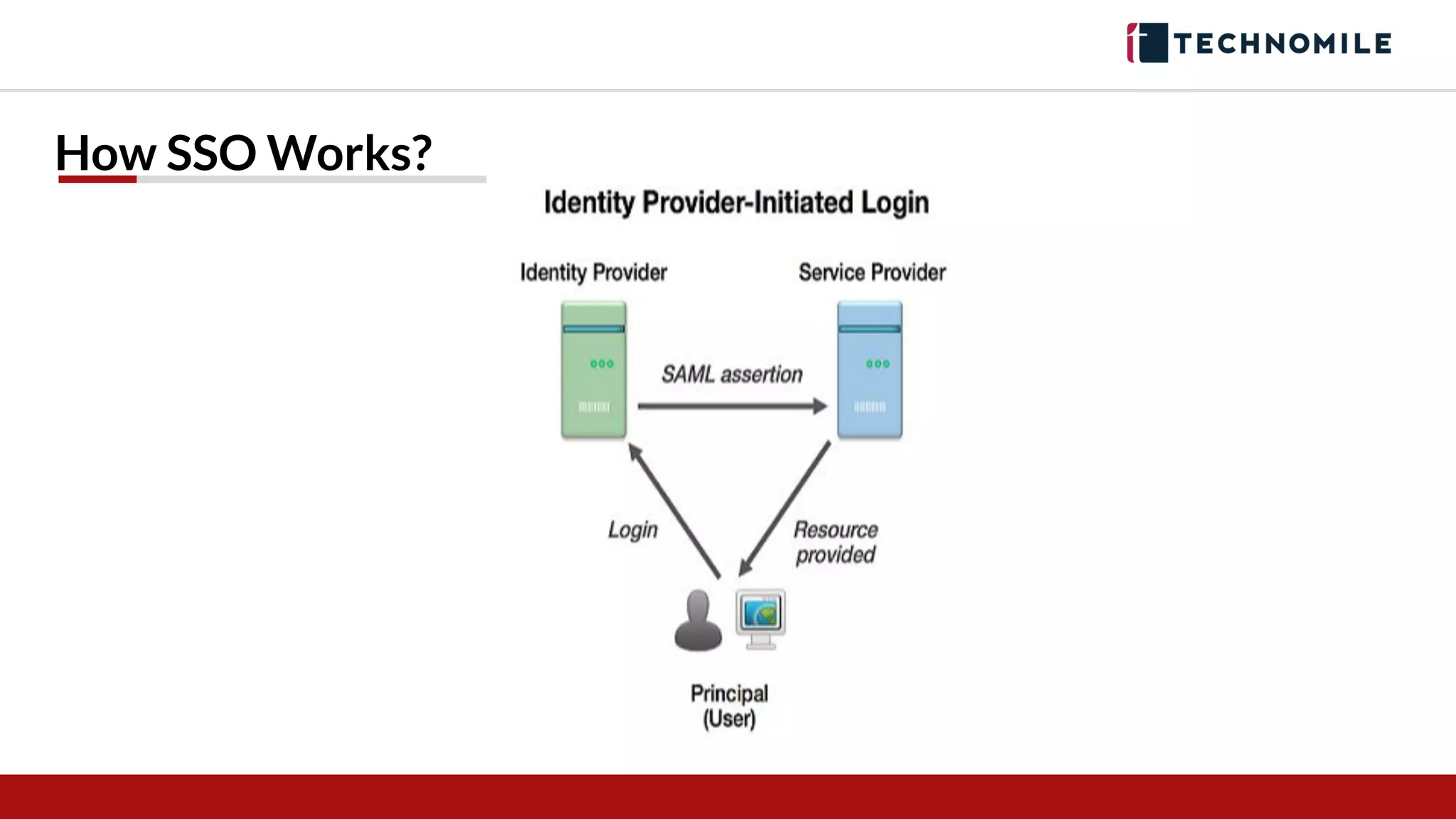
The document discusses cross-platform integration using web services, including REST and SOAP, and highlights the key characteristics and advantages of each. It also details the process of creating a connected app in Salesforce to enable authentication and single sign-on (SSO), along with demos of each step. Furthermore, it compares REST and SOAP, outlining when to use each based on application requirements.






![Steps for Creation of Connected App
1. Go to Salesforce instance
2. Search for App in Setup>>App Manager (New Connected App)
3. Create New App Add the required fields
4. [App name, API name, Email, Select Enable Auth Setting => Call Back URL,
Selected Auth Scope => Full Access(Api)/Desired]
5. After app is ready store Consumer Key & Consumer Secret for further
usage.
6. Get the Security Token or Reset it.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/integrationstepupsession-200607121817/75/Integration-step-up-session-12-2048.jpg)