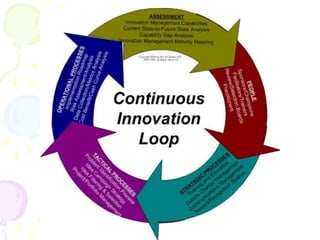
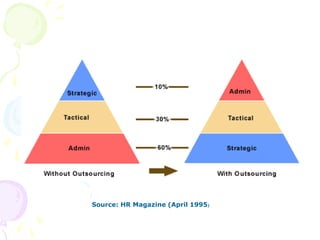
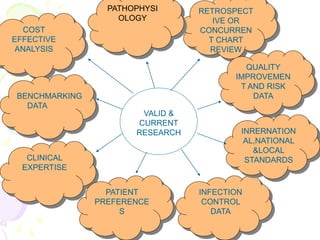
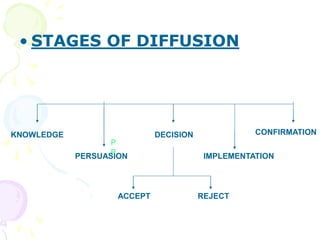
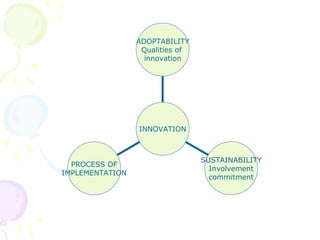
This document discusses various innovations in nursing education, clinical practice, and other areas of nursing. It describes innovations such as handheld computers, e-learning, high-fidelity simulation, evidence-based practice, wireless technology, and magnet hospital status. The document emphasizes that innovation is needed to maintain and improve quality of care, address growing health demands, and overcome workforce shortages.