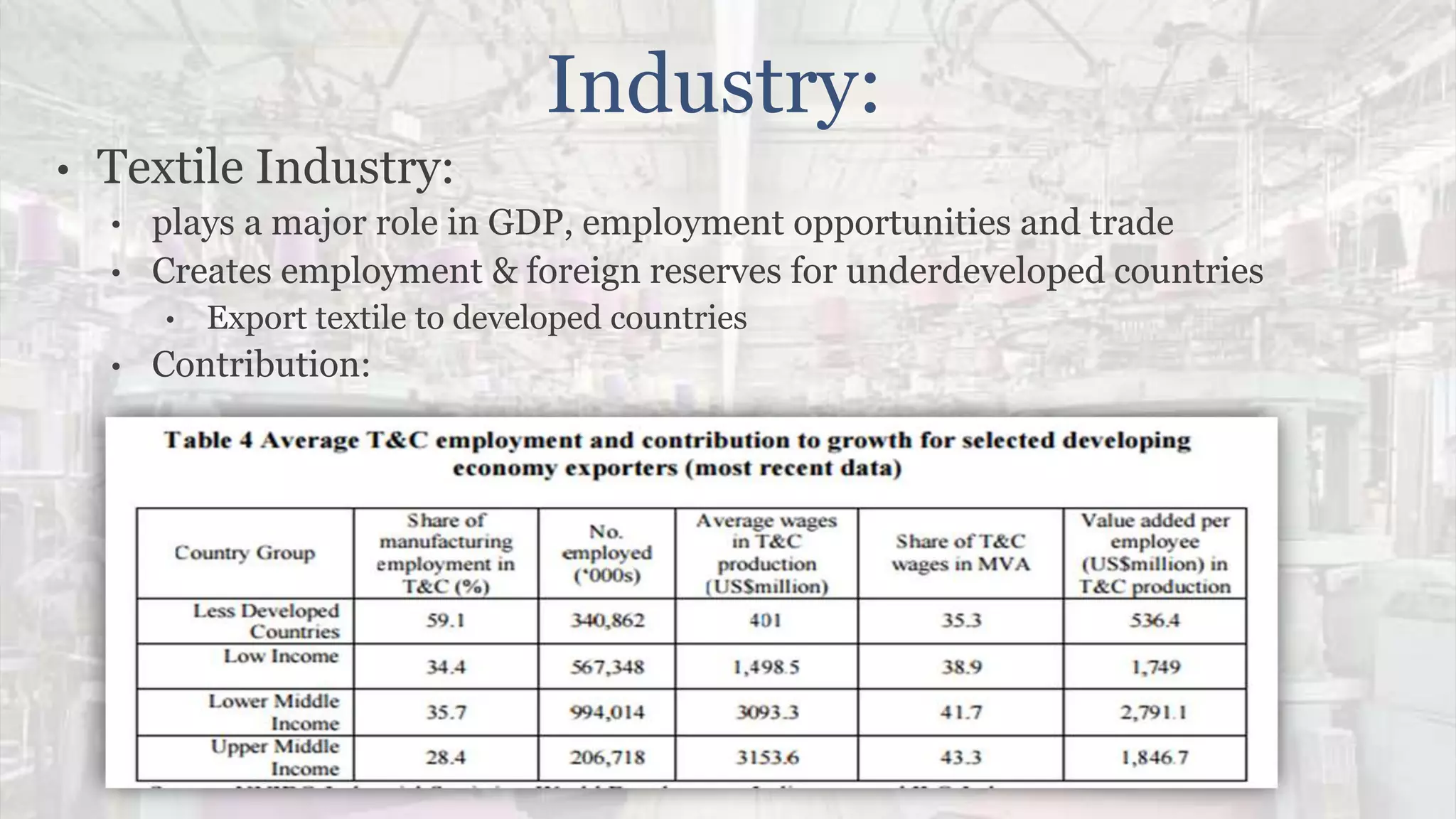
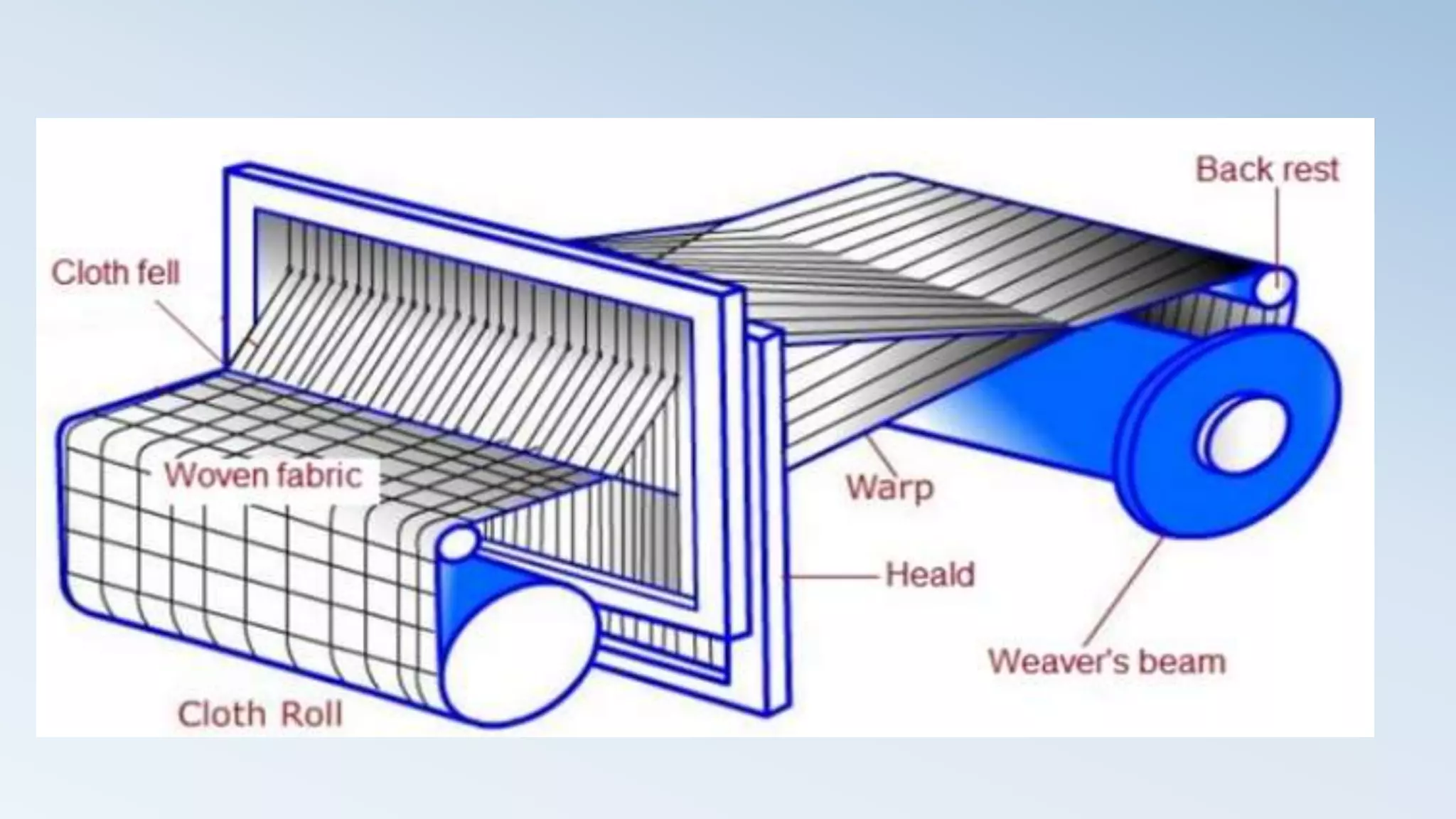
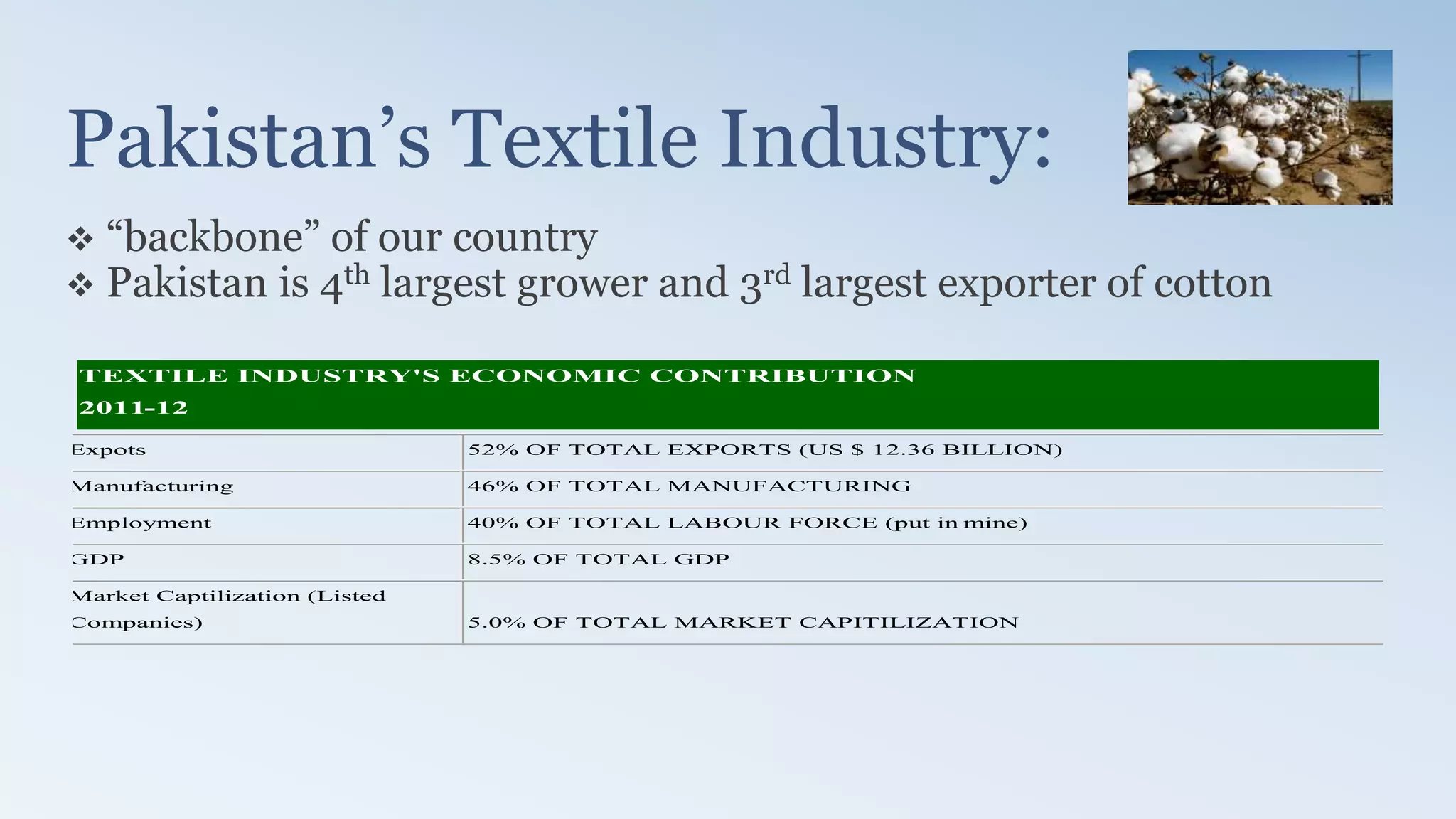
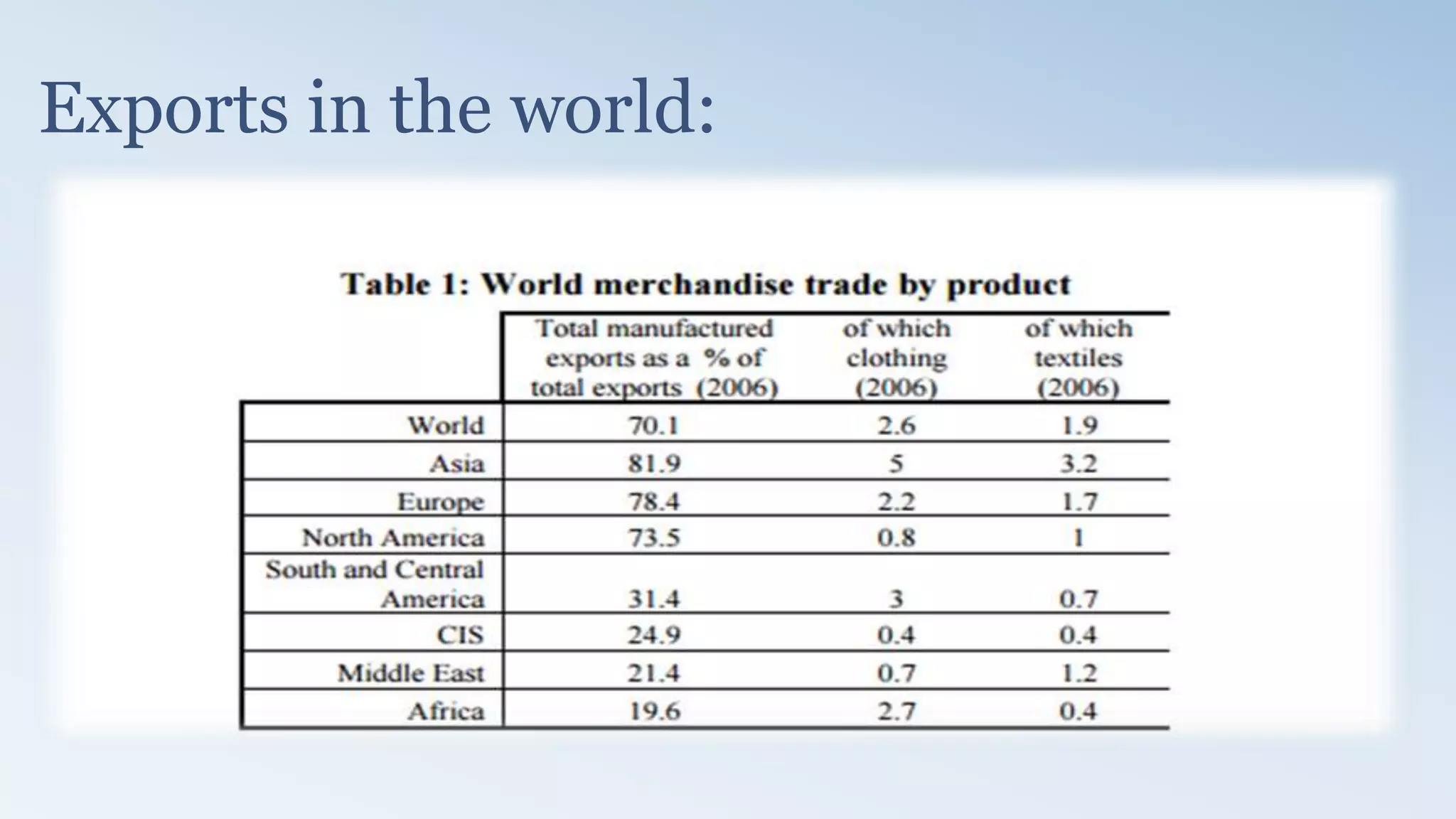
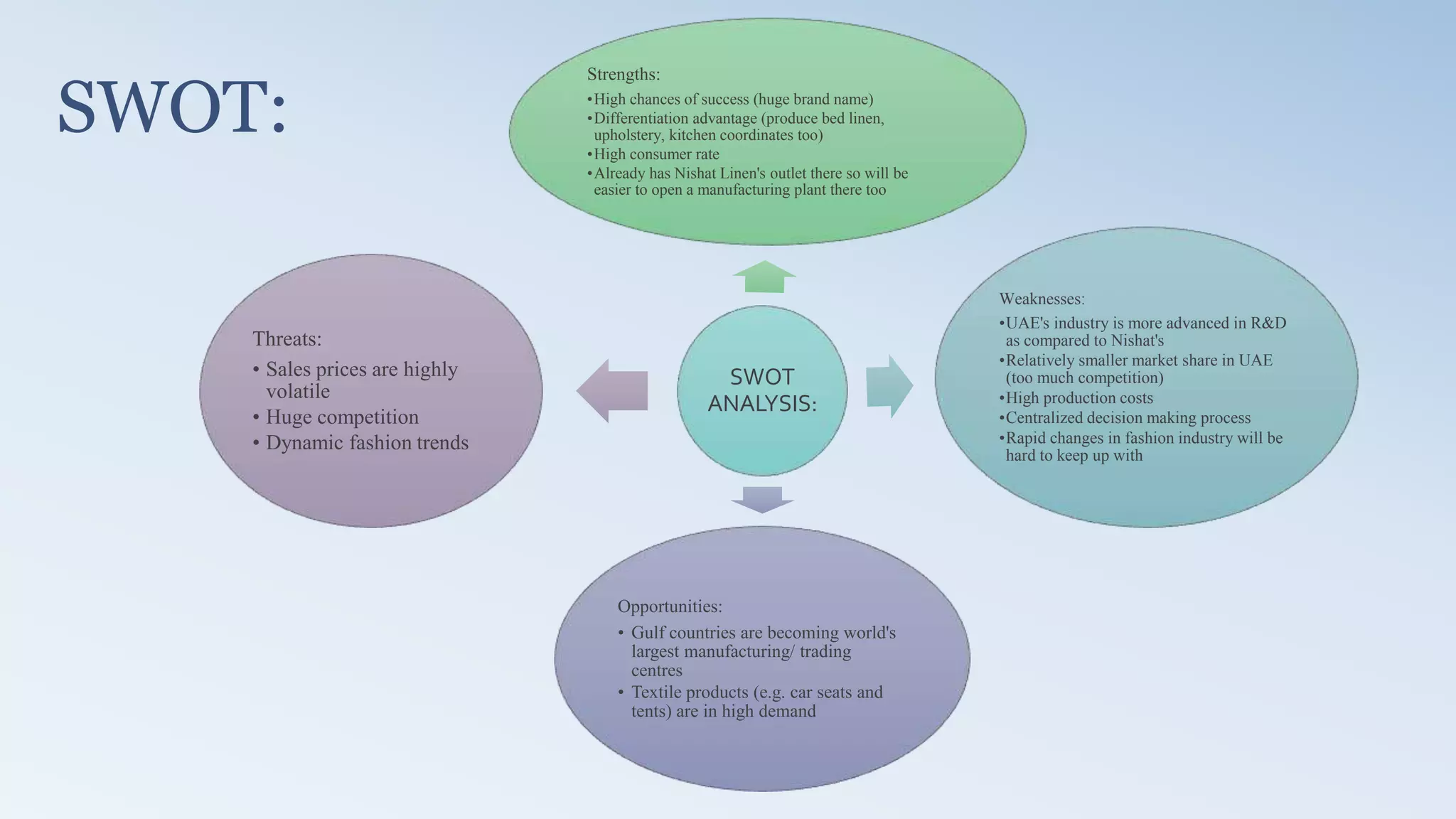
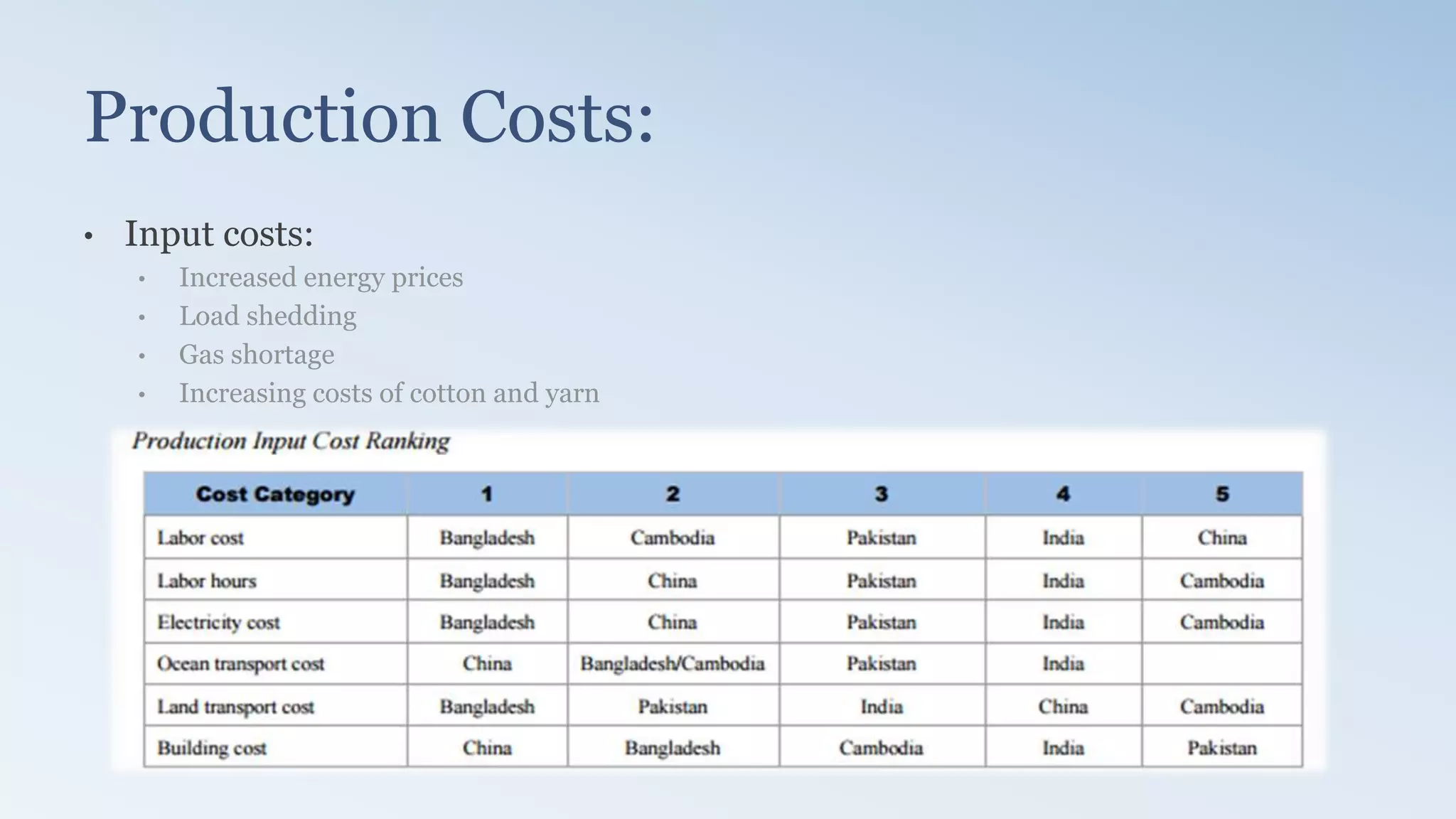
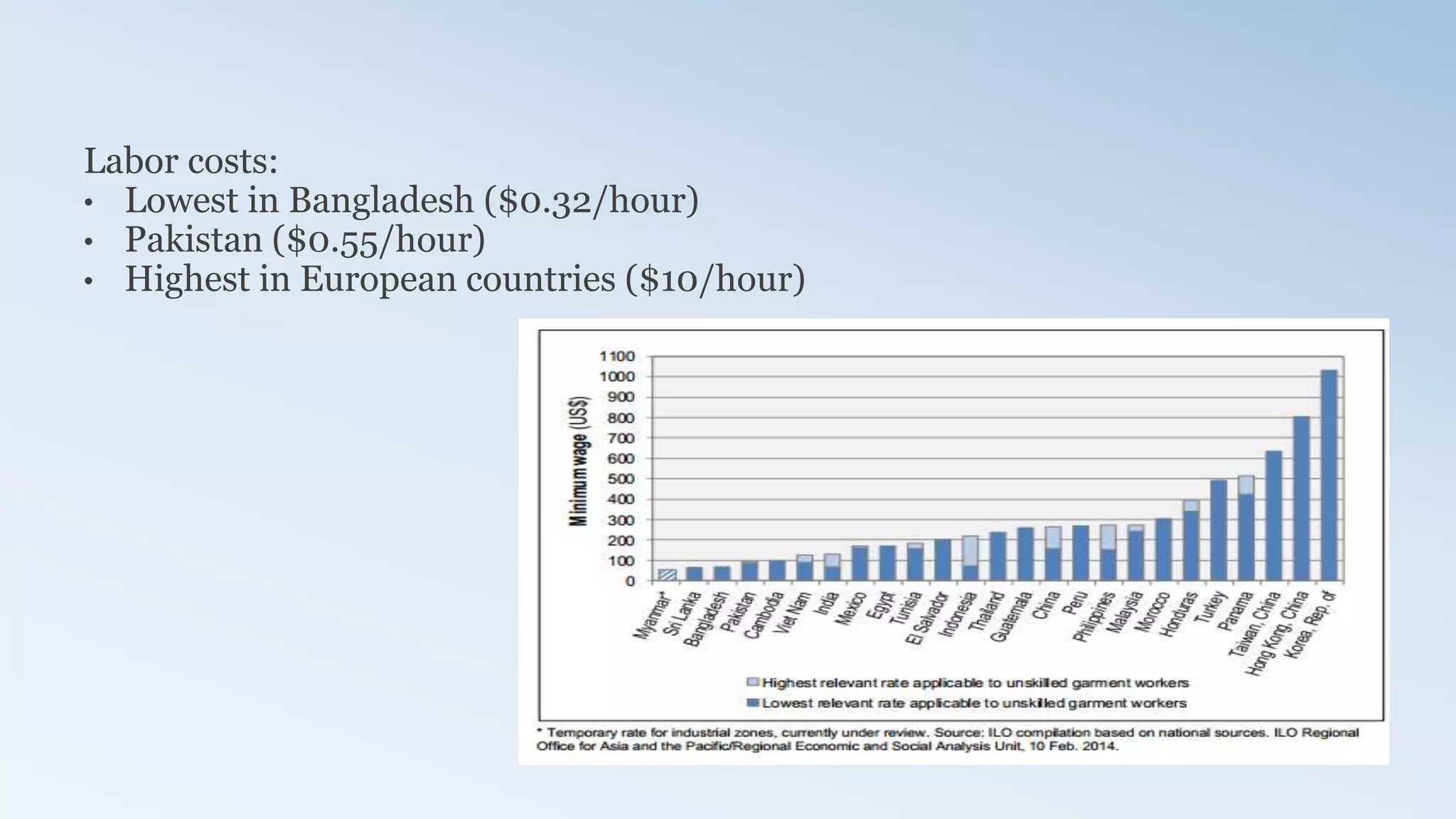
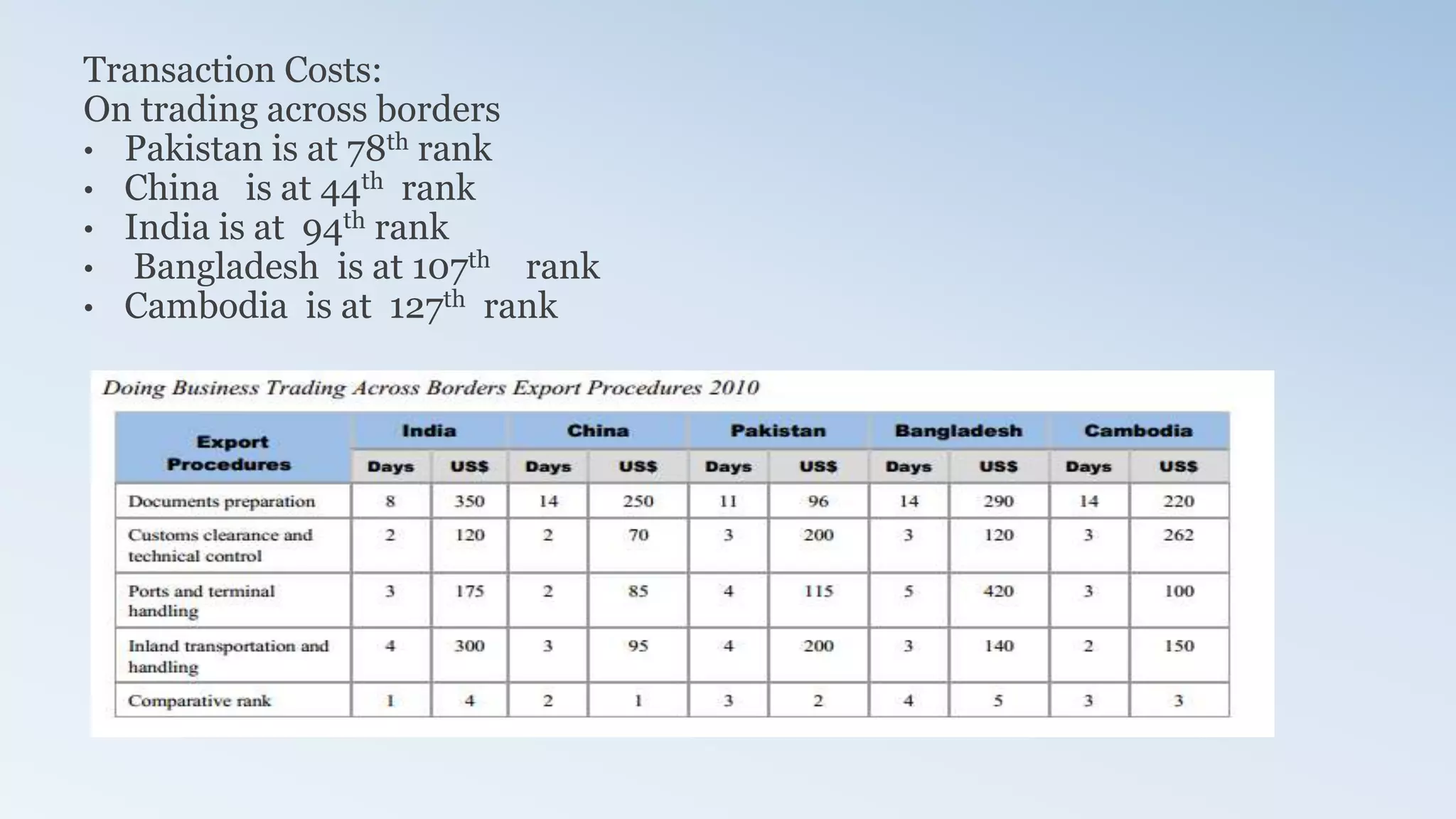
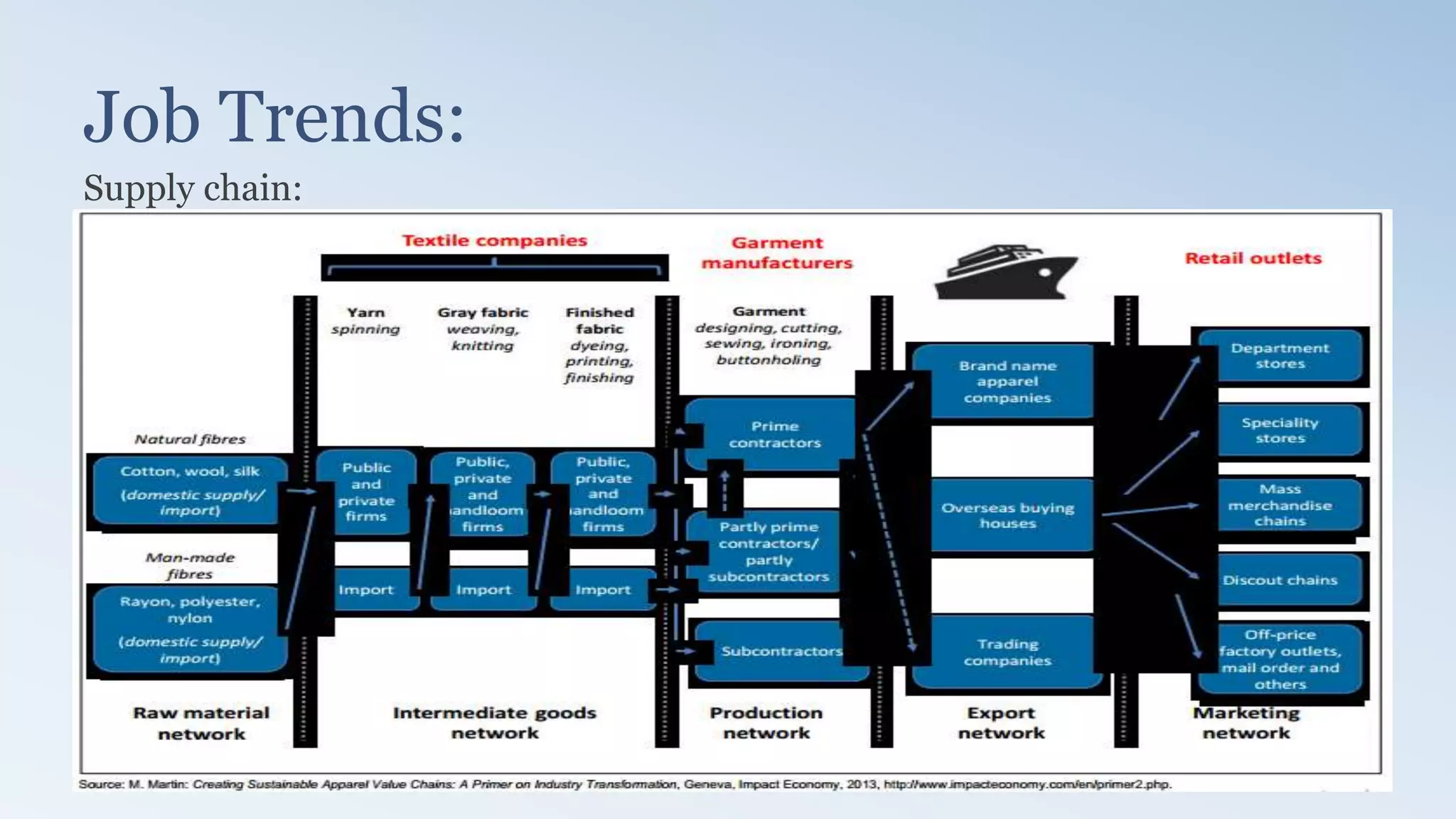
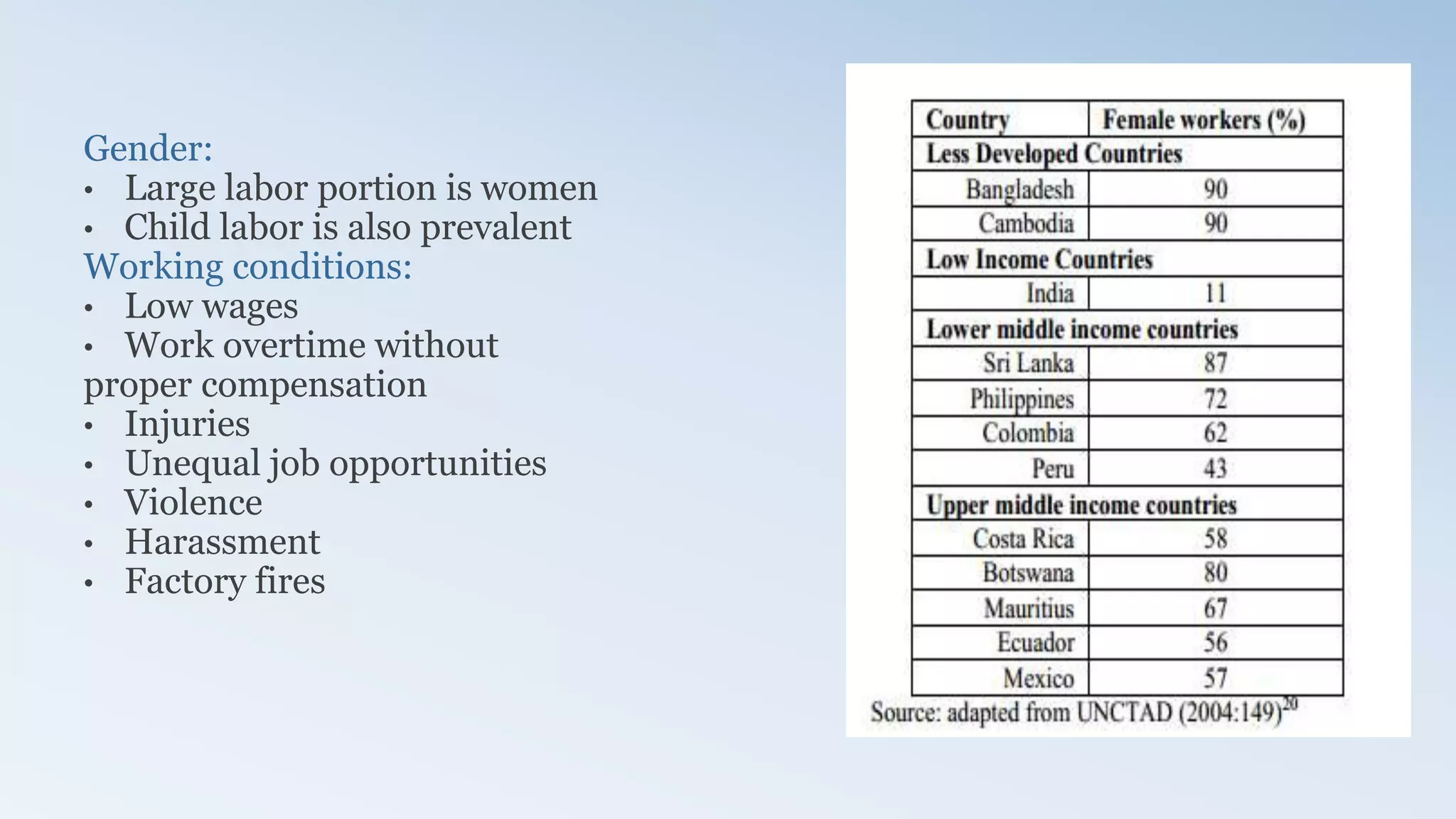
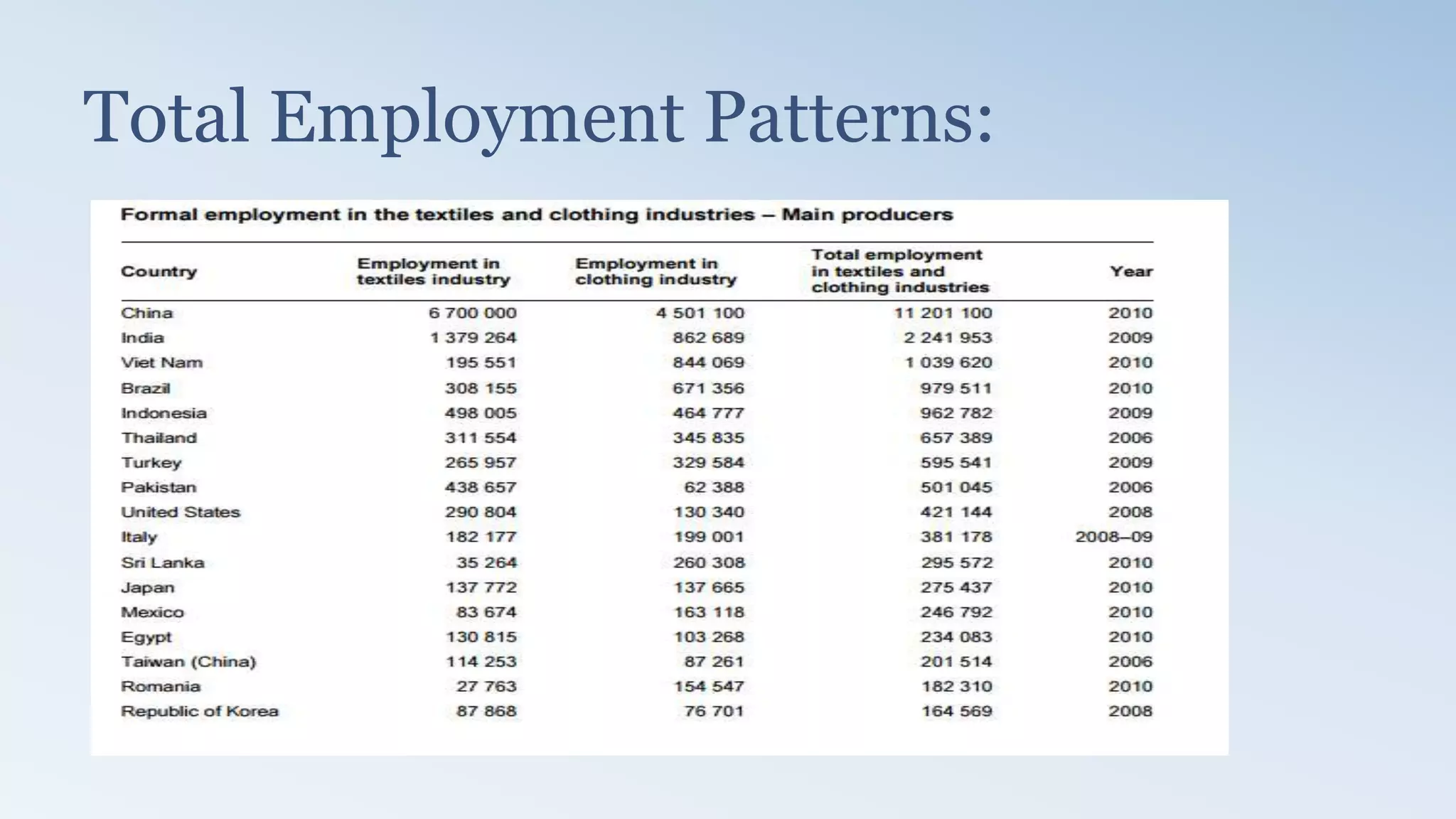
The document provides a detailed analysis of the textile industry, emphasizing its significance in GDP contribution, employment, and trade for both developed and underdeveloped countries, particularly highlighting Pakistan's textile sector as a key player. It outlines the features of textiles, market trends, challenges, and opportunities for companies like Nishat Textile Mills, proposing strategies for foreign direct investment and market penetration in Dubai. The analysis concludes with recommendations for Nishat to expand into other markets once established in Dubai.