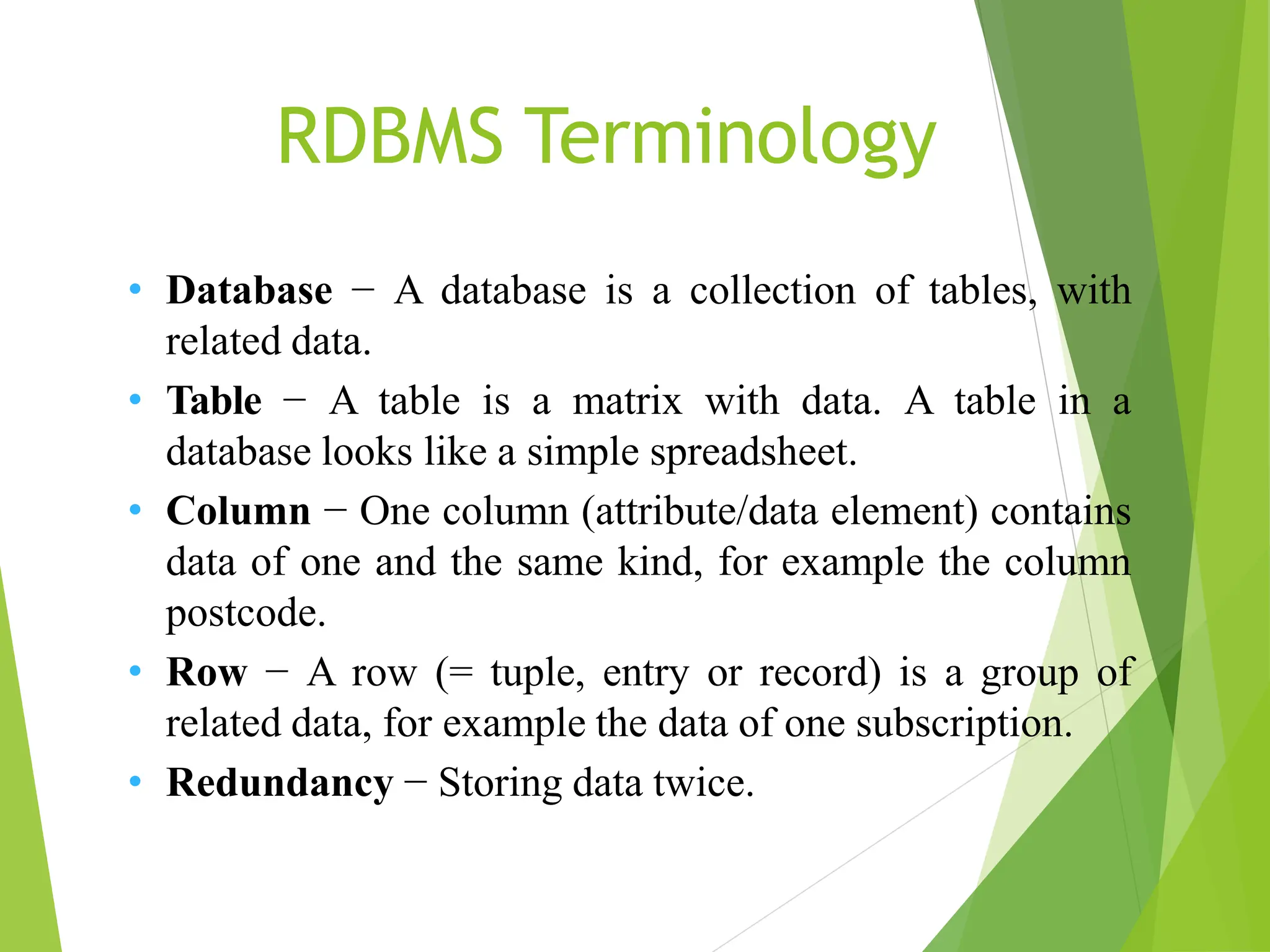
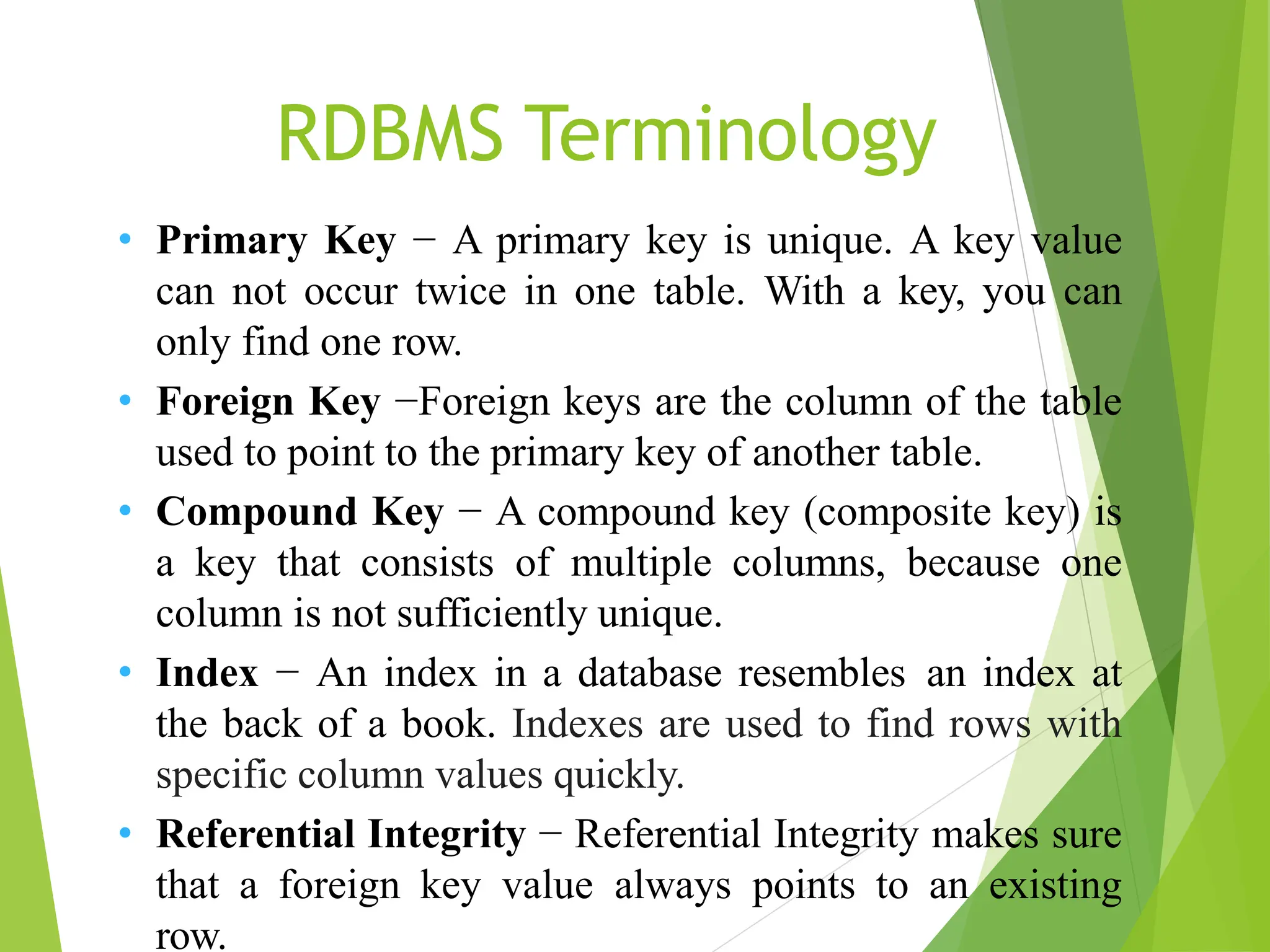
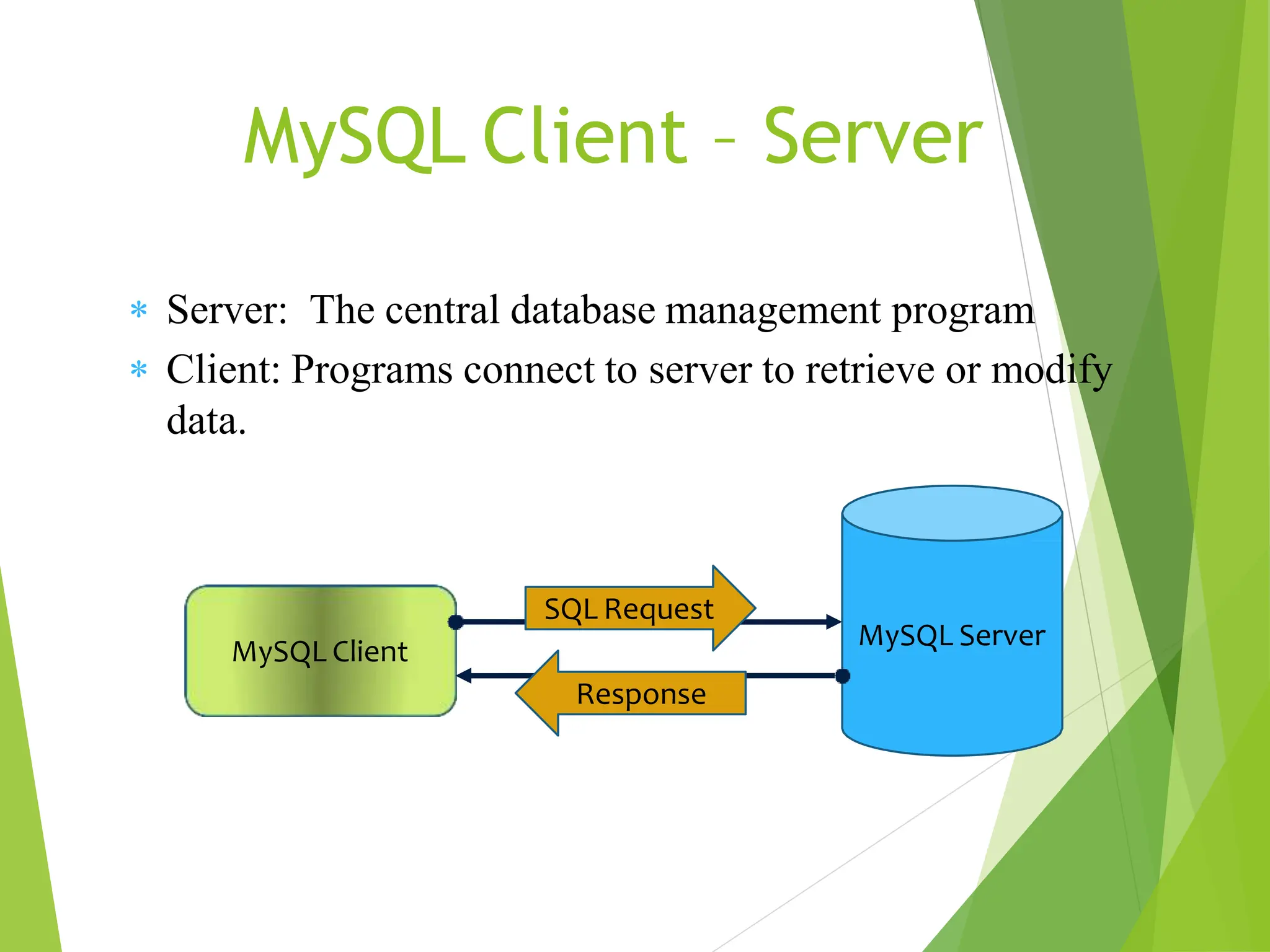
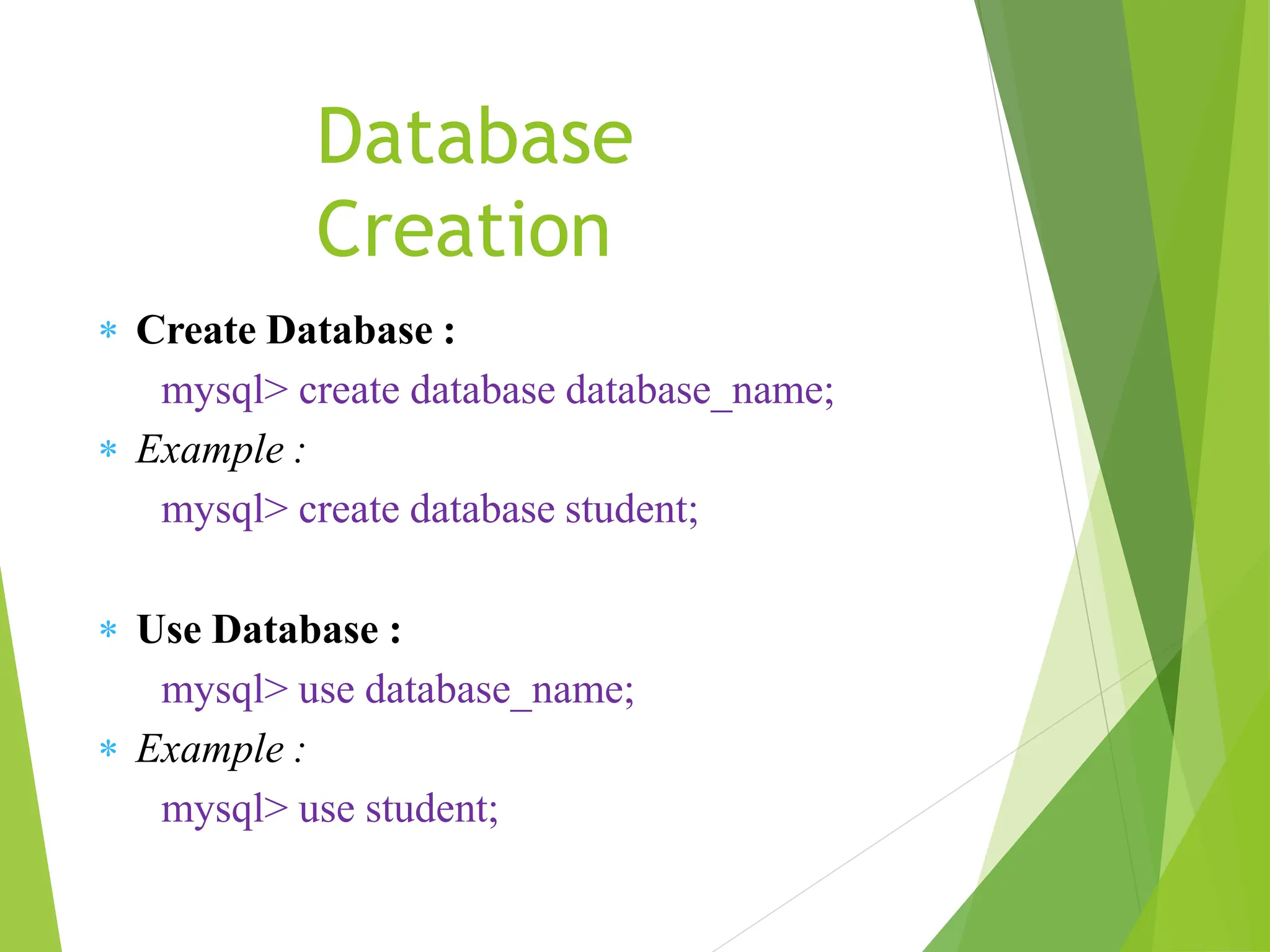
MySQL is an open-source relational database management system (RDBMS) that supports structured query language (SQL) and operates on various platforms like Windows, Linux, and macOS. It organizes data into tables with relationships defined by primary and foreign keys, facilitating efficient data management and retrieval. MySQL is suitable for both small and large applications, offering features such as high availability, security, and the ability to handle large data volumes.