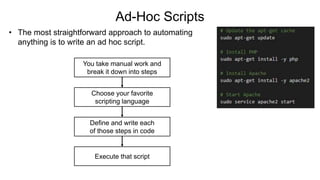
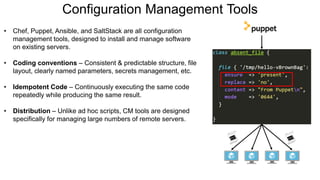
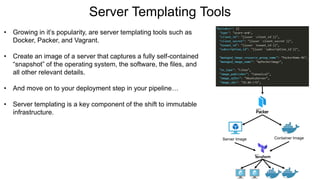
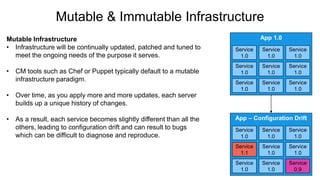
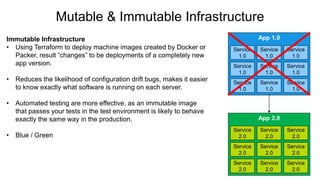
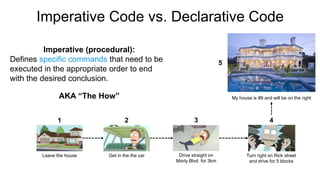
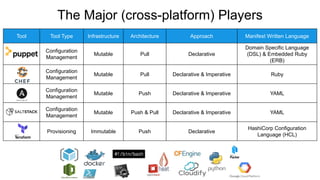
This document provides an overview of infrastructure as code concepts and tools. It begins with an introduction to infrastructure as code and how it allows infrastructure to be provisioned and maintained through code. It then covers different categories of tools including ad-hoc scripts, configuration management tools, server templating tools, and provisioning tools. Examples like Packer and Terraform are demonstrated. The document also discusses concepts like mutable vs immutable infrastructure and imperative vs declarative code. It profiles major infrastructure as code players and frameworks. Finally it touches on best practices and the benefits of infrastructure as code.