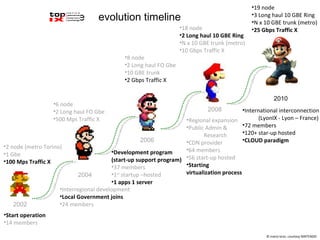
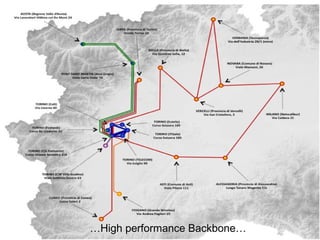
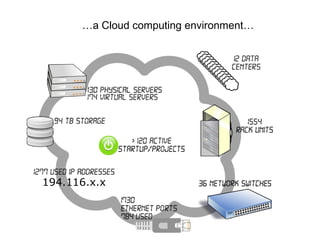
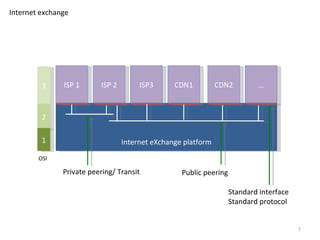
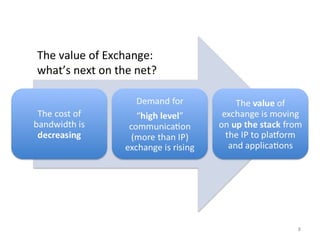
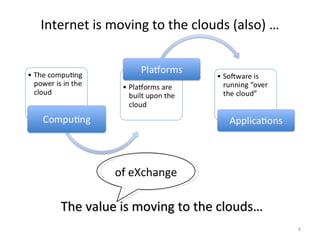
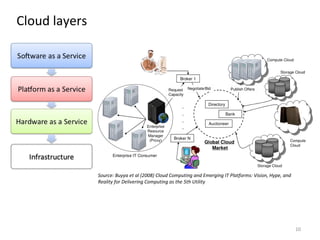
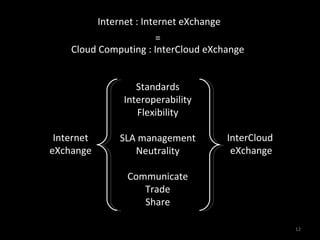
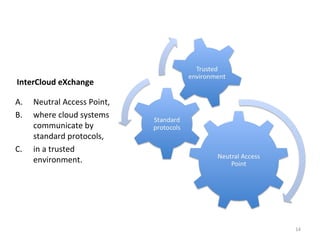
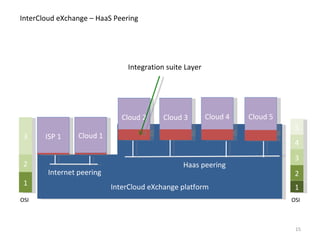
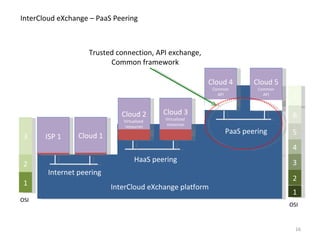
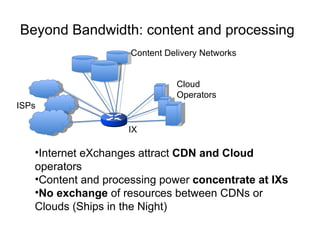
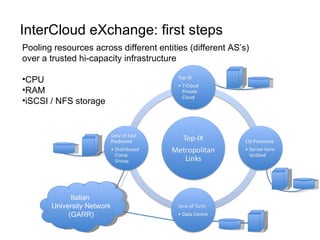
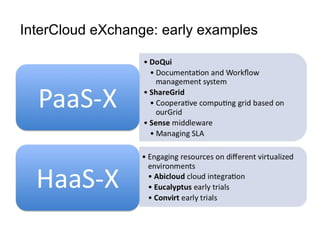
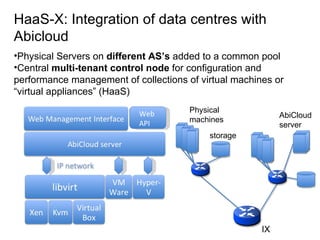
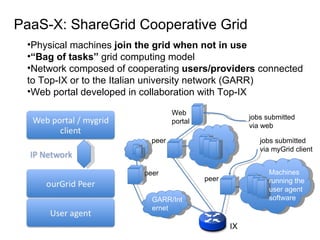
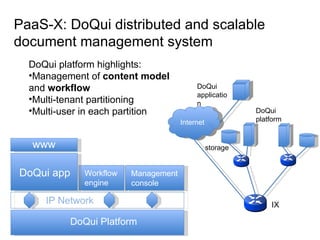
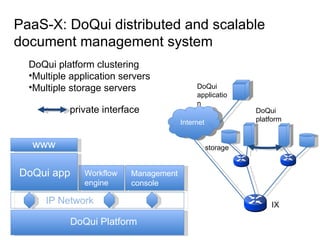
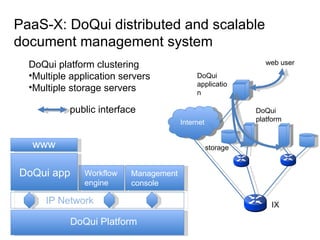
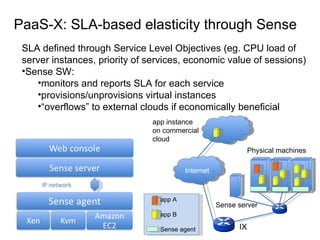
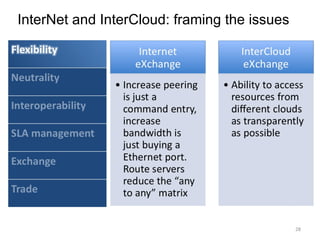
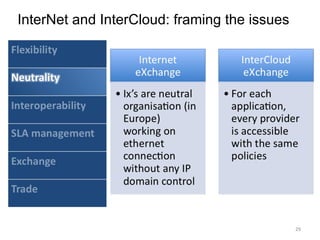
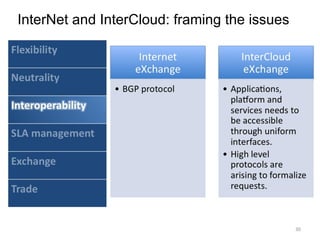
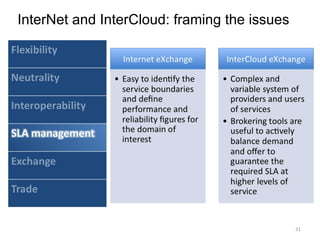
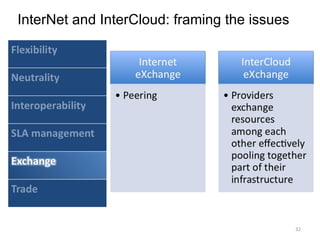
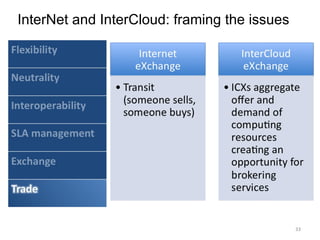
The document describes the evolution of TOP-IX, an internet exchange point in Piedmont, Italy, and its role in facilitating cloud computing and resource exchange. It began in 2002 with 14 members and has since expanded its infrastructure and membership. TOP-IX now aims to define an inter-cloud architecture to address issues like interoperability and resource exchange between clouds through an InterCloud exchange point, applying the peering model of internet exchange. This could provide benefits like flexibility, neutral access, and standard protocols for communication and resource sharing across cloud systems.