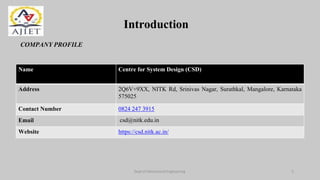
The document presents an internship report detailing tasks performed at the Centre for System Design (CSD) at NITK Surathkal, focusing on reverse engineering an e-bicycle and utilizing SolidWorks for component design. Key activities included understanding software tools, measuring e-bicycle components, and designing various parts like the utility box, frame, wheels, and braking systems. The experience enhanced skills in mechanical design and collaboration, underscoring the internship's role in career development and practical knowledge in engineering.