This document discusses how big data and analytics can help address the COVID-19 pandemic. It begins by defining big data and describing its key characteristics of volume, velocity, and variety. It then discusses how the pandemic has led to a large volume of health data and different data types. The document proposes a framework for collecting, analyzing and applying this data through descriptive, diagnostic, predictive and prescriptive analytics. This framework could help with tasks like epidemic monitoring, early warning, tracing virus sources, and recommending best courses of action. In closing, the document lists several references on big data applications for public health surveillance, resource allocation, and investigating COVID-19 symptoms.











![Big Data and COVID-19 [contd..]
– Several data digitized include
• Patient location
• Proximity
• Patient-Reported Travel
• Co-Morbidity
• Patient Physiology
• Current Symptoms
– Big Data Analytics renders itself useful to
• Scientists
• Health Workers
• Epidemiologists
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/innovativeproject1-211208035408/85/Innovative-project1-12-320.jpg)
![PROPOSED FRAMEWORK [2]
[2]
14
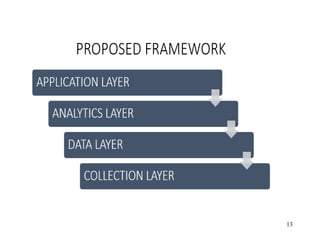
1. Telecommunication Operations
2. Internet
3. Electronic Medical Record
4. Hospital Information System
5. Government Information System
6. Epidemic Prevention System
7. Smart Device
8. Questionnaire
Collection Layer](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/innovativeproject1-211208035408/85/Innovative-project1-14-320.jpg)
![PROPOSED FRAMEWORK [3]
[2]
15
1. Location Data
2. Travel Data
3. Medical Data
4. Health Status Data
5. News Media Data
6. Government Data
7. Online Consumption of Data
Data Layer](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/innovativeproject1-211208035408/85/Innovative-project1-15-320.jpg)
![PROPOSED FRAMEWORK [4]
16
1. Descriptive Analysis
2. Diagnostic Analysis
3. Predictive Analysis
4. Prescriptive Analysis
Analytics Layer](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/innovativeproject1-211208035408/85/Innovative-project1-16-320.jpg)
![PROPOSED FRAMEWORK [5]
17
1. Personnel Tracking
2. Epidemic Surveillance
3. Early Warning
4. Tracing of virus sources
5. Drug Screening
6. Medical Treatment
7. Resource Allocation
8. Production & Delivery
Epidemic Monitoring
And
Surveillance Layer
[Application]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/innovativeproject1-211208035408/85/Innovative-project1-17-320.jpg)




![REFERENCES
1. S. Sharma and V. Mangat, "Technology and Trends to Handle Big Data:
Survey," 2015 Fifth International Conference on Advanced Computing &
Communication Technologies,Haryana,2015,266-271.[DOI: 10.1109/
ACCT.2015.121]
2. Burghard C: Big Data and Analytics Key to Accountable Care Success.
2012, IDC Health Insights.[URL:https://www.waysquare.com/big-data-
and-analytics-key-to-accountable-care-success/]
3. Feldman B, Martin EM, Skotnes T: “Big Data in Healthcare Hype and
Hope.” October 2012.Dr.Bonnie 360.
4. Raghupathi W, Raghupathi V. Big data analytics in healthcare: promise
and potential. Health Inf Sci Syst.2014.
5. Ginsberg J, Mohebbi M H, Patel R, et al. Detecting influenza epidemics
using search engine query data.Nature,2009, 457(7232):1012-1014
22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/innovativeproject1-211208035408/85/Innovative-project1-22-320.jpg)


