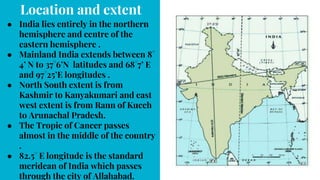
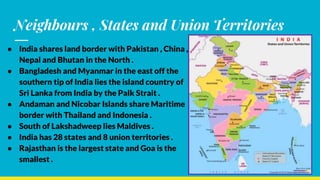
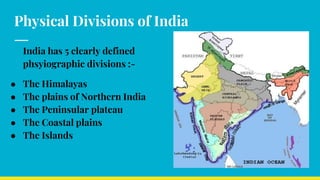
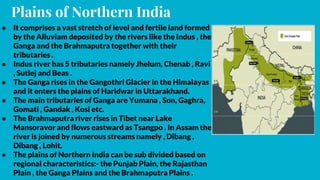
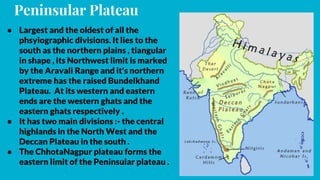
India has distinct geographical features. It lies in northern hemisphere between latitudes 8°4’ N to 37°6’N and longitudes 68°7’ E to 97°25’E. India shares land borders with Pakistan, China, Nepal, Bhutan and maritime borders with Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Myanmar, Thailand and Indonesia. India has 28 states and 8 union territories divided into 5 physical divisions - the Himalayas, northern plains, peninsular plateau, coastal plains and islands. The Himalayas include the highest mountains and the northern plains are fertile gangetic plains formed by major rivers. The peninsular plateau is the oldest division with the central highlands and Deccan plateau. Coastal