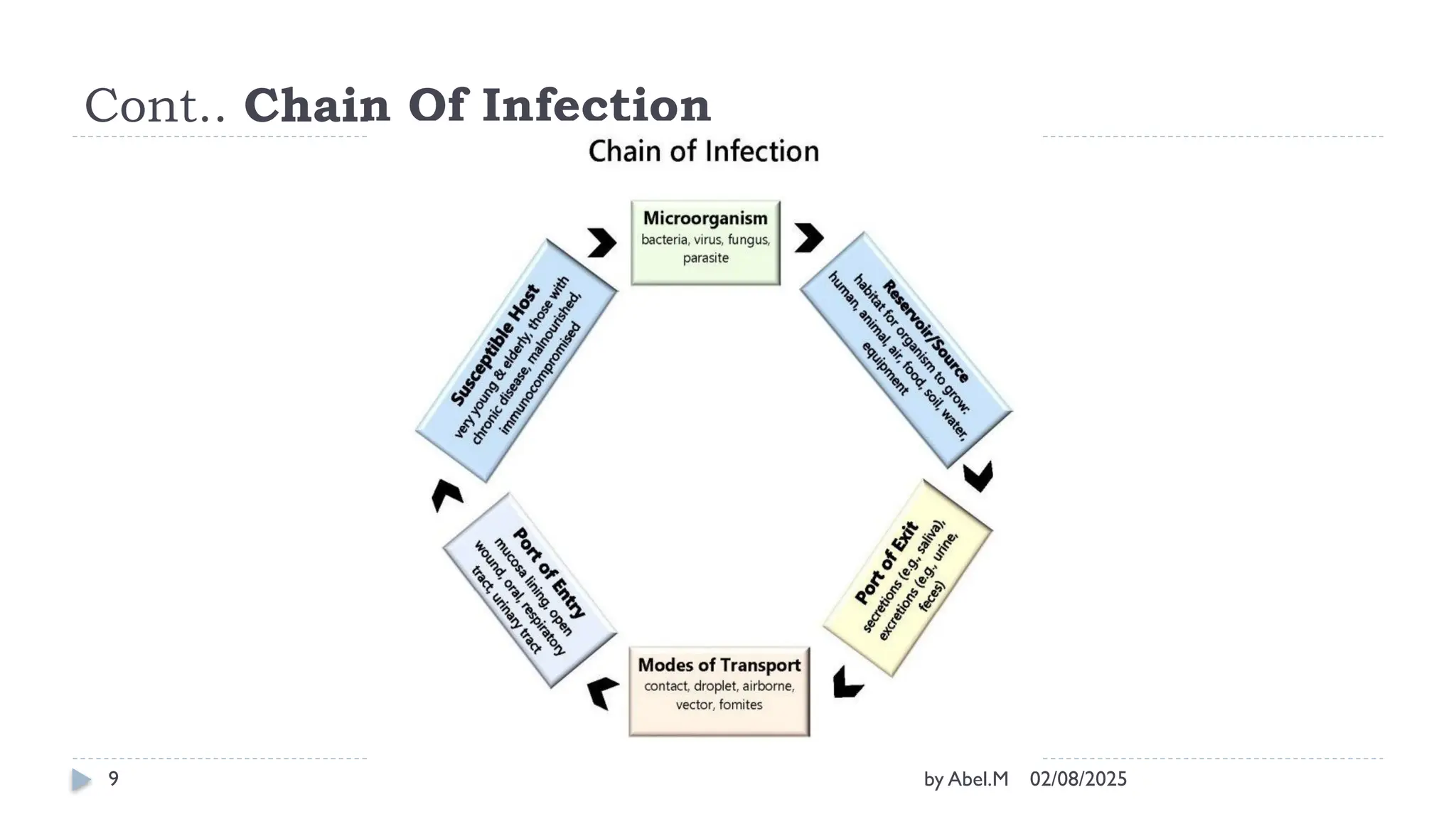
The document outlines infection prevention practices in healthcare, emphasizing the principles of infection control, modes of transmission, and basic aseptic techniques. It defines the chain of infection and strategies to break it through proper hand hygiene, personal protective equipment, and maintenance of a sterile environment. Additionally, it details the principles of sterile and aseptic techniques critical for safeguarding patients during surgical procedures.