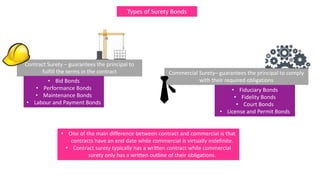
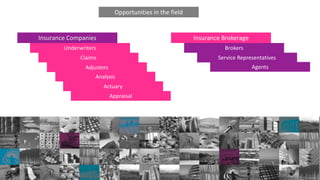
The document outlines the fundamentals of the insurance industry, including key terms, types of insurance, and the roles of various stakeholders. It distinguishes between personal and commercial insurance, as well as surety bonds, explaining their functions and legal frameworks. Additionally, it highlights the necessity of insurance in providing financial stability and peace of mind to individuals and businesses.