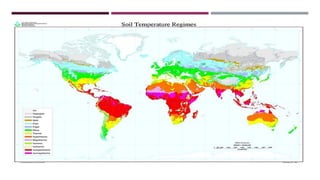
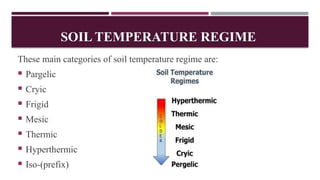
The document discusses the importance of soil temperature regimes in soil science, which significantly influence plant growth and soil management. It details various soil temperature categories based on mean annual soil temperature, including pargelic, cryic, frigid, mesic, thermic, hyperthermic, and iso. Understanding these regimes is crucial for soil classification, usage, and crop selection.