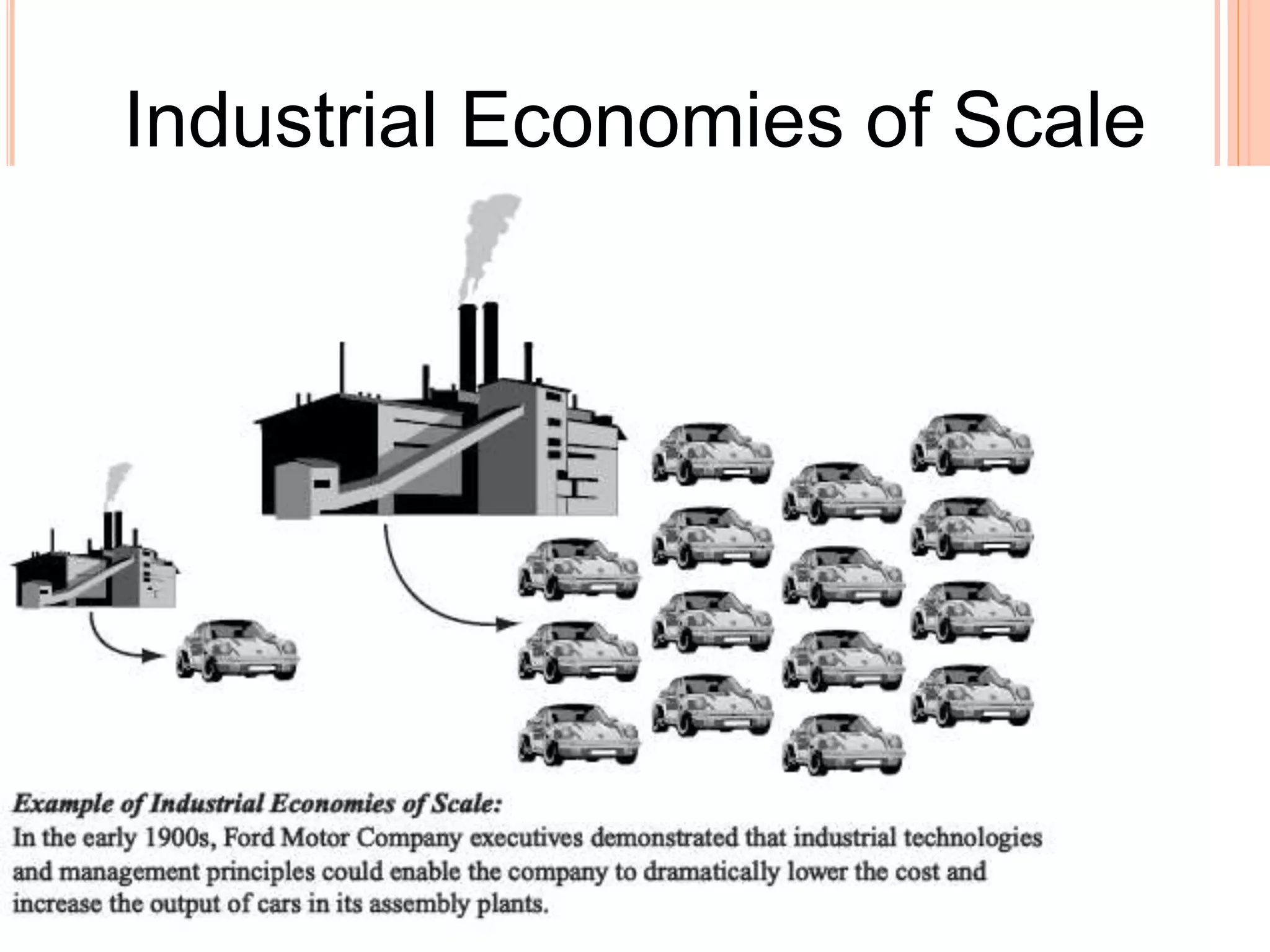
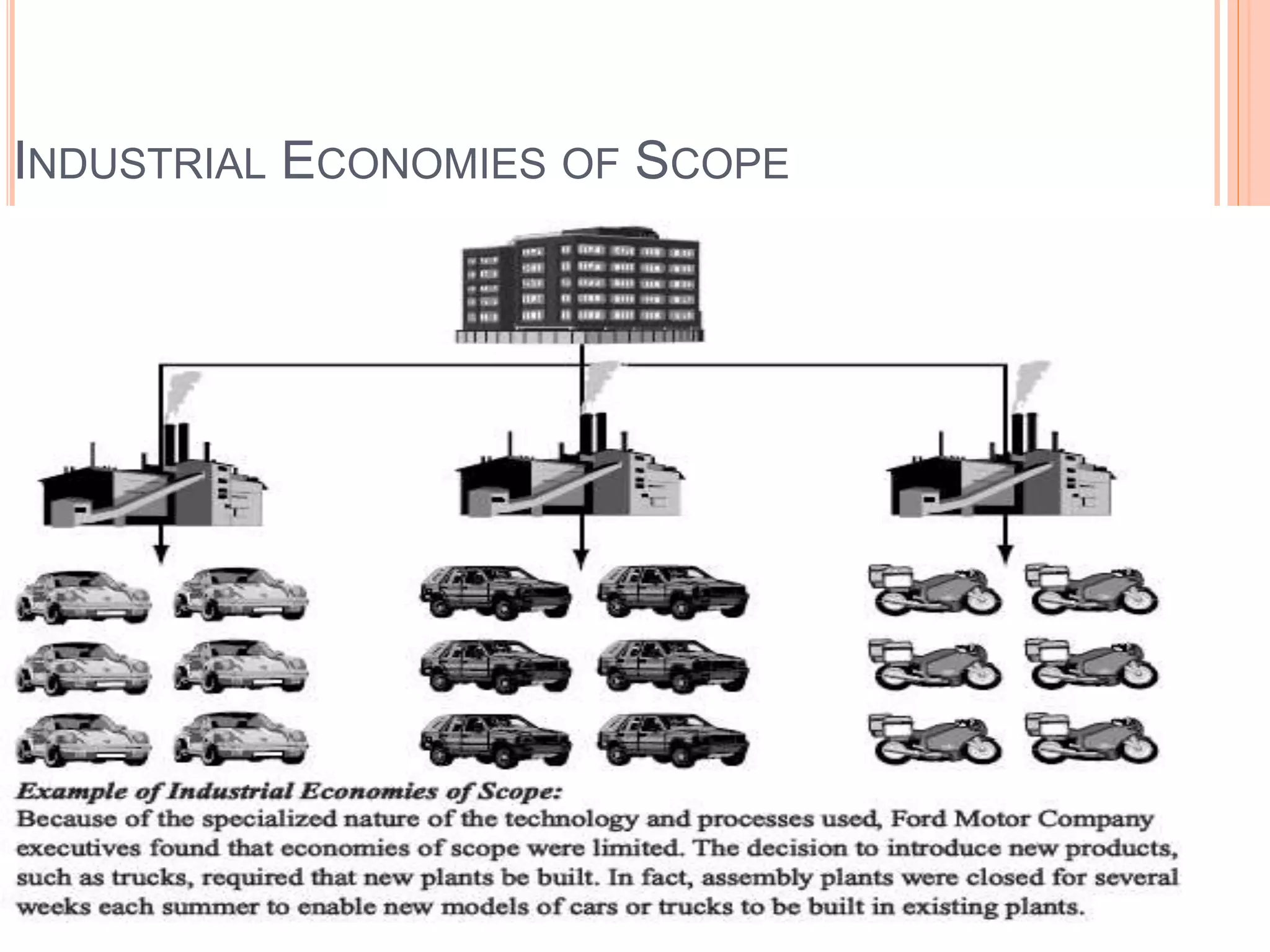
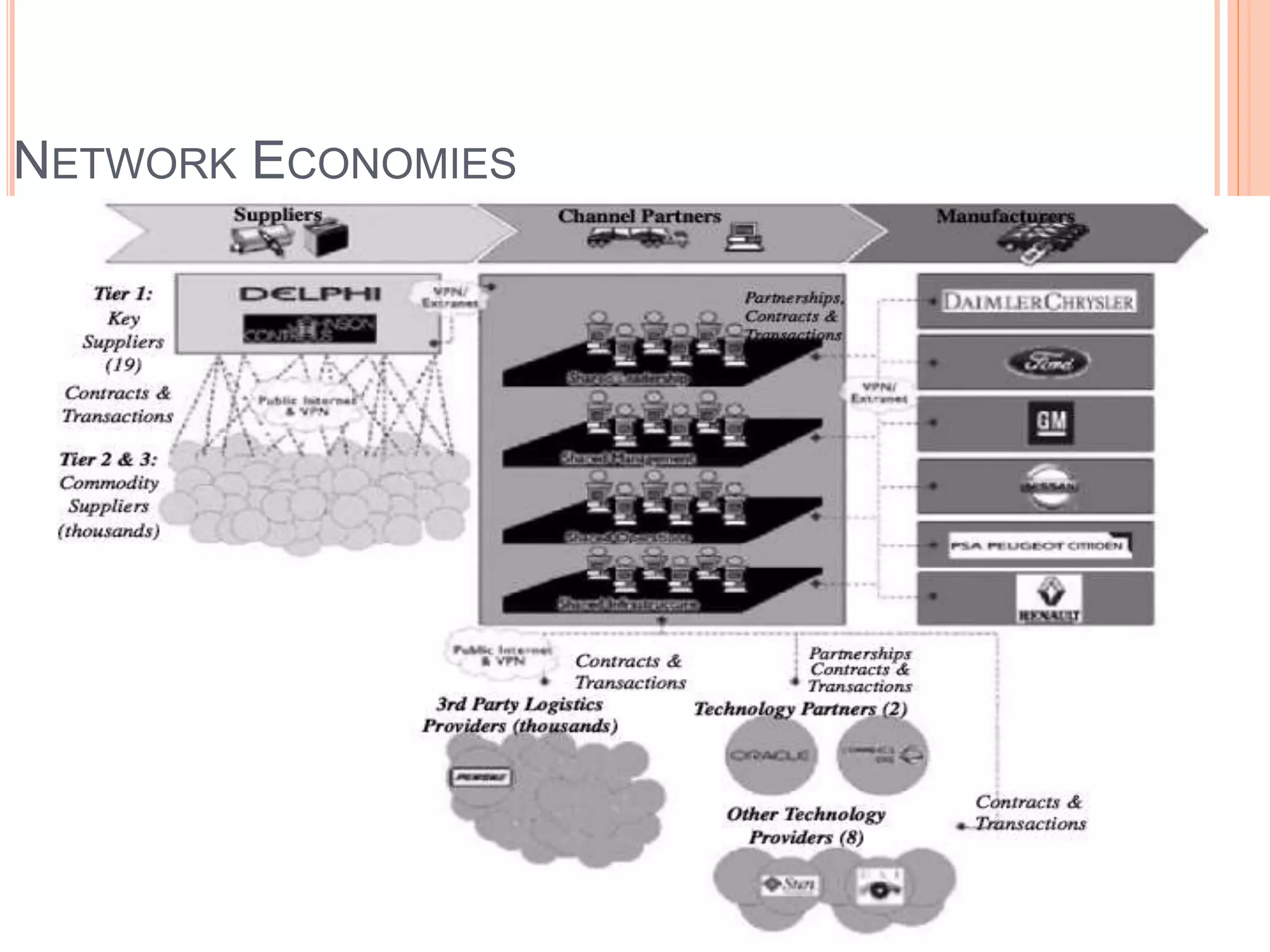
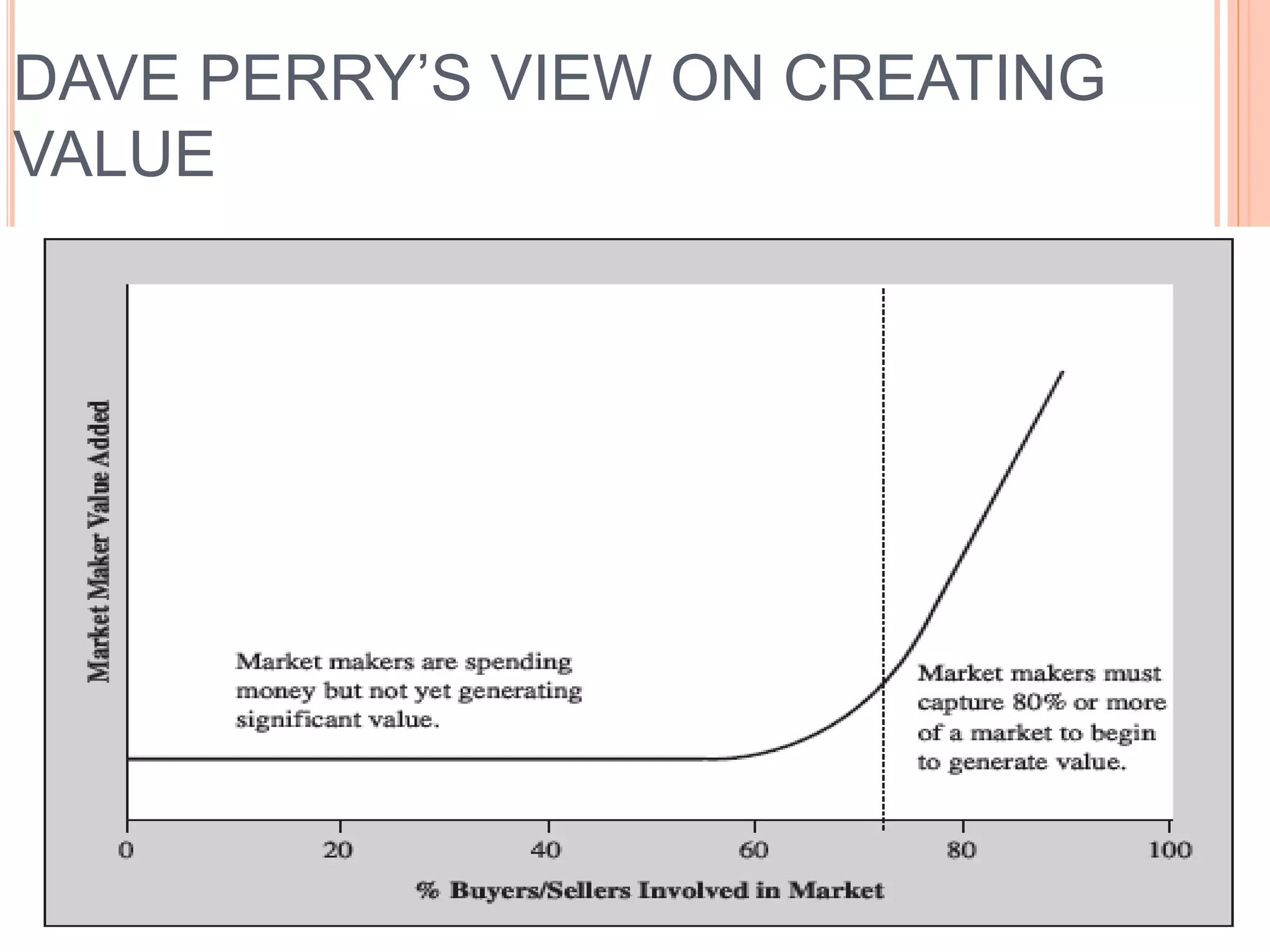
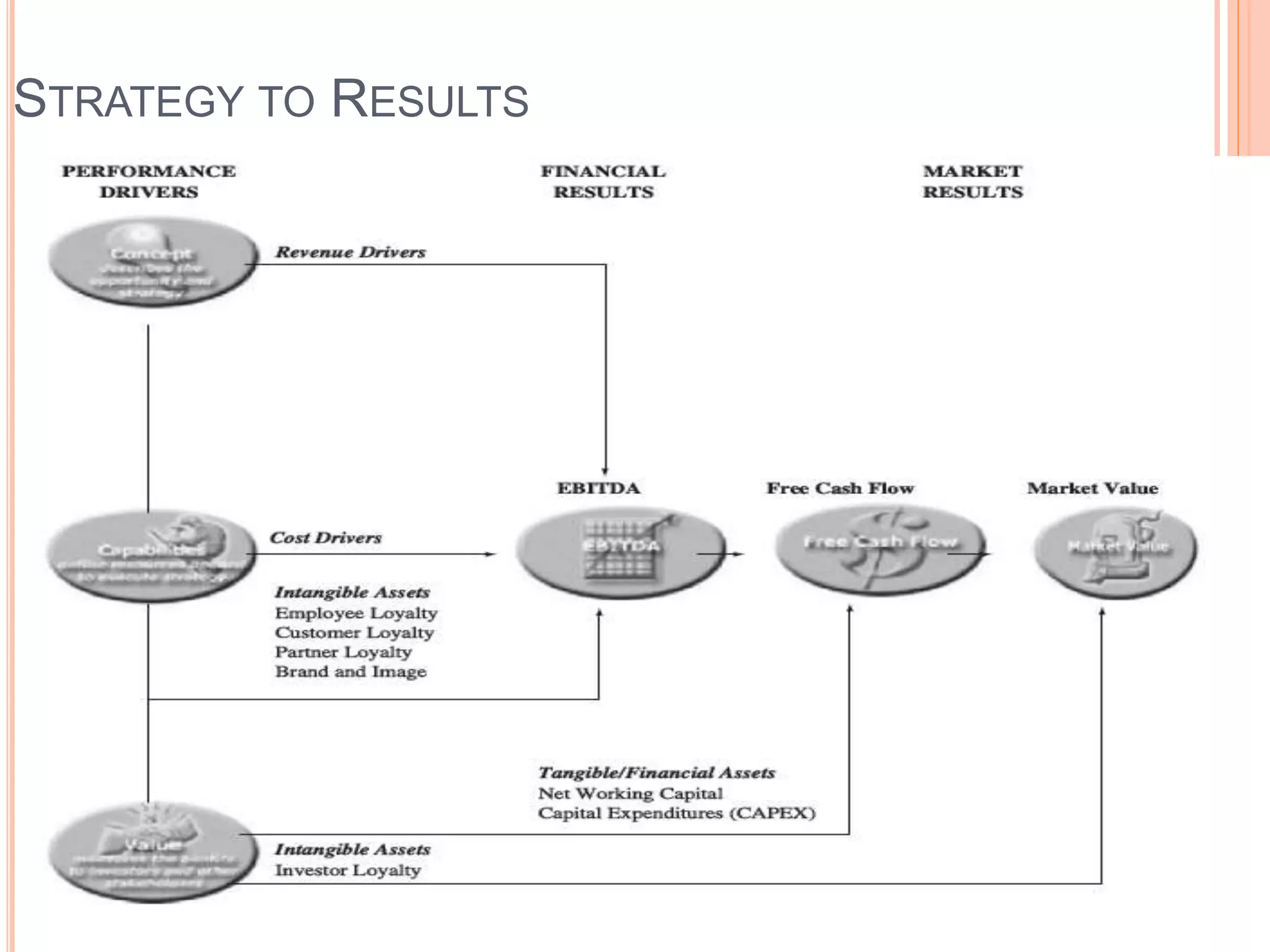
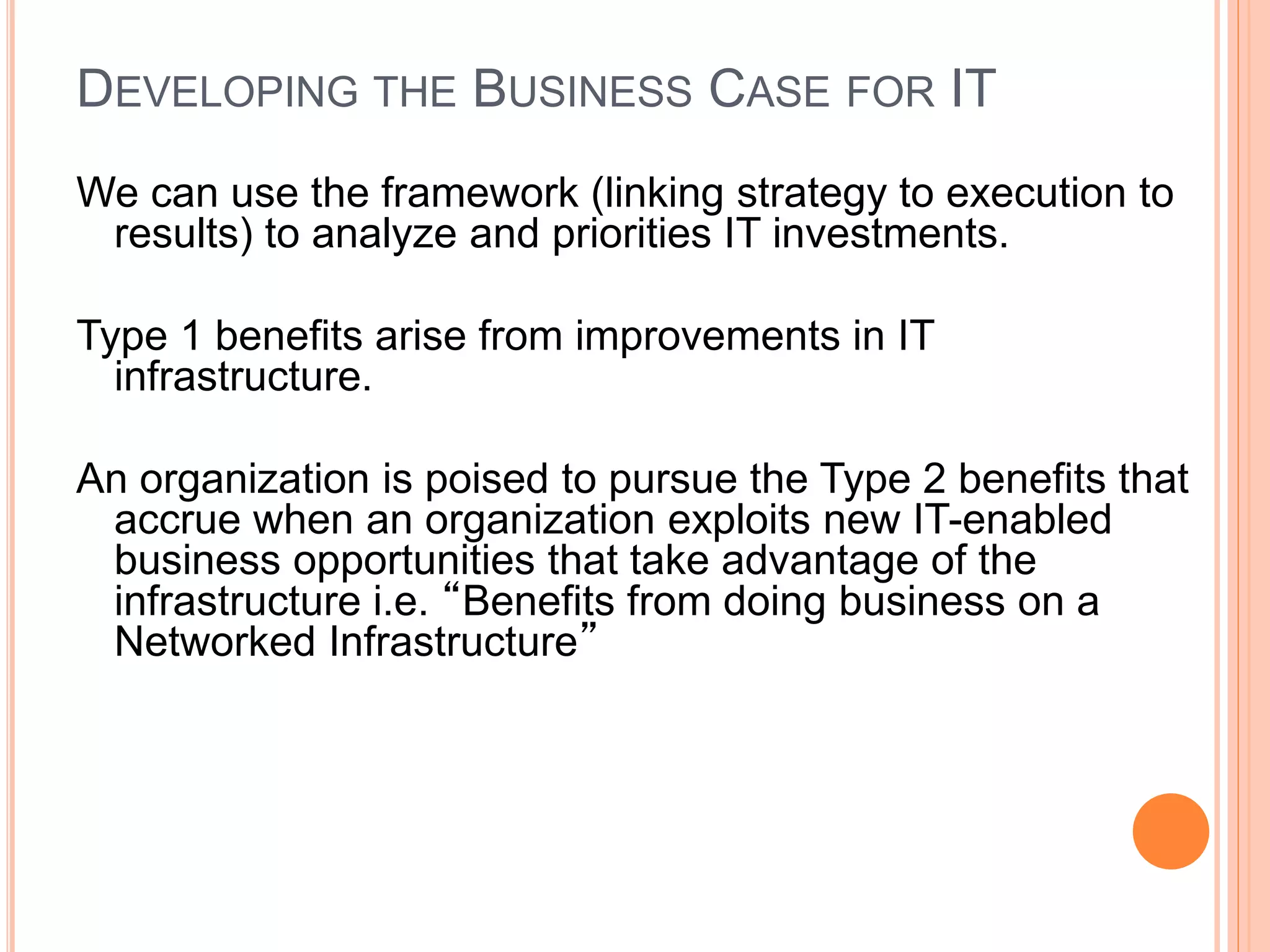
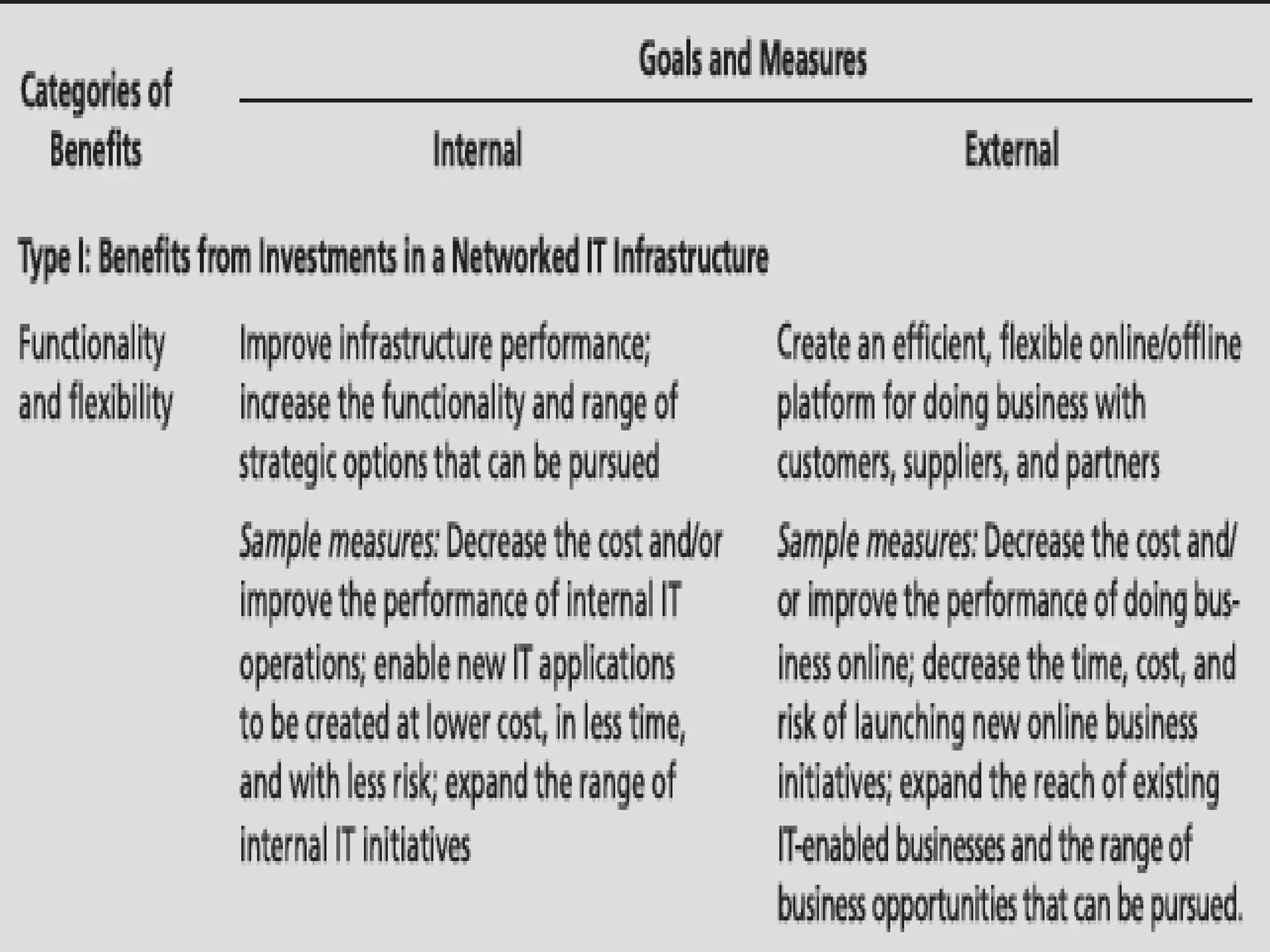
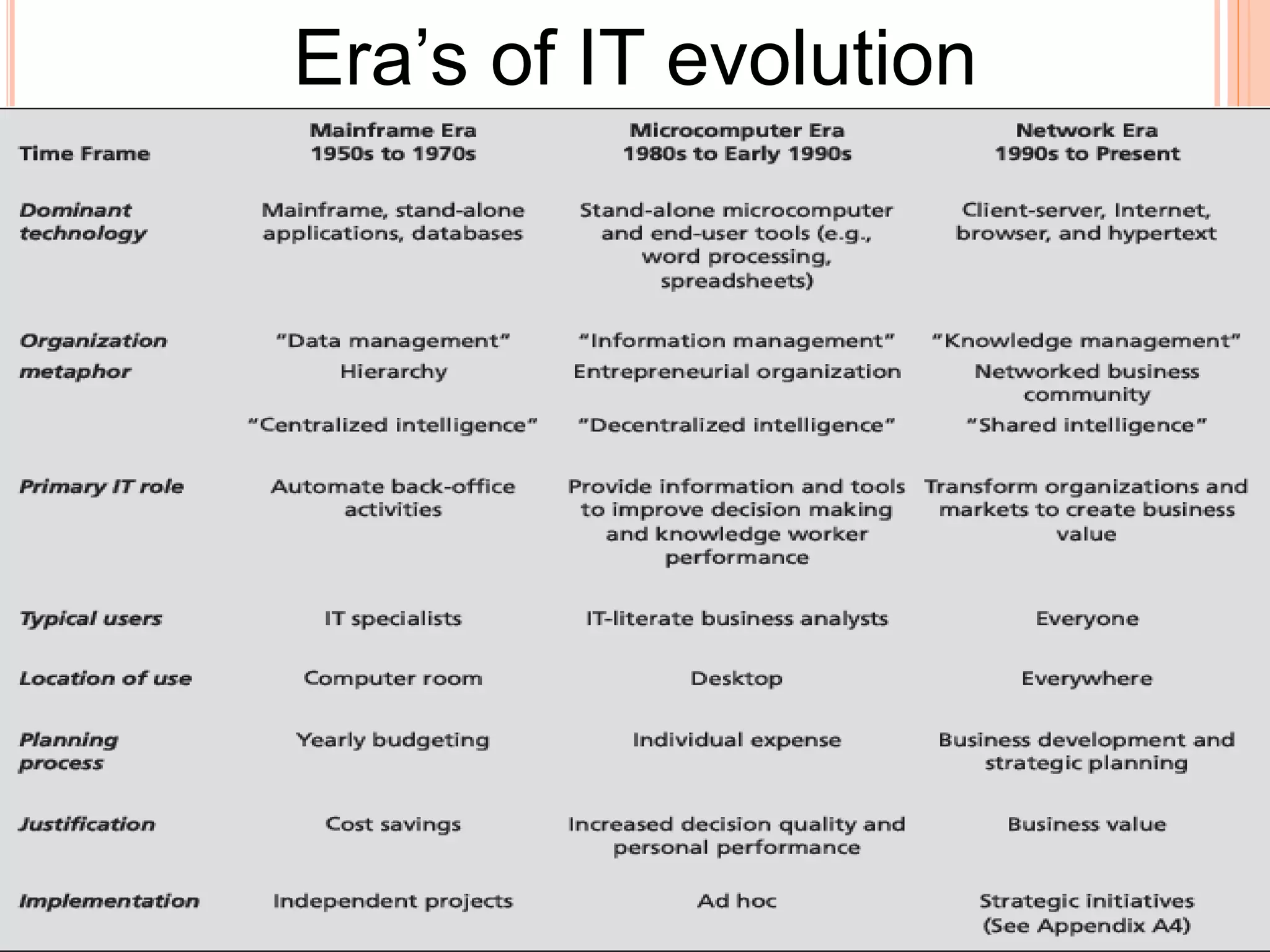
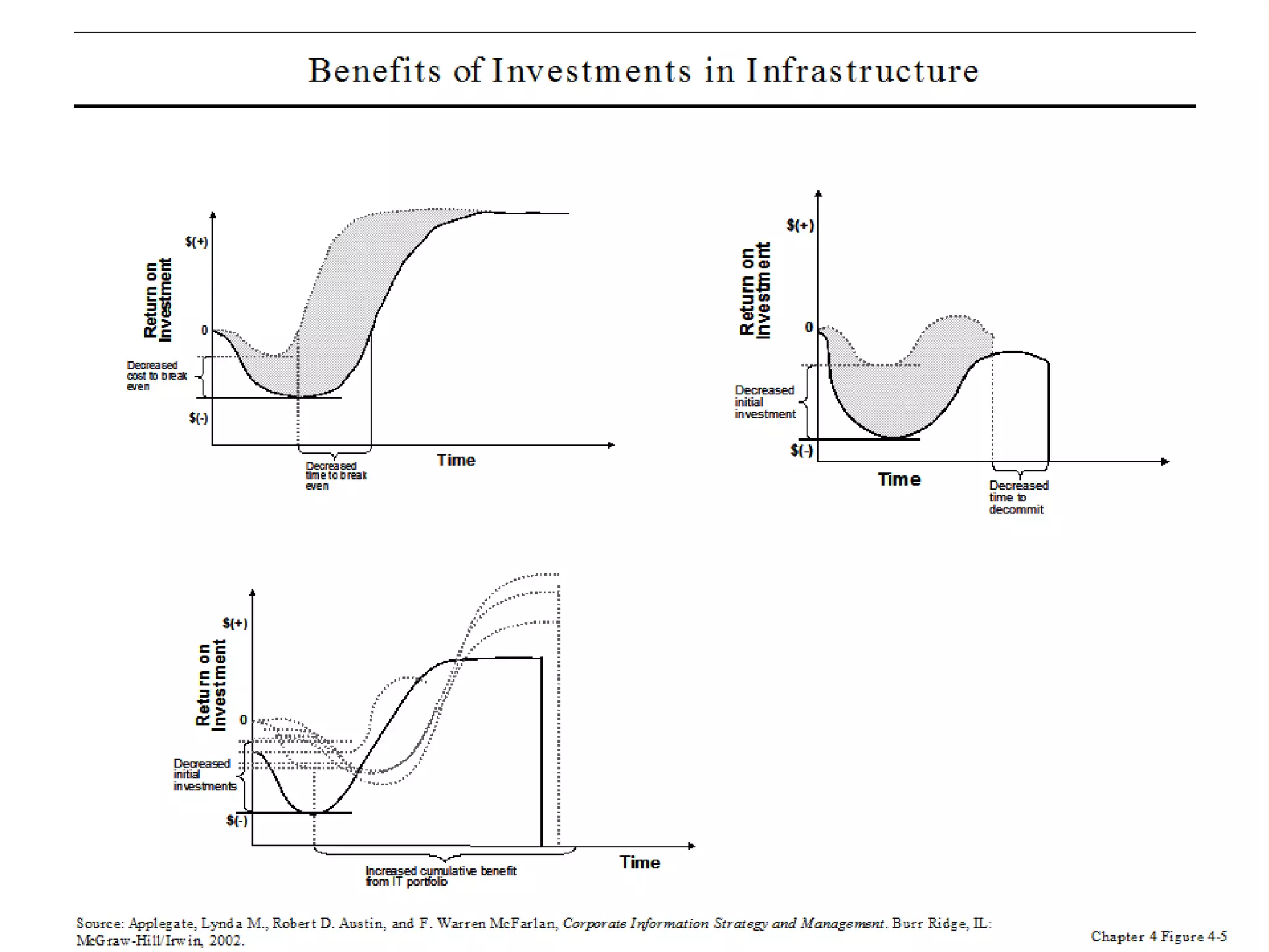
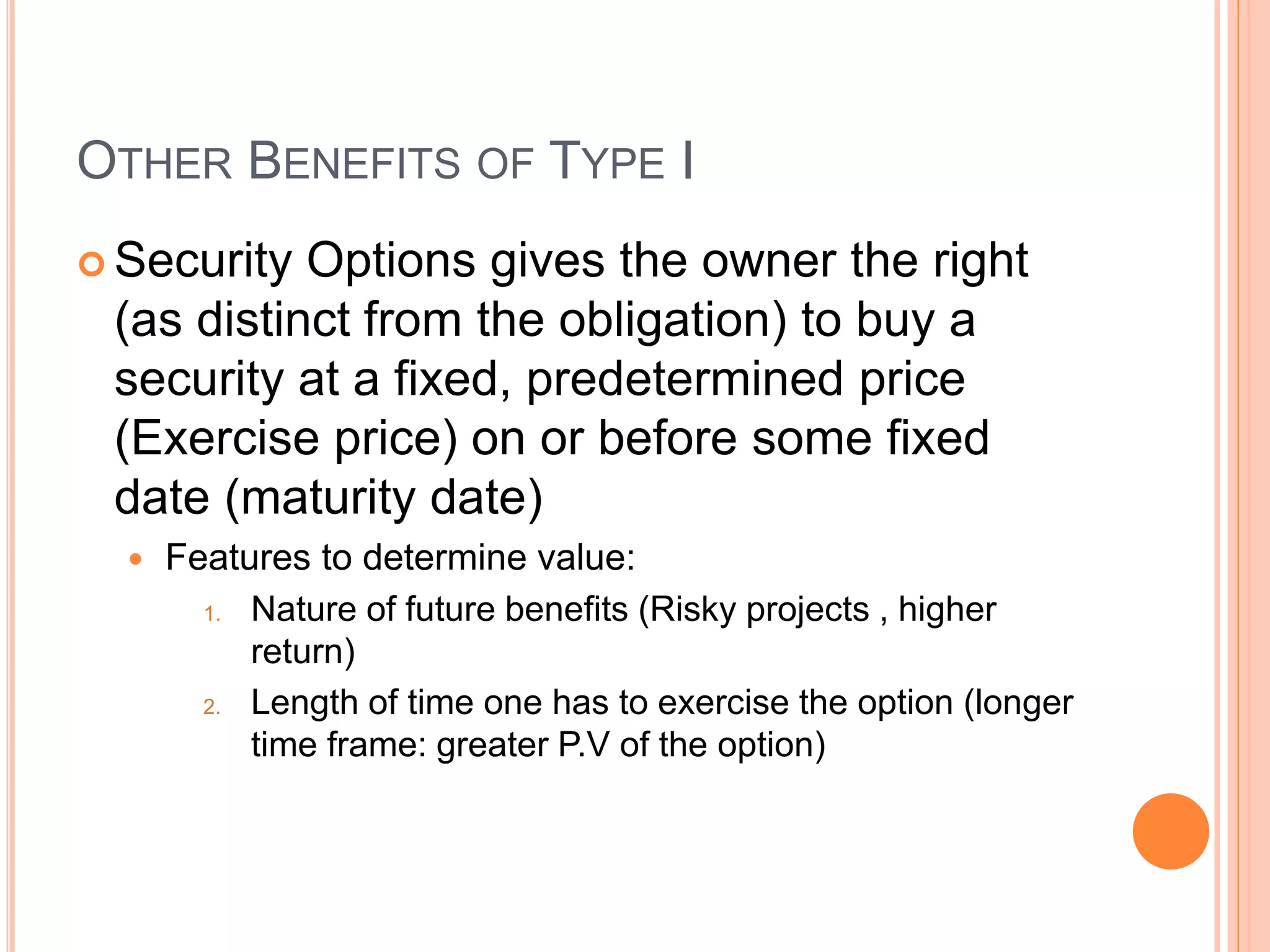
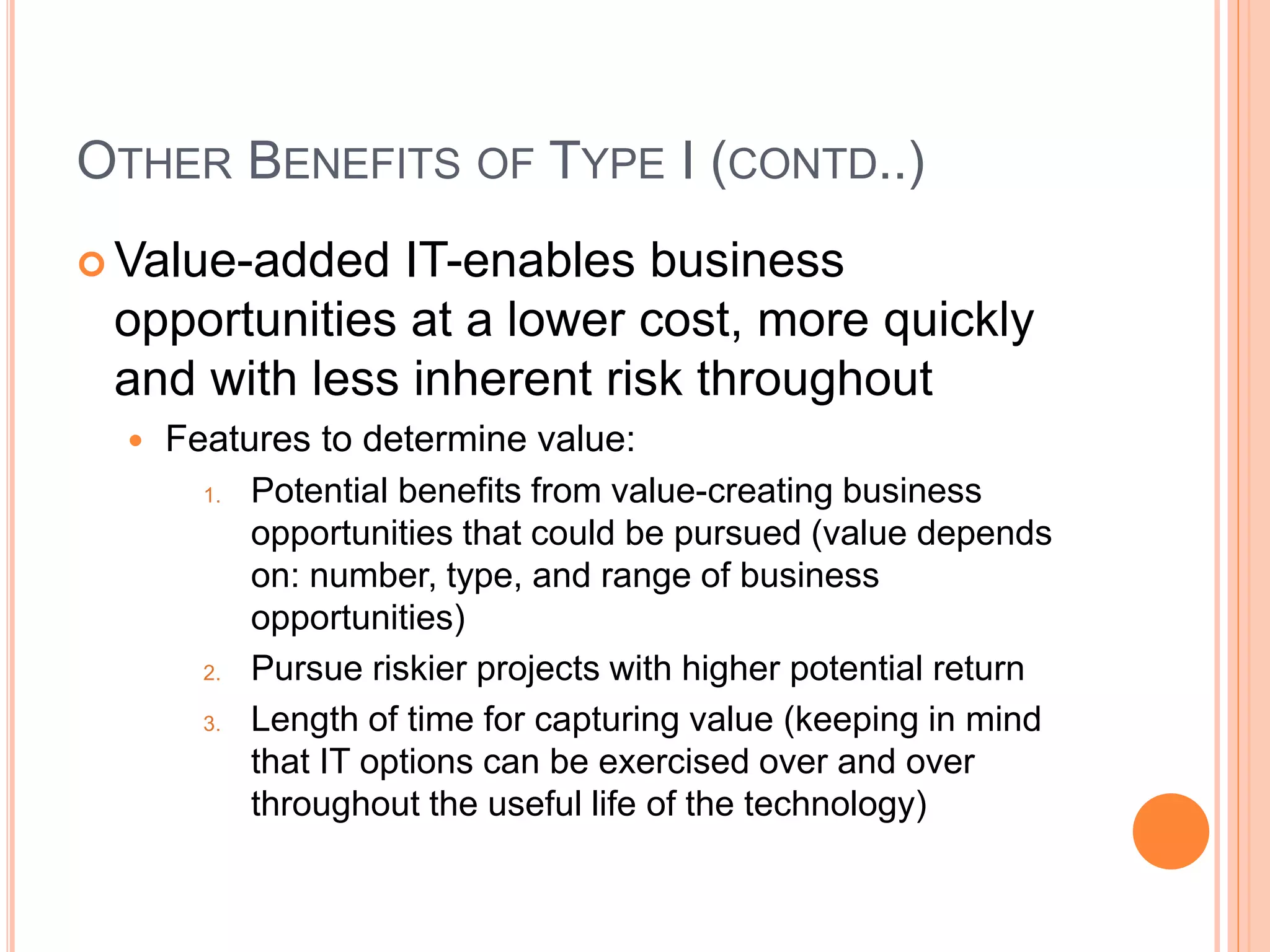
This document summarizes a chapter about corporate information structure and competitive strategy. It discusses three main topics: changing economies, linking strategies to execution and results, and developing the business case for IT. It describes how economies are shifting from industrial to networked models based on common infrastructures. Presenters are identified for each topic. The benefits of investing in IT infrastructure include lower costs, faster product launches, and strategic options. Developing the business case involves analyzing benefits from infrastructure improvements and new business opportunities enabled by technology.