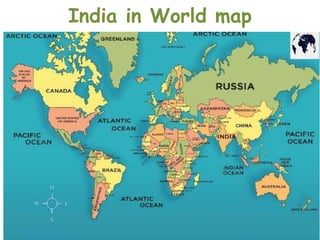
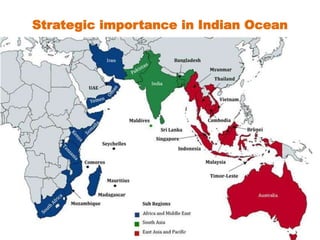
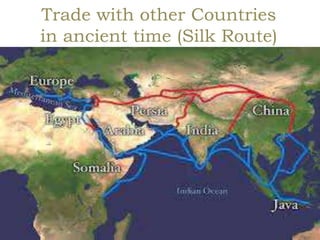
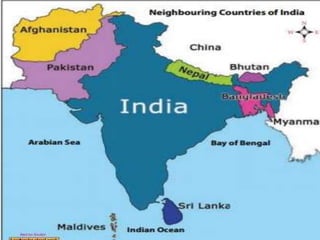
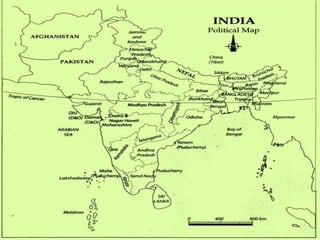
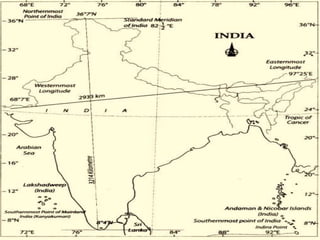
This document provides information about India's size, location, and geographical relationships. It notes that India lies in the Northern Hemisphere between latitudes 8°4'N to 37°6'N and longitudes 68°7'E to 97°25'E. India is the 7th largest country by area, covering 3.28 million square kilometers, with a coastline of 7,516 km. It is located in South Asia and shares land borders with Pakistan, Afghanistan, China, Nepal, Bangladesh, Bhutan, and Myanmar.