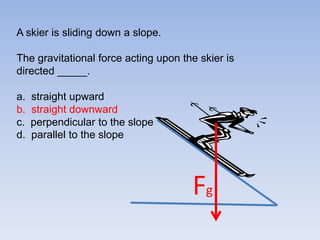
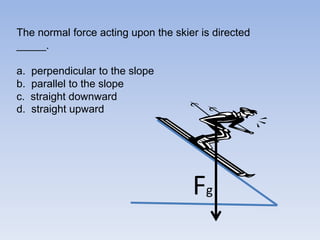
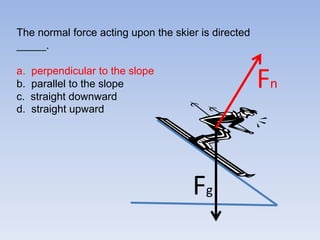
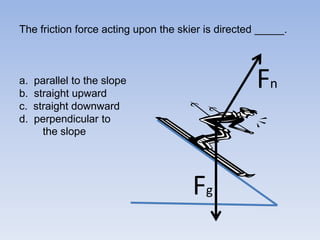
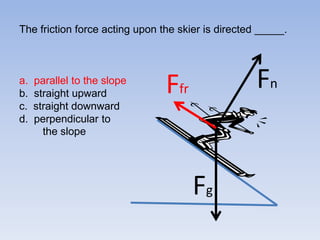
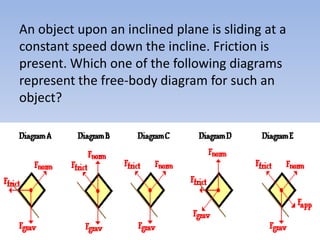
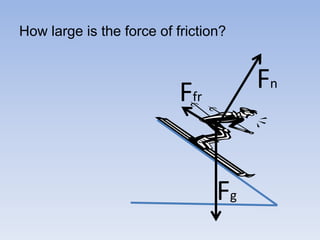
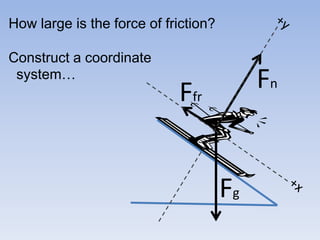
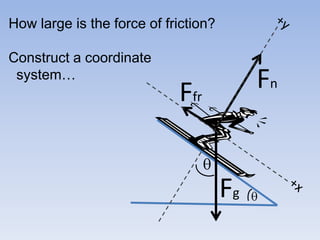
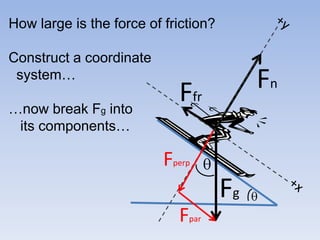
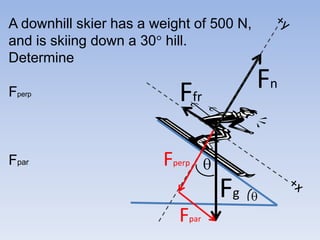
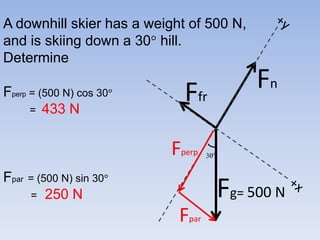
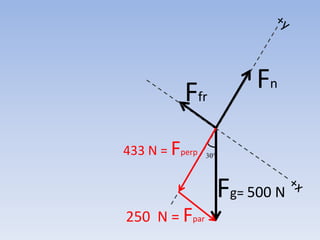
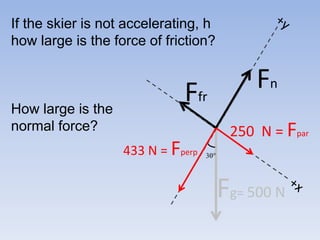
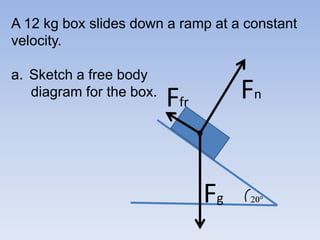
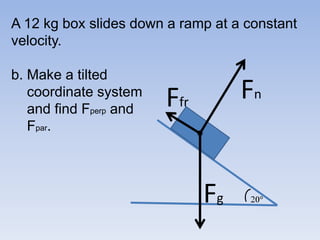
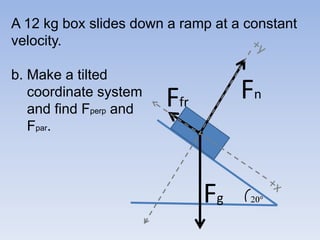
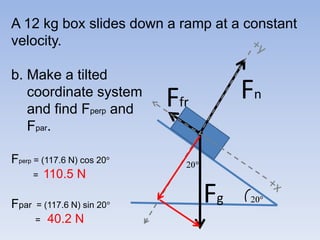
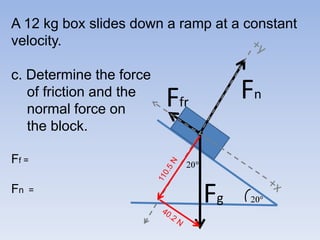
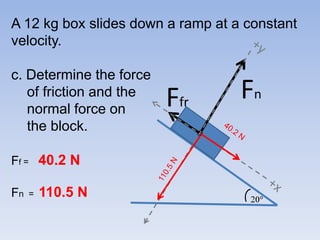
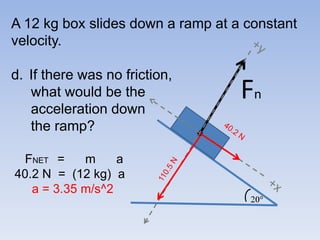
A skier is sliding down a slope. The gravitational force acting on the skier is directed perpendicular to the slope. The normal force is directed perpendicular to the slope, pushing the skier into the slope. The friction force is parallel to the slope, opposing the skier's motion down the slope. For an object on an inclined plane sliding at constant velocity, the force of friction equals the component of gravity parallel to the plane, and the normal force equals the component of gravity perpendicular to the plane.