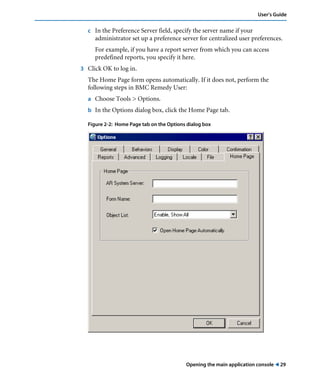
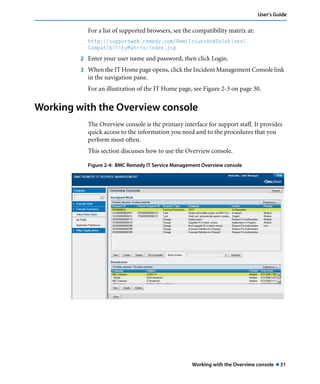
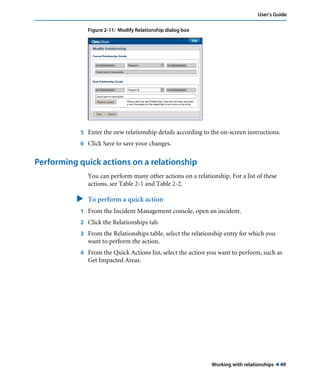
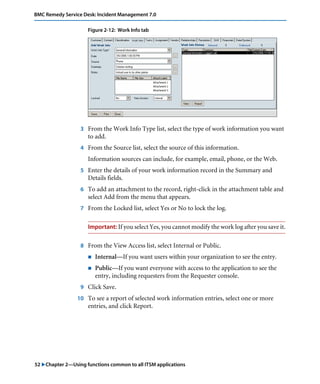
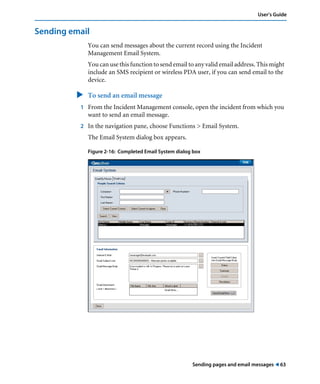
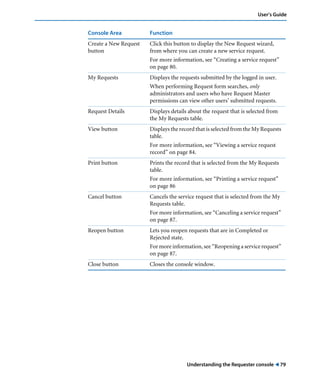
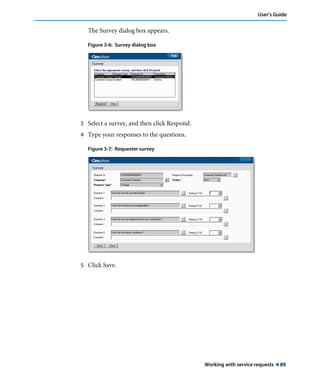
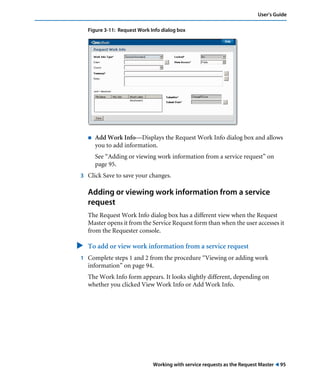
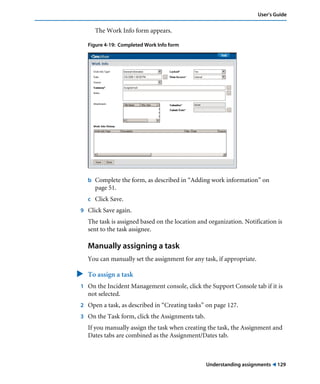
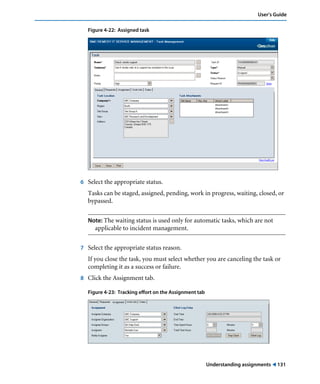
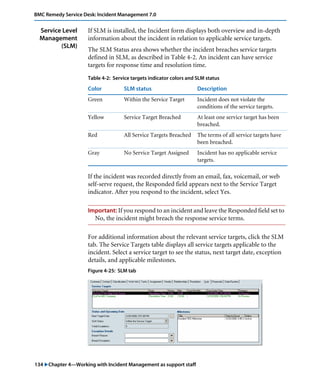
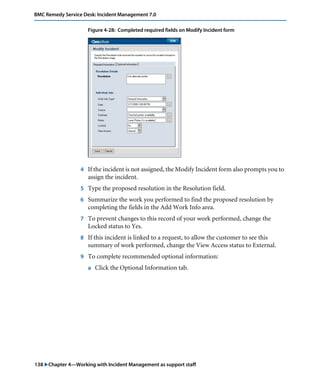
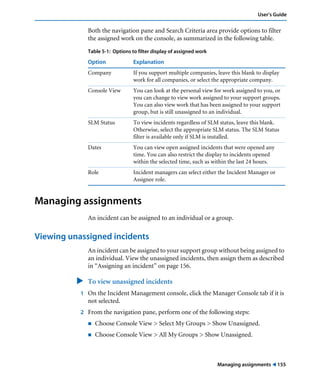
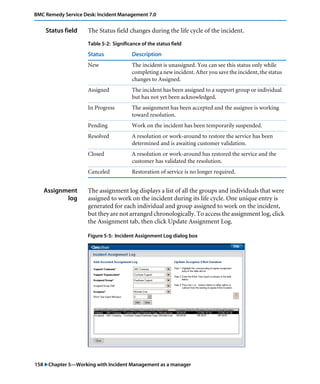
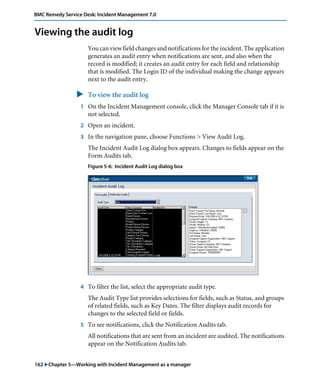
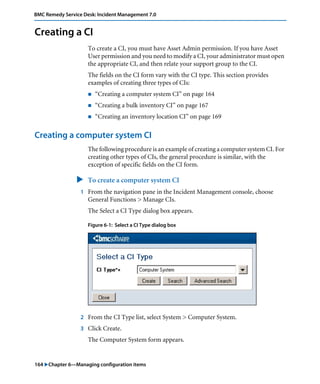
This document is the user guide for BMC Remedy ServiceDesk: Incident Management 7.0. It provides an overview of the product and its features. The guide is intended for various users, including requesters, support staff, and incident managers. It describes how to perform common functions in ITSM applications and how to work with the different console views to log, track, assign, resolve and close service requests and incidents.