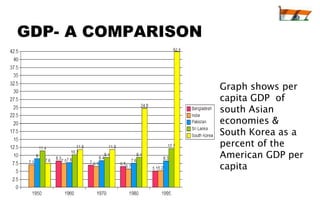
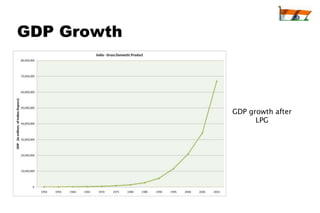
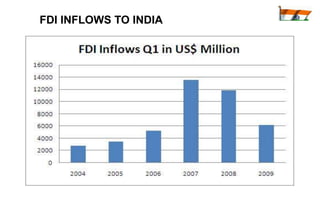
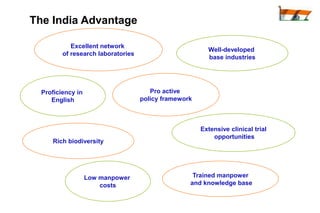
The document summarizes India's economic development over time. It notes that India will become the 3rd largest economy in the world by 2032 according to Goldman Sachs projections. India adopted socialist policies from 1947-1991, which led to slow growth. After adopting liberalization, privatization, and globalization policies in 1991, India's economy grew significantly faster. Major industries now include services, telecommunications, pharmaceuticals, and information technology.