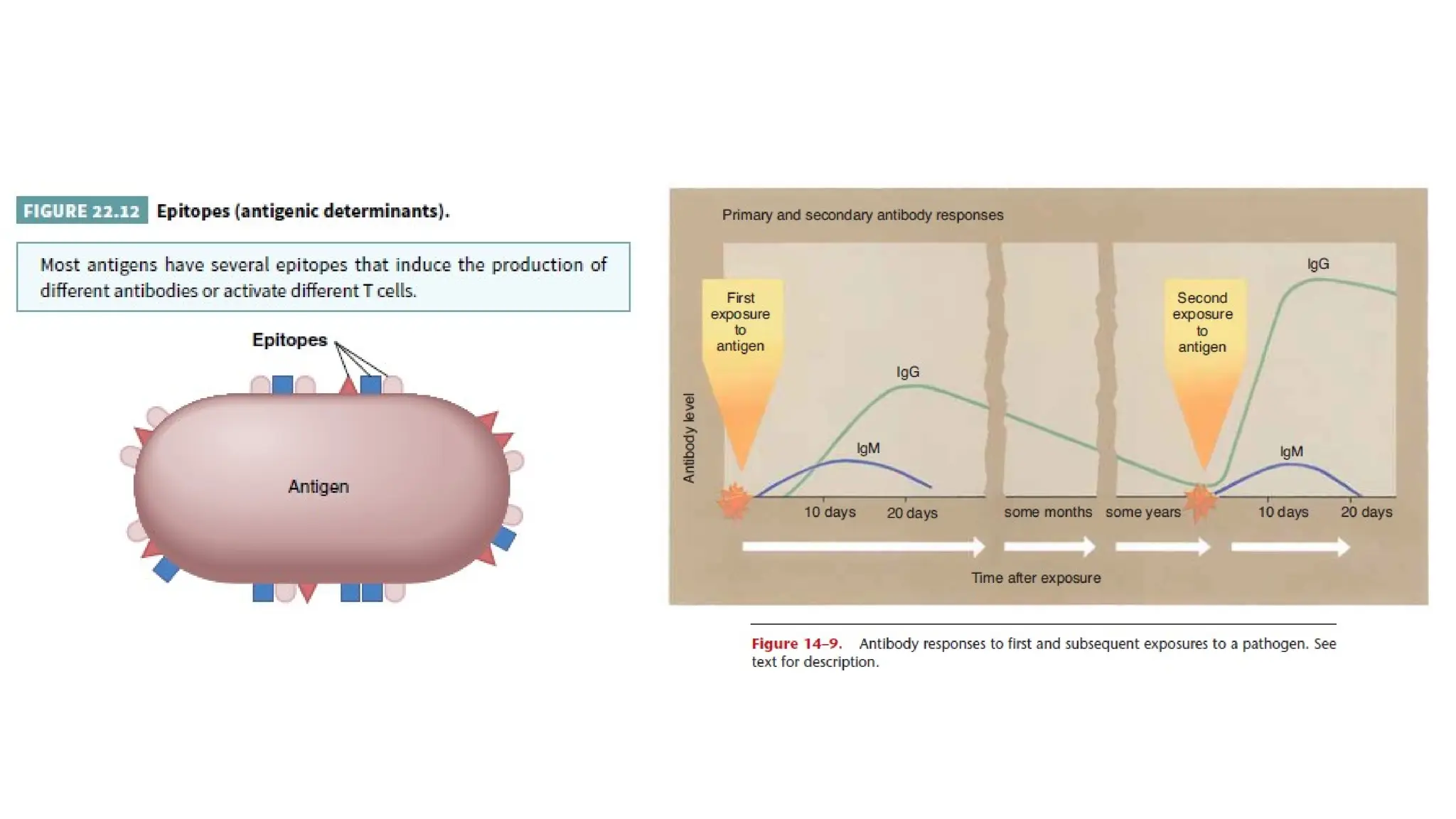
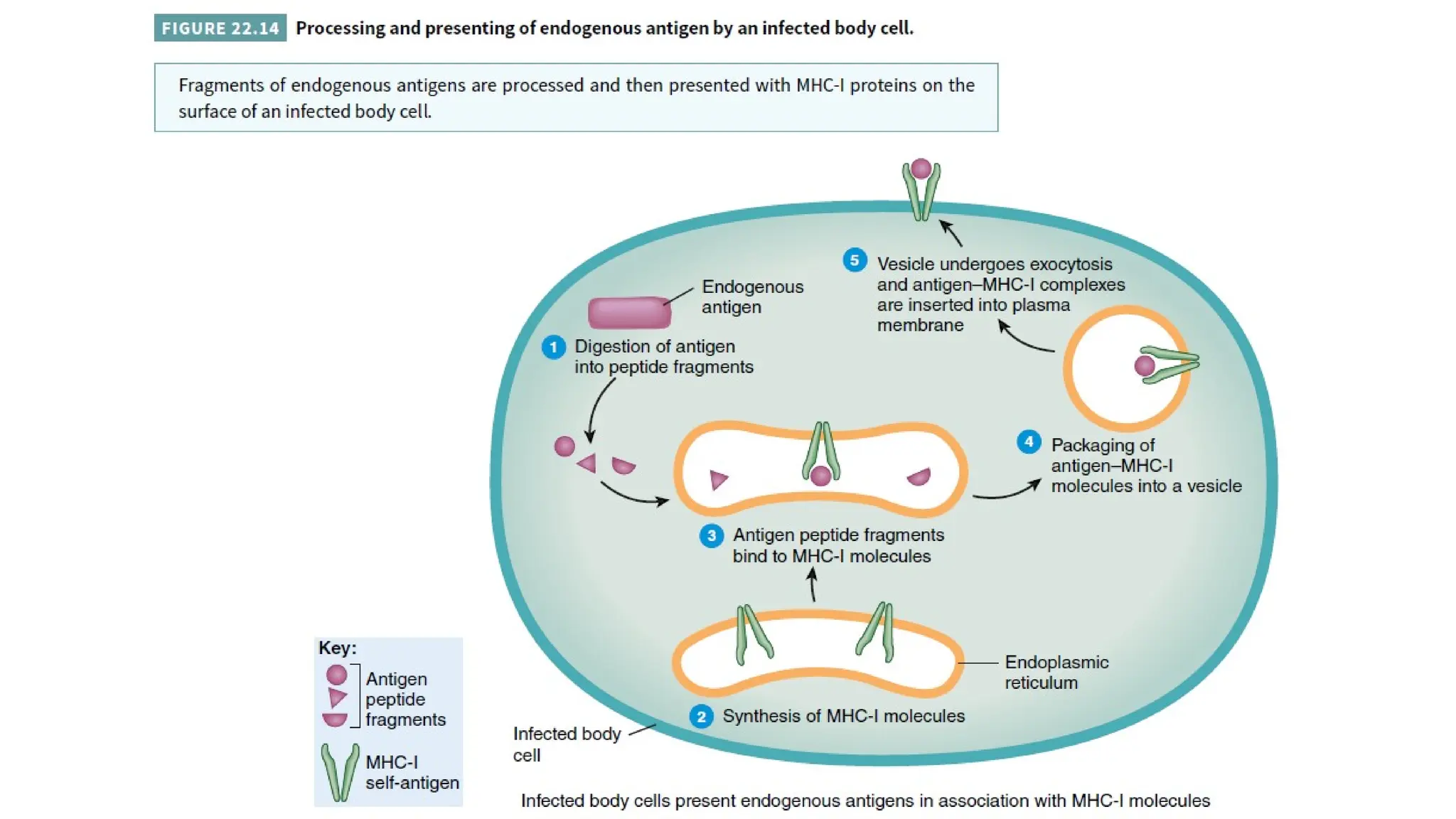
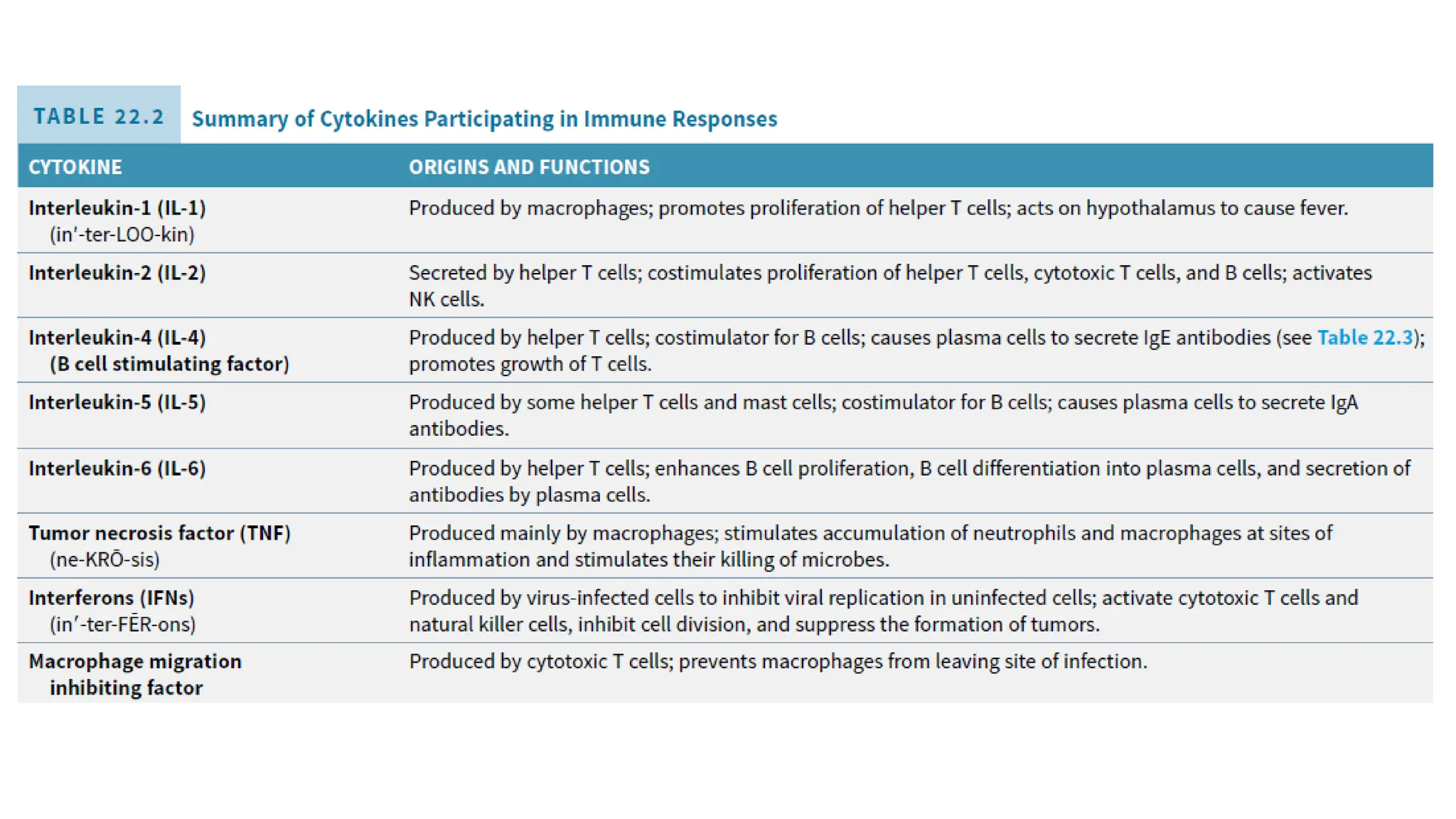

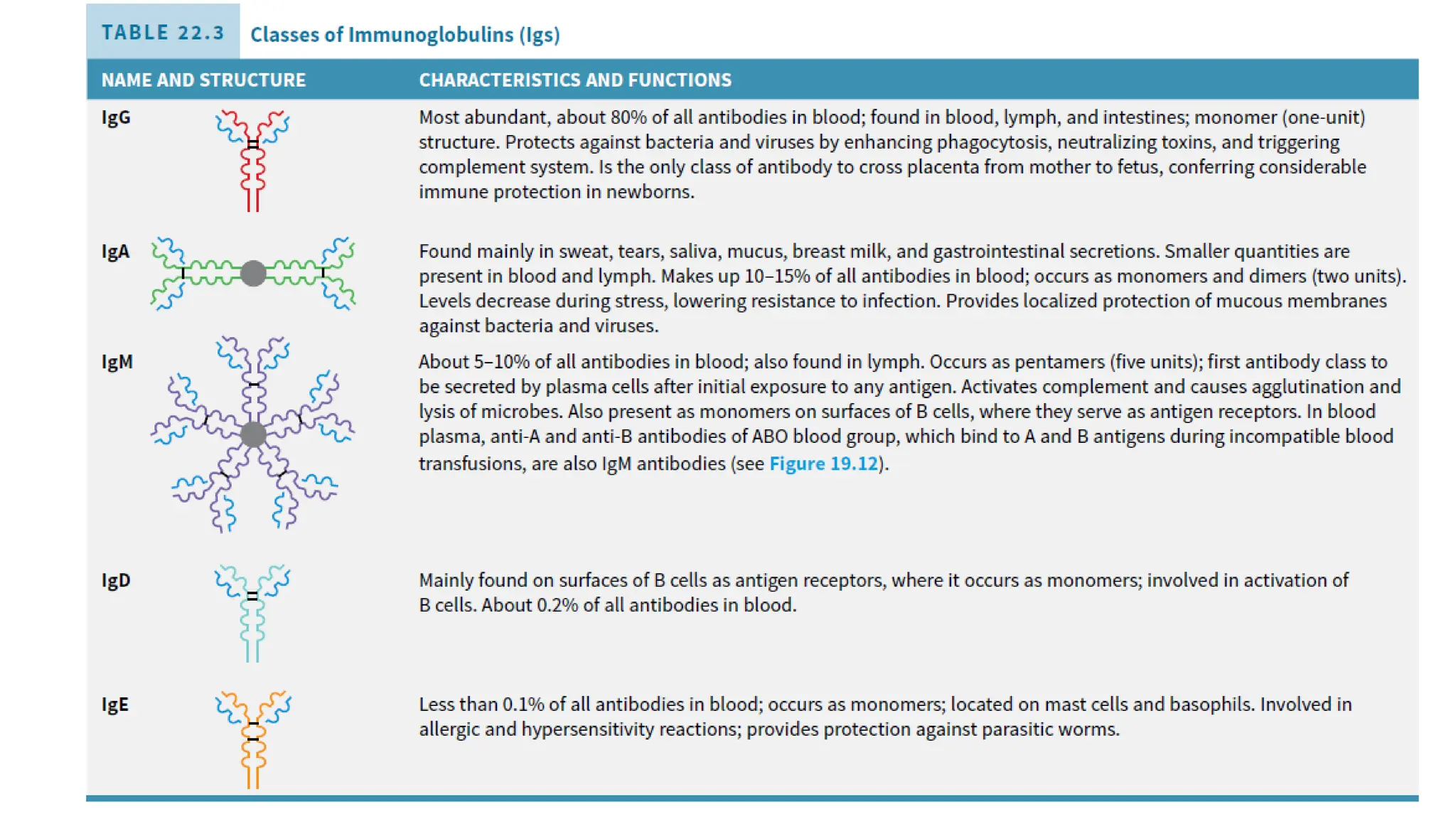

The document outlines the components and functions of the lymphatic system, including lymph, lymph vessels, and lymphoid organs such as lymph nodes, spleen, and thymus, where lymphocytes mature. It describes immunity, distinguishing between innate immunity—which is nonspecific and does not create memory—and adaptive immunity that responds to foreign antigens including bacteria, viruses, and malignant cells. The text also details various barriers and defensive cells involved in innate immunity, highlighting their roles in protecting the body from infections.








































