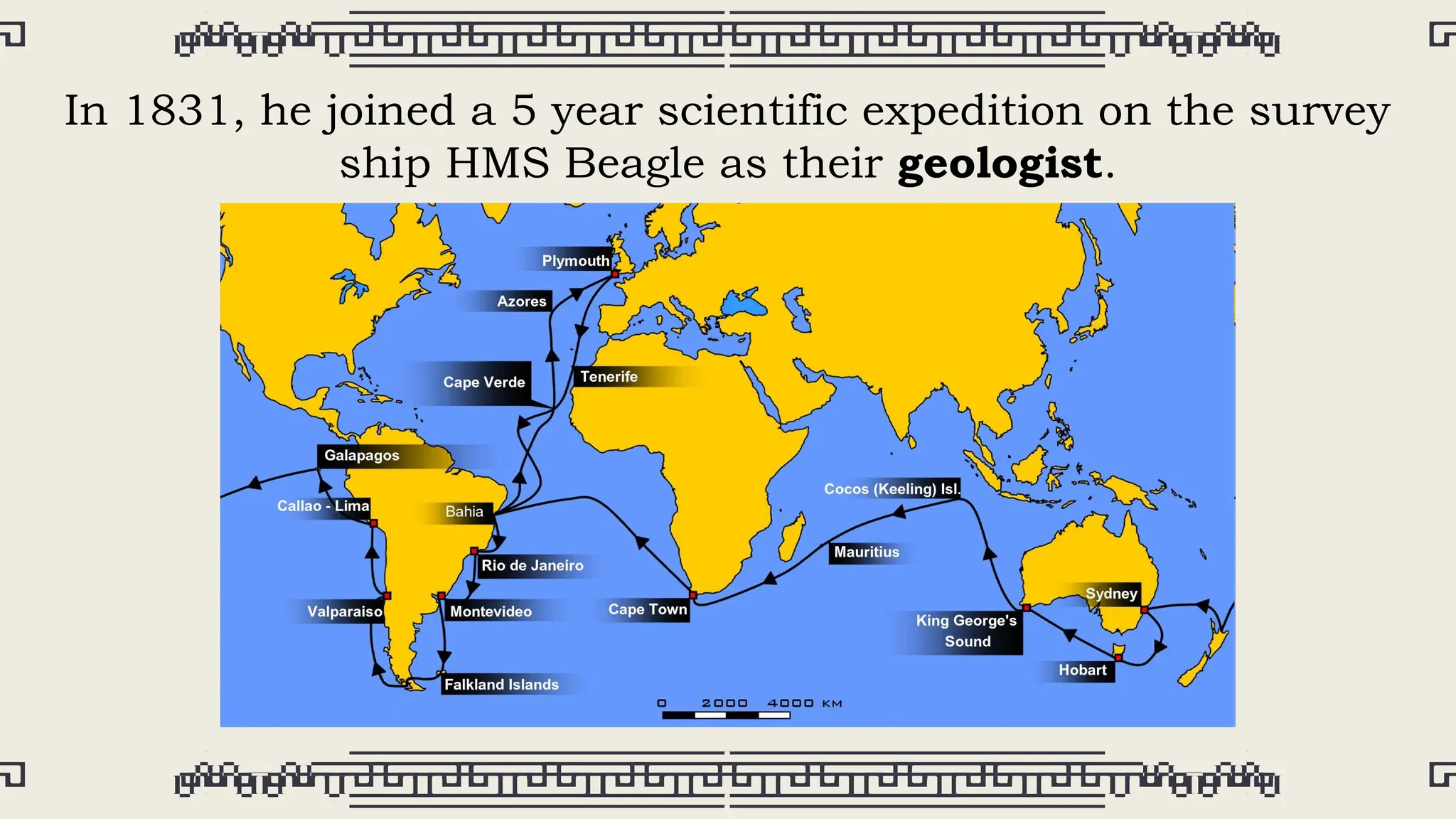
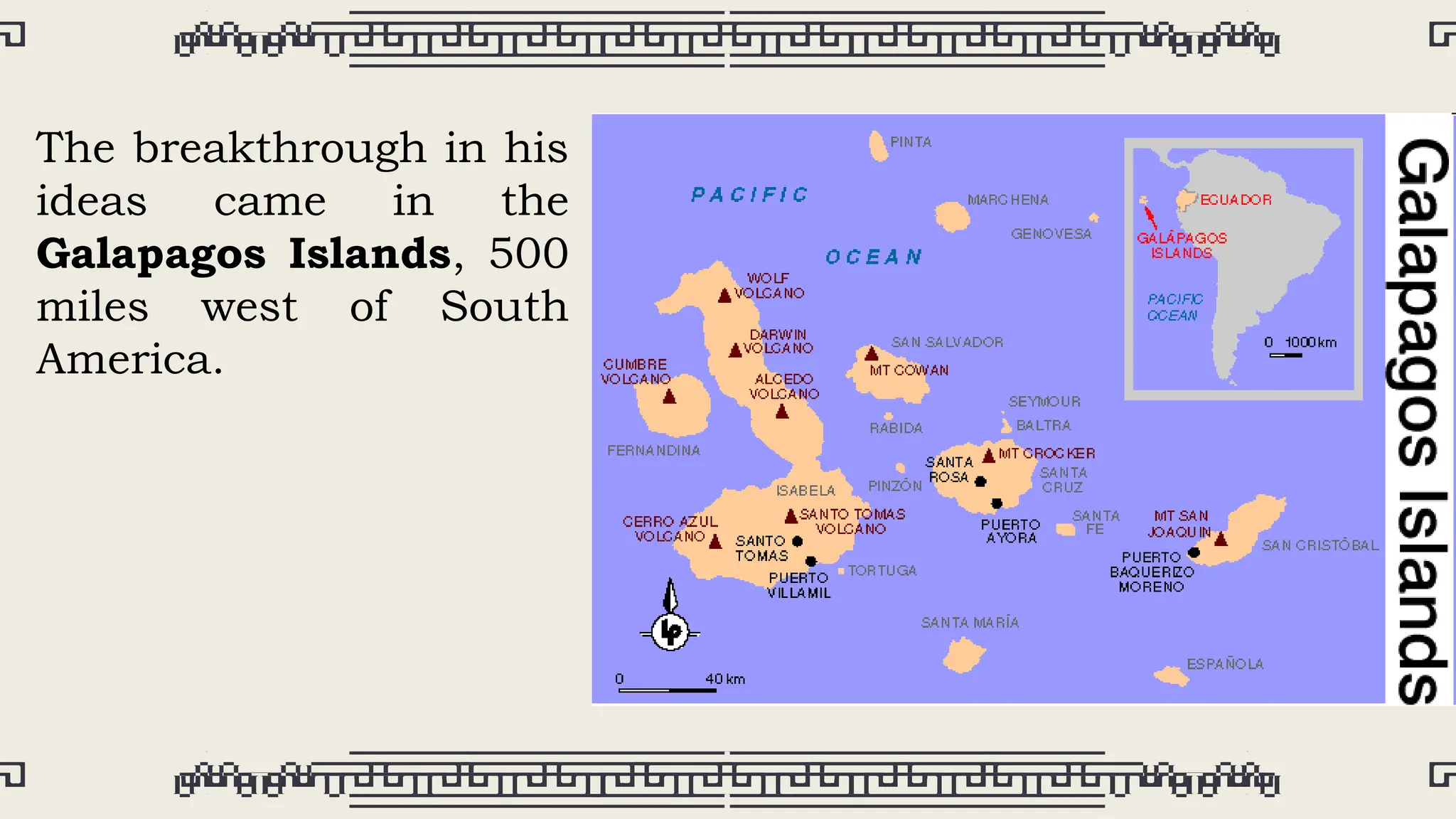
Charles Darwin, born on February 12, 1809, in England, became a pivotal figure in the development of evolutionary theory after his voyage on the HMS Beagle. Influenced by the work of geologist Charles Lyell and demographer Thomas Malthus, he formulated the concept of natural selection, which he published in 'On the Origin of Species' in 1859, challenging prevailing beliefs about creation. Darwin's ideas, which suggested that humans evolved from earlier species, sparked significant controversy and transformed scientific understanding of human origins before his death in 1882.