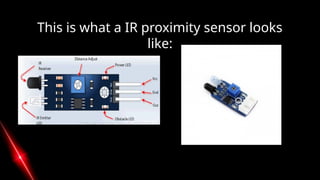
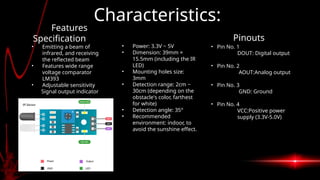
Infrared proximity sensors emit and receive infrared light to detect obstacles, utilizing a transmitter and a receiver to measure reflected light intensity. They are widely applied in robotics, automation, security, and mobile devices, characterized by features like adjustable sensitivity and a detection range of 2cm to 30cm. While offering advantages such as non-contact sensing and resistance to environmental factors, they also have limitations including varying accuracy and angular detection constraints.