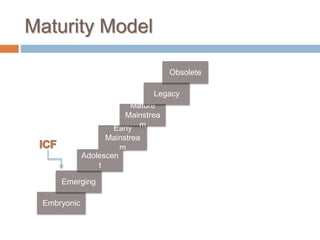
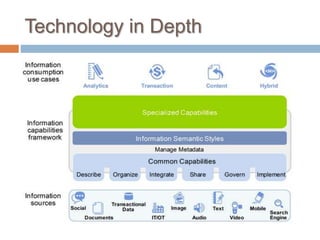
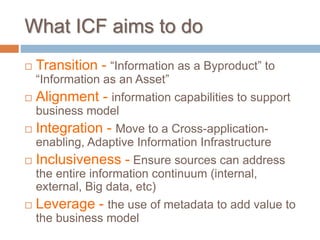
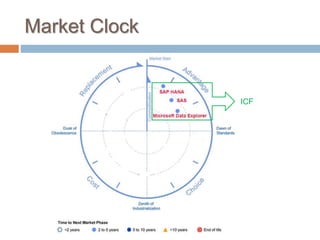
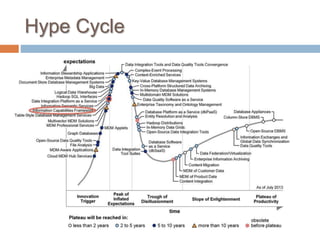
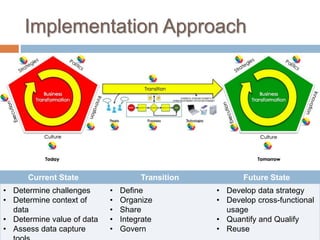
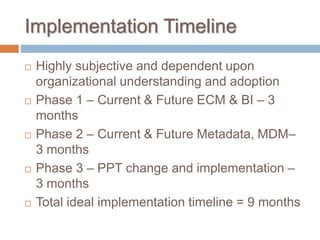
The Information Capabilities Framework (ICF) is a strategic tool designed to help organizations maximize the value of their information assets through improved data management and integration. It emphasizes a capability-driven approach over technology silos and aims to enhance decision-making, agility, and compliance. The framework is intended to support organizations in evolving their information infrastructure over a period of 5-10 years for greater flexibility and effectiveness.